This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

The 4th century was the time period which lasted from 301 to 400. In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 to build the city soon called Nova Roma ; it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor.

Year 301 (CCCI) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Postumius and Nepotianus. The denomination 301 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 350 (CCCL) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sergius and Nigrinianus. The denomination 350 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 336 (CCCXXXVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Nepotianus and Facundus. The denomination 336 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Julius Nepos was de iure and de facto Western Roman Emperor from AD 474 to 475 and then only de iure until his death in 480. He was also the ruler of Roman Dalmatia from AD 468 to 480. Some historians consider Nepos to be the final Western Roman Emperor, while others consider the western line to have ended with Romulus Augustulus in AD 476. In contrast, the Eastern Roman Empire and its line of emperors survived this period.

Year 460 (CDLX) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Magnus and Apollonius. The denomination 460 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Valerius Maximus was a Latin writer and author of a collection of historical anecdotes : Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX
Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX. He worked during the reign of Tiberius.

Magnentius was a usurper of the Roman Empire from 350 to 353.

Flavia Maximiana Theodora, also known as Theodora, was a Roman Empress, wife of Constantius Chlorus.
The Constantinian dynasty is an informal name for the ruling family of the Roman Empire from Constantius Chlorus to the death of Julian in 363. It is named after its most famous member, Constantine the Great who became the sole ruler of the empire in 324. The dynasty is also called Neo-Flavian because every Constantinian emperor bore the name Flavius, similarly to the rulers of the first Flavian dynasty in the 1st century.

The Diocese of Tarazona is a Roman Catholic bishopric located in north-eastern Spain, in the provinces of Zaragoza, Soria, Navarre and
La Rioja, forming part of the autonomous communities of Aragón, Castile-Leon, Navarre and La Rioja. The diocese forms part of the ecclesiastical province of Zaragoza, and is thus suffragan to the Archdiocese of Zaragoza.

The Duchy of Cantabria was a march created by the Visigoths in northern Spain to watch their border with the Cantabrians and Basques. Its precise extension is unclear in the different periods, but seems likely that it included Cantabria, parts of Northern Castile, La Rioja, and probably western areas of Biscay and Álava.
Eutropia was the daughter of Emperor Constantius Chlorus and of Flavia Maximiana Theodora, and therefore half-sister of Emperor Constantine I.
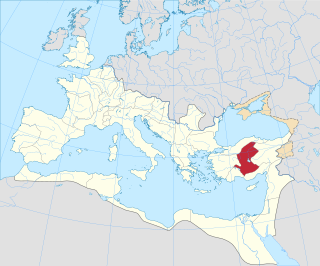
Galatia was the name of a province of the Roman Empire in Anatolia. It was established by the first emperor, Augustus, in 25 BC, covering most of formerly independent Celtic Galatia, with its capital at Ancyra.
Sunieric was a Visigoth general, who collaborated with the Roman army in the re-conquest of Spain on behalf of Emperor Majorian.
The Battle of Arelate was fought in 458 near Arelate (Arles) between Western Roman Emperor Majorian and Visigothic king Theodoric II. After the assassination of Flavius Aetius in 454, the Visigoths began to expand their kingdom at the expense of the crumbling Roman administration in Gaul and Hispania. When Majorian became emperor in 457, the Visigoths under king Theodoric II had just recently defeated the Suebic Kingdom in north-west Hispania and were consolidating their hold on the rest of the peninsula.
Titus Flavius Postumius Titianus was a Roman statesman who served as Senator and Consul suffectus.
Virius Nepotianus was a Roman statesman who served as Consul of the Roman Empire in AD 336. He was a member of the Constantinian dynasty.











