A geographic information system (GIS) is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data. GIS applications are tools that allow users to create interactive queries, analyze spatial information, edit data in maps, and present the results of all these operations. GIS sometimes refers to geographic information science (GIScience), the science underlying geographic concepts, applications, and systems.

Topography is the study of the shape and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area could refer to the surface shapes and features themselves, or a description.
The Forestry Commission is a non-ministerial government department responsible for forestry in England. It was formerly also responsible for Forestry in Wales and Scotland, however on 1 April 2013 Forestry Commission Wales merged with other agencies to become Natural Resources Wales, whilst two new bodies were established in Scotland on 1 April 2019. The commission was set up in 1919 to expand Britain's forests and woodland after depletion during the First World War. To do this, the commission bought large amounts of former agricultural land, eventually becoming the largest land owner in Britain. The Commission is divided into three divisions: Forestry England, Forestry Commission and Forest Research.

In the United Kingdom, an ancient woodland is a woodland that has existed continuously since 1600 or before in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. Before those dates, planting of new woodland was uncommon, so a wood present in 1600 was likely to have developed naturally.
Geocoding is the computational process of transforming a physical address description to a location on the Earth's surface. Reverse geocoding, on the other hand, converts geographic coordinates to a description of a location, usually the name of a place or an addressable location. Geocoding relies on a computer representation of address points, the street / road network, together with postal and administrative boundaries.

The Caledonian Forest is the name given to the former temperate rainforest of Scotland.

The Survey of India is India's central engineering agency in charge of mapping and surveying. Set up in 1767 to help consolidate the territories of the British East India Company, it is one of the oldest Engineering Departments of the Government of India. Its members are from Survey of India Service cadre of Civil Services of India and Army Officers from the Corps of Engineers. It is headed by the Surveyor General of India.At present, Survey of India is headed by Lt Gen Girish Kumar, VSM.
A cadastre is a comprehensive land recording of the real estate or real property's metes-and-bounds of a country.

Spatial analysis or spatial statistics includes any of the formal techniques which study entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques, many still in their early development, using different analytic approaches and applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data.
Bonpas Creek is a tributary of the Wabash River in Illinois. It rises to the east of Olney in Richland County, Illinois. Flowing south, it forms the boundary between Edwards and Wabash counties. The creek is 58.4 miles (94.0 km) long. It joins the Wabash near Grayville, Illinois. In the last 2 miles (3 km) of its watercourse, it occupies part of a former Wabash oxbow bend. As such, the creek now also forms part of the state boundary between White County, Illinois, and Gibson County, Indiana, as flows past Grayville in the former channel.
MapInfo Pro is a desktop geographic information system (GIS) software product produced by Pitney Bowes Software and used for mapping and location analysis. MapInfo Pro allows users to visualize, analyze, edit, interpret, understand and output data to reveal relationships, patterns, and trends. MapInfo Pro allows users to explore spatial data within a dataset, symbolize features, and create maps.
Geospatial metadata is a type of metadata that is applicable to objects that have an explicit or implicit geographic extent, i.e. are associated with some position on the surface of the globe. Such objects may be stored in a geographic information system (GIS) or may simply be documents, data-sets, images or other objects, services, or related items that exist in some other native environment but whose features may be appropriate to describe in a (geographic) metadata catalog.

Web mapping is the process of using the maps delivered by geographic information systems (GIS) in World Wide Web. A web map on the World Wide Web is both served and consumed, thus web mapping is more than just web cartography, it is a service by which consumers may choose what the map will show. Web GIS emphasizes geodata processing aspects more involved with design aspects such as data acquisition and server software architecture such as data storage and algorithms, than it does the end-user reports themselves.

The Sylva Foundation is an environmental organisation focusing on trees and forestry established in 2006, and registered as a charity in England and Wales in 2009 and with the Office of the Scottish Charity Regulator in 2010. The organisation was co-founded by Sir Martin Wood and Dr Gabriel Hemery. Its office is at the Sylva Wood Centre in Long Wittenham in Oxfordshire, England.

Lady Park Wood National Nature Reserve is a 45-hectare (110-acre) nature reserve straddling the borders of Gloucestershire in England and Monmouthshire in Wales. Most of the wood is in Wales but it is managed under agreement with Natural England.

The United Kingdom, being in the British Isles, is ideal for tree growth, thanks to its mild winters, plentiful rainfall, fertile soil and hill-sheltered topography. Growth rates for broadleaved (hardwood) trees exceed those of mainland Europe, while conifer (softwood) growth rates are three times those of Sweden and five times those of Finland. In the absence of people, much of Great Britain would be covered with mature oaks, except for Scotland. Although conditions for forestry are good, trees do face damage threats arising from fungi, parasites and pests.
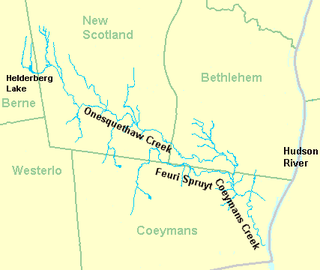
Coeymans Creek is a 7.3-mile-long (11.7 km) tributary of the Hudson River in Albany County, New York in the United States.

Scotland, being in the British Isles, is ideal for tree growth, thanks to its mild winters, plentiful rainfall, fertile soil and hill-sheltered topography. As of 2019 approximately 18.5 % of the country was wooded, compared to a European Union (EU) average of 43 %. Approximately 4,700 km2 of Scotland’s forests and woodlands are publicly owned by the Scottish Government via Forestry and Land Scotland, and are termed the National Forest Estate.

Basil Matthew Stuart Dunlop is a retired Chartered Forester, FICFor and author who lives in the Cairngorms National Park.

Argyll Forest Park is a forest park located on the Cowal peninsula in Argyll and Bute, Scottish Highlands. Established in 1935, it was the first forest park to be created in the United Kingdom. The park is managed by Forestry and Land Scotland, and covers 211 km2 in total.
1) Nelson, D. 2010. The Native Woodland Survey of Scotland (NWSS). Scottish Forestry Vol 64 (3).
2) Robertson, P. & Grieve, Y. 2010. Quality Assuring a National Native Woodland Survey. Scottish Forestry Vol 64 (4).
3) Grieve, Y. 2011. The Native Woodland Survey of Scotland dataset: what you get and how to get it! Scottish Forestry Vol 65 (1).













