
The Balkans, also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographic area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish Straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Mount Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty, which was signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a system of collective security: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the perceived threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa.

The Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC) is a post–Cold War, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) institution. The EAPC is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and Central Asia. States meet to cooperate and discuss political and security issues. It was formed on 29 May 1997 at a Ministers’ meeting held in Sintra, Portugal, as the successor to the North Atlantic Cooperation Council (NACC), which was created in 1991.

The Partnership for Peace (PfP) is a North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) program aimed at creating trust between the member states of NATO and other states in Europe, including post-Soviet states; 20 states are members. The program contains six areas of cooperation, which aims to build relationships with partners through military-to-military cooperation on training, exercises, disaster planning and response, science and environmental issues, professionalization, policy planning, and relations with civilian government.

Chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear defence are protective measures taken in situations in which chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear warfare hazards may be present. CBRN defence consists of CBRN passive protection, contamination avoidance, and weapons of mass destruction mitigation.
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are, in alphabetical order: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Greece, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, and Turkey. Sometimes, Moldova and Slovenia are also included. The largest city of the region is Istanbul, followed by Bucharest, Sofia, Belgrade, and Athens.

The Directorate-General for European Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations, formerly known as the European Community Humanitarian Aid Office, is the European Commission's department for overseas humanitarian aid and for civil protection. It aims to save and preserve life, prevent and alleviate human suffering and safeguard the integrity and dignity of populations affected by natural disasters and man-made crises. Since September 2019, Janez Lenarčič is serving as Commissioner for Crisis Management in the Von der Leyen Commission.

The Ministry of the Russian Federation for Civil Defence, Emergency Situations and Elimination of Consequences of Natural Disasters, also known as the Ministry of Emergency Situations or internationally as EMERCOM, is a Russian government agency overseeing the civil emergency services in Russia.
Partnership for Peace Information Management System (PIMS) is a US Department of Defense Bilateral Cooperative Development Program started in 1996 to enable collaboration and communication between Partnership for Peace (PfP) countries and the NATO community.

The 2006 Riga summit or the 19th NATO Summit was a NATO summit held in the Olympic Sports Centre, Riga, Latvia from 28 to 29 November 2006. The most important topics discussed were the War in Afghanistan and the future role and borders of the alliance. Further, the summit focused on the alliance's continued transformation, taking stock of what has been accomplished since the 2002 Prague Summit. NATO also committed itself to extending further membership invitations in the upcoming 2008 Bucharest Summit. This summit was the first NATO summit held on the territory of a former USSR republic.

The Defence Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear Centre is a United Kingdom military facility at Winterbourne Gunner in Wiltshire, south of Porton Down and about 4 miles (6 km) northeast of Salisbury. It is a tri-service location, with the Army being the lead service. The centre is responsible for all training issues relating to chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear (CBRN) defence and warfare for the UK's armed forces.

The accession of Albania to NATO took place in 2009. Albania's relationship with the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) began in 1992 when it joined the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. In 1994, it entered NATO's Partnership for Peace, which began Albania's process of accession into the alliance. In 1999, the country received a Membership Action Plan (MAP). The country received an invitation to join at the 2008 Bucharest Summit and became a full member on April 1, 2009.

North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It is a landlocked country bordering Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's 1.83 million people. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Romani, Serbs, Bosniaks, Aromanians and a few other minorities.

Fatmir Besimi is a Macedonian politician and economist of Albanian ethnicity. He currently served for Minister of Finance in North Macedonia, He also served twice as Minister of Economy then Minister of Defence and after that he was Deputy Prime Minister of the Government of the Republic of Macedonia in charge of European Affairs. In 2010 he was selected as one of the top European Ministers in the group of Young Global Leaders by World Economic Forum.
The Movement Coordination Centre Europe (MCCE) is a multinational military movement control centre located at Eindhoven Airport in the Netherlands. Its 28 member states are predominantly drawn from NATO and the European Union (EU). The centre is staffed by 32 military and civilian personnel from the participating countries. The main purpose of the MCCE is coordinating and optimising the use of airlift, sealift and land movement assets of the armed forces of the member countries.

The Georgia–Georgia National Guard Partnership is one of 22 European partnerships that make up the U.S. European Command State Partnership Program and one of 65 worldwide partnerships that make-up the National Guard State Partnership Program. The Georgia National Guard has maintained a strong State Partnership program with the Republic of Georgia since 1994. Since then, Georgia has put itself on the path of acceptance into NATO, in large part due to the State Partnership Program.
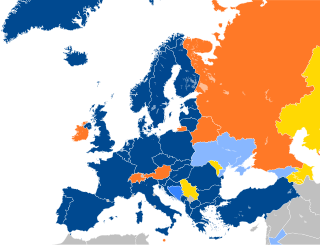
NATO maintains foreign relations with many non-member countries across the globe. NATO runs a number of programs which provide a framework for the partnerships between itself and these non-member nations, typically based on that country's location. These include the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council and the Partnership for Peace.

The EU Centres of Excellence on Chemical, Biological, Radiological and Nuclear Risk Mitigation is an initiative of the European Union which was launched in 2010. The Initiative addresses the mitigation of and preparedness for risks related to CBRN material and agents. The origin of these risks can be criminal, accidental or natural. The CBRN CoE Initiative seeks to boost cooperation at national, regional and international levels, and to develop a common and coherent CBRN risk mitigation policy at national and regional level. Risk mitigation comprises prevention, preparedness and post-crisis management.

The Open Balkan is an economic and political zone of three member states in the Balkans, those being Albania, North Macedonia and Serbia. The zone has a total area of 131,935 km2 (50,940 sq mi) and an estimated total population of almost 12 million. The official languages are Albanian, Macedonian and Serbian. Its administrative centres are the cities of Belgrade, Skopje and Tirana. With the establishment of the zone, all three member states aim to increase trade and cooperation as well as improve bilateral relations.

Armenia and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization have maintained a formal relationship since 1992, when Armenia joined the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. Armenia officially established bilateral relations with NATO in 1994 when it became a member of NATO's Partnership for Peace (PfP) programme. In 2002, Armenia became an Associate Member of the NATO Parliamentary Assembly.



















