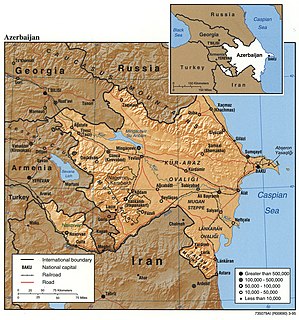
Azerbaijan is situated in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Three physical features dominate Azerbaijan: the Caspian Sea, whose shoreline forms a natural boundary to the east; the Greater Caucasus mountain range to the north; and the extensive flatlands at the country's center. About the size of Portugal or the US state of Maine, Azerbaijan has a total land area of approximately 86,600 square kilometers, less than 0.5% of the land area of the former Soviet Union. Of the three Transcaucasian states, Azerbaijan has the greatest land area. Special administrative subdivisions are the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, which is separated from the rest of Azerbaijan by a strip of Armenian territory, and the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Region, entirely within Azerbaijan. The status of Nagorno-Karabakh was under negotiation in 1994.

The Kura is an east-flowing river south of the Greater Caucasus Mountains which drains the southern slopes of the Greater Caucasus east into the Caspian Sea. It also drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus while its main tributary, the Aras drains the south side of those mountains. Starting in northeastern Turkey, it flows through Turkey to Georgia, then to Azerbaijan, where it receives the Aras as a right tributary, and enters the Caspian Sea at Neftçala. The total length of the river is 1,515 kilometres (941 mi).

Mingachevir, is the fourth-largest city in Azerbaijan with a population of about 104,500. It is known as city of lights because of its hydroelectric power station on the Kur River, which splits the city in half.

The water bodies of Azerbaijan were formed over a long geological timeframe and changed significantly throughout that period. This is particularly evidenced by remnants of ancient rivers found throughout the country. The country's water systems are continually changing under the influence of natural forces and human introduced industrial activities. Artificial rivers (canals) and ponds are a part of Azerbaijan's water systems.

The Mingachevir reservoir is a large reservoir in northwestern Azerbaijan. It is the largest reservoir in the Caucasus.

Falakro Oros is a mountain in the Drama regional unit, eastern Greek Macedonia, northern Greece. The elevation of its highest summit, Profitis Ilias, is 2232 meters above the sea level. There is a ski resort on the mountain.

The Iori is a river in the South Caucasus that originates in the Greater Caucasus Mountains in eastern Georgia and continues in Azerbaijan, where it is also known as Gabirry (Qabirry) and flows into the Mingachevir reservoir. It is 320 kilometres (200 mi) long. It starts in the mountains north of Tbilisi, flows south toward that city, swings east and flows through the lowlands parallel to and between the Alazani River (north) and the Kura River (south).

The Mingachevir Dam is the largest hydroelectric power station in the South Caucasus, is located over Kur river and not far from Mingachevir city.
The Shamkir reservoir is a large reservoir in the Shamkir Rayon of northwestern Azerbaijan. It is the second largest reservoir in the Caucasus after the Mingachevir reservoir.
The Agstafachay reservoir is a large reservoir in the Agstafa Rayon of northwestern Azerbaijan.
Khanbulanchay reservoir, also known as Khanbulaqchay reservoir, is a lake in Lankaran Rayon of southeastern Azerbaijan. The name means "the spring of the khan" in Azerbaijani language.
The Yenikend reservoir is a large reservoir in the Shamkir Rayon of northwestern Azerbaijan. It is the third largest reservoir in the Caucasus after the Mingachevir and Shamkir reservoirs.
The Varvara reservoir is a reservoir near Mingachevir, Azerbaijan.

Bozdağ is a town in İzmir Province, Turkey
Bozdag means "gray mountain" in Turkish and it may refer to
The Shirvan steppe is part of the Kur-Araz Lowland of Azerbaijan and is located on the left bank of the Kura River.

Akhurian Reservoir is a reservoir on the Akhurian River between Armenia and Turkey. The reservoir has a surface area of 54 km² and a volume of 525 million cubic meters. It is one of the largest reservoirs in the Caucasus, smaller than the Mingachevir reservoir and the Shamkir reservoir in Azerbaijan.

The Hasanbey Zardabi Natural History Museum is a natural history museum in Baku, Azerbaijan.
National Policy Dialogues on Integrated Water Resources Management in Azerbaijan for managing water resources are aimed at developing a state strategy based on "Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes” of United Nations Economic Commission for Europe and European Union Water Framework Directive and the “Water and Health” Protocol of that convention as well as other principles of the United Nations and the EU.
The climate in most parts of Azerbaijan is arid. In order to expand the areas of irrigation in dry climate and to provide grape and orchards with water, many small and large reservoirs have been created. There are 140 reservoirs in the country. The total volume of reservoirs is 21.5 km3. Most reservoirs are regulated and used for irrigation. Reservoirs and hydroelectric stations created in the rivers Kura, Araz and Tartar are Shamkir, Mingachevir, Yenikend, Varvara, Araz and Sarsang. They are used to ensure the use of energy, irrigation and water supply.













