The North Dakota Century Code is the collection of all the statutes passed by the North Dakota Legislative Assembly since the state's admission to the Union. It also includes the North Dakota Constitution.

A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs a city, state, or country. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by legislative bodies; they are distinguished from case law or precedent, which is decided by courts, and regulations issued by government agencies.

The North Dakota Legislative Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of North Dakota. The Legislative Assembly consists of two chambers, the lower North Dakota House of Representatives, with 94 representatives, and the upper North Dakota Senate, with 47 senators. The state is divided into 47 constituent districts, with two representatives and one senator elected from each district. Members of both houses are elected without term limits. Due to the Legislative Assembly being a biennial legislature, with the House and Senate sitting for only 80 days in odd-numbered years, a Legislative Council oversees legislative affairs in the interim periods, doing longer-term studies of issues, and drafting legislation for consideration of both houses during the next session.

The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States or America, is a country comprising 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories, and various possessions. At 3.8 million square miles, the United States is the world's third or fourth largest country by total area and is slightly smaller than the entire continent of Europe's 3.9 million square miles. With a population of over 327 million people, the U.S. is the third most populous country. The capital is Washington, D.C., and the largest city by population is New York City. Forty-eight states and the capital's federal district are contiguous in North America between Canada and Mexico. The State of Alaska is in the northwest corner of North America, bordered by Canada to the east and across the Bering Strait from Russia to the west. The State of Hawaii is an archipelago in the mid-Pacific Ocean. The U.S. territories are scattered about the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, stretching across nine official time zones. The extremely diverse geography, climate, and wildlife of the United States make it one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries.
The numbering system for the Century Code is a three-part number, with each part separated by a hyphen. The first part refers to the title, the second to the chapter, and the third to the section. For example, Section 54-35-01 refers to the first section in Chapter 35 of Title 54 (the section deals with the legislative management of the North Dakota Legislative Assembly).
The decimal point system is used to designate sections that have been inserted between two consecutively numbered sections. For example, Title 12 deals with Corrections, Parole, and Probation, while Title 13 deals with Debtor and Creditor Relationship. The state Criminal Code (which alphabetically falls between the titles) is thus numbered Title 12.1.

In criminal justice, particularly in North America, correction, corrections, and correctional, are umbrella terms describing a variety of functions typically carried out by government agencies, and involving the punishment, treatment, and supervision of persons who have been convicted of crimes. These functions commonly include imprisonment, parole and probation. A typical correctional institution is a prison. A correctional system, also known as a penal system, thus refers to a network of agencies that administer a jurisdiction's prisons and community-based programs like parole and probation boards;. This system is part of the larger criminal justice system, which additionally includes police, prosecution and courts. Jurisdictions throughout Canada and the US have ministries or departments, respectively, of corrections, correctional services, or similarly-named agencies.
Parole is a permanent release of a prisoner who agrees to certain conditions before the completion of the maximum sentence period, originating from the French parole. The term became associated during the Middle Ages with the release of prisoners who gave their word.
Probation in criminal law is a period of supervision over an offender, ordered by the court instead of serving time in prison.

The Code of Laws of the United States of America is the official compilation and codification of the general and permanent federal statutes of the United States. It contains 53 titles. The main edition is published every six years by the Office of the Law Revision Counsel of the House of Representatives, and cumulative supplements are published annually. The official version of those laws not codified in the United States Code can be found in United States Statutes at Large.
Interstate 780 (I-780) is an Interstate Highway in the San Francisco Bay Area of the U.S. state of California. It serves to connect Interstate 80 in Vallejo with Interstate 680 just north of the Benicia-Martinez Bridge in Benicia. It closely parallels the Carquinez Strait for its entire route. Originally, this segment was part of I-680 before that Interstate was extended and rerouted to Fairfield. The city-maintained Curtola Parkway continues west from I-80 to State Route 29 in Vallejo.
The Constitution of South Africa is the supreme law of the Republic of South Africa. It provides the legal foundation for the existence of the republic,it sets out the rights and duties of its citizens, and defines the structure of the government. The current constitution, the country's fifth, was drawn up by the Parliament elected in 1994 in the South African general election, 1994. It was promulgated by President Nelson Mandela on 18 December 1996 and came into effect on 4 February 1997, replacing the Interim Constitution of 1993.

State Route 160 is a state highway in the U.S. state of California consisting of two sections. The longer, southern, section is a scenic highway through the alluvial plain of the Sacramento River, linking SR 4 in Antioch with Sacramento via the Antioch Bridge. The northern section, separated from the southern by Sacramento city streets, is the North Sacramento Freeway, running from the 16th Street Bridge over the American River to Interstate 80 Business towards Roseville.

The coat of arms of North Dakota was created for use by the state government and National Guard units. An image of the coat of arms is seen on the flag of the Governor of North Dakota and a short discussion of its use can be found at the North Dakota state government website.

The Penal Code of California forms the basis for the application of criminal law in the American state of California. It was originally enacted in 1872 as one of the original four California Codes, and has been substantially amended and revised since then.
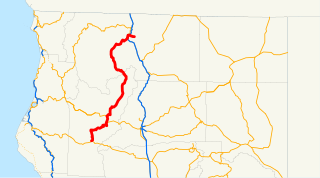
State Route 3 is a state highway in the U.S. state of California. It runs from SR 36 north along the shore of Trinity Lake, Fort Jones and Etna. The route approaches Yreka, intersecting with Interstate 5 (I-5), and turns east to Montague. The road was numbered SR 3 in 1964, and most of it has been part of the state highway system since 1933.
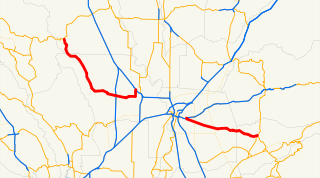
State Route 16 is a state highway in the northern region of the U.S. state of California that runs from Route 20 in Colusa County to Route 49 just outside Plymouth in Amador County. Much of the route through the Sacramento area is unsigned as it runs on a concurrency with the I-5 and US 50 freeways.

The Constitution of Argentina is the basic governing document of Argentina, and the primary source of existing law in Argentina. Its first version was written in 1853 by a Constitutional Assembly gathered in Santa Fe, and the doctrinal basis was taken in part from the United States Constitution. It was then reformed in 1860, 1866, 1898, 1949, 1957, and the current version is the reformed text of 1994.

State Route 34 is a short state highway in the U.S. state of California.

The Code of Virginia is the statutory law of the U.S. state of Virginia, and consists of the codified legislation of the Virginia General Assembly. The 1950 Code of Virginia is the revision currently in force. The previous official versions were the Codes of 1819, 1849, 1887, and 1919, though other compilations had been printed privately as early as 1733, and other editions have been issued that were not designated full revisions of the code.
Fair debt collection broadly refers to regulation of the United States debt collection industry at both the federal and state level. At the Federal level, it is primarily governed by the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA). In addition, many U.S. states also have debt collection laws that regulate the credit and collection industry and give consumer debtors protection from abusive and deceptive practices. Many state laws track the language of the FDCPA, so that they are sometimes referred to as mini-FDCPAs.
This article explains the citation of United Kingdom legislation, including the systems used for legislation passed by devolved parliaments and assemblies, for secondary legislation, and for prerogative instruments. This subject is relatively complex both due to the different sources of legislation in the United Kingdom, and because of the different histories of the constituent countries of the United Kingdom.
The Civil Code of California is a collection of statutes for the State of California. The code is made up of statutes which govern the general obligations and rights of persons within the jurisdiction of California. It was based on a civil code originally prepared by David Dudley Field II for the state of New York. It is one of the 29 California Codes and was among the first four enacted in 1872.
In many jurisdictions in the US, roads were run along every section line, giving access to previously remote areas and serving in many instances as firebreaks. A road or arterial in which the centerline is laid out along a section line boundary is often referred to as a section line road or section line arterial. In Lubbock, Texas, Oklahoma City; Boise, Idaho; metropolitan areas of Arizona ; and much of the Las Vegas Valley, all major thoroughfares run along section lines, producing a readily identifiable grid.
In the United States, the law regarding murder varies by jurisdiction. In most U.S. jurisdictions there is a hierarchy of acts, known collectively as homicide, of which first degree murder and felony murder are the most serious, followed by second degree murder, followed by voluntary manslaughter and involuntary manslaughter which are not as serious, and ending finally in justifiable homicide, which is not a crime at all. However, because there are at least 52 relevant jurisdictions, each with its own criminal code, this is a considerable simplification.

A "Little Miller Act" is a U.S. state statute, based upon the federal Miller Act, that requires prime contractors on state construction projects to post bonds guarantying the performance of their contractual duties and/or the payment of their subcontractors and material suppliers.
Laws regarding incest in the United States vary widely between jurisdictions regarding both the definition of the offense and penalties for its commission.













