
In computer programming, assembly language, often referred to simply as Assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported.

A mnemonicdevice, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding.
The major system is a mnemonic technique used to aid in memorizing numbers.
A mnemonic link system, sometimes also known as a chain method, is a method of remembering lists that is based on creating an association between the elements of that list. For example, when memorizing the list, one could create a story about a "dog stuck in an envelope, mailed to an unlucky thirteen black cat playing with yarn by the window". It is argued that the story would be easier to remember than the list itself.

Johnny Mnemonic is a 1995 cyberpunk film directed by Robert Longo in his directorial debut. Based on the 1981 story of the same name by William Gibson, it stars Keanu Reeves and Dolph Lundgren. Reeves plays the title character, a man with an overloaded, cybernetic brain implant designed to store information. The film portrays Gibson's dystopian, prophetic view of 2021 with the world wracked by a tech-induced plague, awash with conspiracies, and dominated by megacorporations, with strong East Asian influences.
In computer engineering, Halt and Catch Fire, known by the assembly mnemonic HCF, is an idiom referring to a computer machine code instruction that causes the computer's central processing unit (CPU) to cease meaningful operation, typically requiring a restart of the computer. It originally referred to a fictitious instruction in IBM System/360 computers, making a joke about its numerous non-obvious instruction mnemonics.

Memorization is the process of committing something to memory. It is a mental process undertaken in order to store in memory for later recall visual, auditory, or tactical information.
Piphilology comprises the creation and use of mnemonic techniques to remember many digits of the mathematical constant π. The word is a play on the word "pi" itself and of the linguistic field of philology.

"Johnny Mnemonic" is a science fiction short story by American-Canadian writer William Gibson. It first appeared in Omni magazine in May 1981, and was subsequently included in Burning Chrome, a 1986 collection of Gibson's short fiction. It takes place in the world of Gibson's cyberpunk novels, predating them by some years, and introduces the character Molly Millions, who plays a prominent role in the Sprawl trilogy of novels.

ROYGBIV is an acronym for the sequence of hues commonly described as making up a rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. There are several mnemonics that can be used for remembering this color sequence, such as the name "Roy G. Biv" or sentences such as "Richard of York Gave Battle in Vain".

Morse code mnemonics are systems to represent the sound of Morse characters in a way intended to be easy to remember. Since every one of these mnemonics requires a two-step mental translation between sound and character, none of these systems are useful for using manual Morse at practical speeds. Amateur radio clubs can provide resources to learn Morse code.

Johnny Mnemonic is a 4 player pinball machine from August 1995, manufactured by Williams Electronic Games, Inc. A total of 2,756 units were produced.
The Little Man Computer (LMC) is an instructional model of a computer, created by Dr. Stuart Madnick in 1965. The LMC is generally used to teach students, because it models a simple von Neumann architecture computer—which has all of the basic features of a modern computer. It can be programmed in machine code or assembly code.
A Latin mnemonic verse or mnemonic rhyme is a mnemonic device for teaching and remembering Latin grammar. Such mnemonics have been considered by teachers to be an effective technique for schoolchildren to learn the complex rules of Latin accidence and syntax. One of their earliest uses was in the Doctrinale by Alexander of Villedieu written in 1199 as an entire grammar of the language comprising 2,000 lines of doggerel verse. Various Latin mnemonic verses continued to be used in English schools until the 1950s and 1960s.
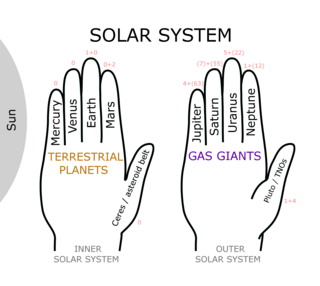
A planetary mnemonic refers to a phrase created to remember the planets and dwarf planet of the Solar System, with the order of words corresponding to increasing sidereal periods of the bodies. One simple visual mnemonic is to hold out both hands side-by-side with thumbs in the same direction. The fingers of hand with palm down represent the terrestrial planets where the left pinkie represents Mercury and its thumb represents the asteroid belt, including Ceres. The other hand represents the gas giants, with its thumb representing Trans Neptunian objects, including Pluto.
Exceptional memory is the ability to have accurate and detailed recall in a variety of ways, including hyperthymesia, eidetic memory, synesthesia, and emotional memory. Exceptional memory is also prevalent in those with savant syndrome and mnemonists.
Elaborative encoding is a mnemonic that relates to-be-remembered information to previously existing memories and knowledge.

Johnny Mnemonic: The Interactive Action Movie is a point-and-click adventure science fiction video game directed by Douglas Gayeton for Macintosh, Microsoft Windows and released by Sony Imagesoft on May 26, 1995. Based on the 1981 short story of the same name by William Gibson, the game has the player take the role of the title character.









