This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

The organic compound citrulline is an α-amino acid. Its name is derived from citrullus, the Latin word for watermelon, from which it was first isolated in 1914 by Koga and Odake. It was finally identified by Wada in 1930.
It has the formula H2NC(O)NH(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a key intermediate in the urea cycle, the pathway by which mammals excrete ammonia by converting it into urea. Citrulline is also produced as a byproduct of the enzymatic production of nitric oxide from the amino acid arginine, catalyzed by nitric oxide synthase.
NO synthase may refer to:
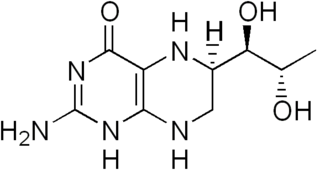
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4, THB), also known as sapropterin, is a cofactor of the three aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes, used in the degradation of amino acid phenylalanine and in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT), melatonin, dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline), and is a cofactor for the production of nitric oxide (NO) by the nitric oxide synthases. Chemically, its structure is that of a reduced pteridine derivative.
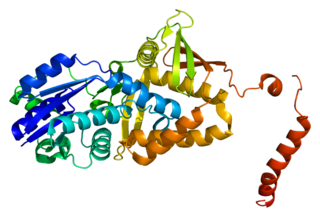
Argininosuccinate synthase or synthetase is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of argininosuccinate from citrulline and aspartate. In humans, argininosuccinate synthase is encoded by the ASS gene located on chromosome 9.

Louis J. Ignarro is an American pharmacologist. For demonstrating the signaling properties of nitric oxide, he was co-recipient of the 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Robert F. Furchgott and Ferid Murad.
An atrial natriuretic peptide receptor is a receptor for atrial natriuretic peptide.
Boettcher cells are a special cell type located in the inner ear.

Endothelial NOS (eNOS), also known as nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) or constitutive NOS (cNOS), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS3 gene located in the 7q35-7q36 region of chromosome 7. This enzyme is one of three isoforms that synthesize nitric oxide (NO), a small gaseous and lipophilic molecule that participates in several biological processes. The other isoforms include neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which is constitutively expressed in specific neurons of the brain and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), whose expression is typically induced in inflammatory diseases.
eNOS is primarily responsible for the generation of NO in the vascular endothelium, a monolayer of flat cells lining the interior surface of blood vessels, at the interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the remainder of the vessel wall. NO produced by eNOS in the vascular endothelium plays crucial roles in regulating vascular tone, cellular proliferation, leukocyte adhesion, and platelet aggregation. Therefore, a functional eNOS is essential for a healthy cardiovascular system.
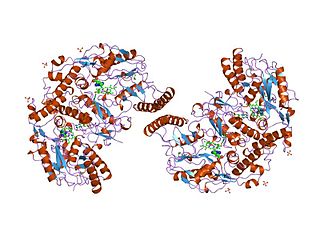
Nitric oxide synthase, inducible is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS2 gene.
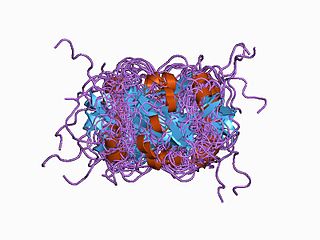
Nitric oxide synthase 1 (neuronal), also known as NOS1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS1 gene.
In the field of enzymology, a dimethylargininase, also known as a dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DYNLL1 gene.

Nitric oxide synthase-interacting protein is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOSIP gene.

7-Nitroindazole, or 7-NI, is a heterocyclic small molecule containing an indazole ring that has been nitrated at the 7 position. Nitroindazole acts as a selective inhibitor for neuronal nitric oxide synthase, a hemoprotein enzyme that, in neuronal tissue, converts arginine to citrulline and nitric oxide (NO). Nitric oxide can diffuse through the plasma membrane into neighbouring cells, allowing cell signalling, so nitroindazole indirectly inhibits this signalling process. Other inhibitors exist such as 3-bromo-7-nitroindazole, which is more potent but less specific, or NPA (N-propyl-L-arginine), which acts on a different site.
Nitric oxide is a molecule and chemical compound with chemical formula of NO. In mammals including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule involved in many physiological and pathological processes. It is a powerful vasodilator with a half-life of a few seconds in the blood. Standard pharmaceuticals such as nitroglycerine and amyl nitrite are precursors to nitric oxide. Low levels of nitric oxide production are typically due to ischemic damage in the liver.

Nitroarginine, or Nω-nitro-L-arginine, is a nitro derivative of the amino acid arginine. It is an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase and hence a vasoconstrictor. As such, it finds widespread use as a biochemical tool in the study of nitric oxide and its biological effects.
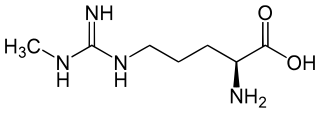
N-Methylarginine is an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase. Chemically, it is a methyl derivative of the amino acid arginine. It is used as a biochemical tool in the study of physiological role of nitric oxide.













