
The Peruvian Armed Forces are the military services of Peru, comprising independent Army, Navy and Air Force components. Their primary mission is to safeguard the country's independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity against any threat. As a secondary mission they participate in economic and social development as well as in civil defense tasks.

Alberto Kenya Fujimori Inomoto is a Peruvian former politician, professor and engineer who served as President of Peru from 28 July 1990 until 22 November 2000, though de facto leadership was reportedly held by Vladimiro Montesinos, the then head of the National Intelligence Service. Frequently described as a dictator, he remains a controversial figure in Peruvian politics. He was sentenced to 25 years in prison for human rights abuses during his presidency but was released on 6 December 2023 following an order by the Constitutional Court of Peru.
Vladimiro Lenin Ilich Montesinos Torres is a Peruvian former intelligence officer who was the long-standing head of Peru's National Intelligence Service (SIN) and was reportedly the de facto leader of Peru while President Alberto Fujimori served as a figurehead leader. Montesinos had strong connections with the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) for over 25 years and was said to have received $10 million from the agency for his government's anti-terrorist activities, with international bank accounts possessed by Montesinos reportedly holding at least $270 million. The United States reportedly supported the candidacy of Fujimori during 1990 Peruvian general election due to his links to Montesinos and ignored human rights abuses performed under Montesinos during the 1990s. In 2000, the infamous "Vladi-videos" came to light when they were broadcast on the news. They were secret videos recorded by Montesinos that showed him bribing elected congressmen into leaving the opposition and joining the pro-Fujimori group of the Congress. The ensuing scandal caused Montesinos to flee the country and prompted Fujimori's resignation.
La Cantuta massacre took place in Peru on 18 July 1992, during the presidency of Alberto Fujimori. Supposed members of Shining Path, including a university professor and nine students from Lima's La Cantuta University, were abducted, tortured, and killed by Grupo Colina, a military death squad. The incident occurred two days after the Shining Path's Tarata bombing, which killed over 40 people in Lima Province.

A self-coup, sometimes known as the Fujimorazo, was performed in Peru in 1992 after President Alberto Fujimori dissolved the Congress as well as the judiciary and assumed full legislative and judicial powers. With the collaboration of the military, the Fujimori government subsequently began to implement objectives of the Green Plan following the coup.

The Centro Nacional de Inteligencia or CNI, is a Mexican intelligence agency controlled by the Secretariat of Security and Civilian Protection.
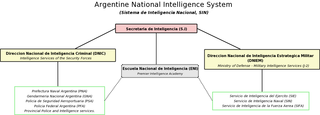
Sistema de Inteligencia Nacional is the official denomination of the Argentine national intelligence community.
The Grupo Colina was a military anti-communist right wing death squad created in Peru that was active from 1990 until 1994, during the administration of president Alberto Fujimori. The group committed several human rights abuses, including an eight-month period of 1991–1992 that saw a total of 34 people killed in the Barrios Altos massacre, the Santa massacre, the Pativilca massacre, and the La Cantuta massacre.

Keiko Sofía Fujimori Higuchi is a Peruvian politician. Fujimori is the eldest daughter of former Peruvian president Alberto Fujimori and Susana Higuchi. From August 1994 to November 2000, she held the role of First Lady of Peru, during her father's administrations. She has served as the leader of the Fujimorist political party Popular Force since 2010, and was a congresswoman representing the Lima Metropolitan Area, from 2006 to 2011. Fujimori ran for president in the 2011, 2016, and 2021 elections, but was defeated each time in the second round of voting.

Peru and the United States established relations on May 2, 1826, following Peru's independence from Spain.
The following activities are supposed to have been done by the Central Intelligence Agency in Peru.

Greece and Peru established diplomatic relations on 5 December 1965. Greece was represented in Peru by its embassy in Brazil until 1992, when the embassy in Lima was opened. Around 150-350 people of Greek descent live in Peru, including Vladimiro Montesinos, the long-standing head of the Peruvian intelligence service, Servicio de Inteligencia Nacional under Alberto Fujimori. Since 1987, Peru has an embassy in Athens.

On Transparency International's 2022 Corruption Perceptions Index, Peru scored 36 on a scale from 0 to 100. When ranked by score, Peru ranked 101st among the 180 countries in the Index, where the country ranked first is perceived to have the most honest public sector. For comparison with worldwide scores, the best score was 90, the average score was 43, and the worst score was 12. For comparison with regional scores, the highest score among the countries of the Americas was 74, the average score was 43 and the lowest score was 14.

The National Directorate of Intelligence (Spanish: Dirección Nacional de Inteligencia), or (DINI), is the premier intelligence agency in Peru. The agency is responsible for national, military and police intelligence, as well as counterintelligence.

The Ministry of the Presidency is a ministry of the Republic of Costa Rica created on 24 December 1961 through Law 2980. Its work prescribed by law consists in providing support to the President of the Republic, serving as a liaison between the Presidency and the other branches of government, civil society and the various ministries.
Censorship in Peru has been prevalent throughout its history. There have been multiple shifts in the level of freedom of the press in Peru, starting in the late 1900s when the country was oppressed, to the early 2000s when the country experienced more freedom; only recently has the country been ranked as partly free. After the neoliberal economic policies implemented in the 1990s stabilized the national economy and led it to an economic boom in the 21st century, usage of TV and access to internet has vastly increased, leading to more spaces of expression.

Luis Carlos Antonio Iberico Núnez is an Argentine-born Peruvian journalist and politician. Throughout his journalistic career, he served in various news stations during the 1980s and 1990s. He gained prominence for his fight against the Alberto Fujimori administration, denouncing several allegations of corruption involving the press. Alongside Fernando Olivera, he presented the first "Vladi-videos" that would prove the major corruption operations headed by Intelligence Chief Vladimiro Montesinos. His role in Fujimori's downfall would gain him support in a career in politics.
El Comercio Group (GEC) is a Peruvian media conglomerate that owns multiple newspapers, television stations and other entities. The largest media conglomerate in Peru and one of the largest in South America, El Comercio Group is owned by the owned by the Miró Quesada family.

Plan Verde was a clandestine military operation developed by the armed forces of Peru during the internal conflict in Peru; it involved the genocide of impoverished and indigenous Peruvians, the control or censorship of media in the nation and the establishment of a neoliberal economy controlled by a military junta in Peru. Initially drafted in October 1989 in preparations for a coup d'état to overthrow President Alan García, the operation was extended into the 1990 Peruvian general election and was reported to be subsequently executed under the government of newly elected president Alberto Fujimori following the 1992 Peruvian coup d'état. Shortly after the coup, Plan Verde was first leaked to the public by Peruvian magazine Oiga, with a small number of other media outlets also reporting access to the plan's documents.













