
In nuclear chemistry, nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises due to the difference in atomic "binding energy" between the atomic nuclei before and after the reaction. Fusion is the process that powers active or "main sequence" stars, or other high magnitude stars.

In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction or a radioactive decay process in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller, lighter nuclei. The fission process often produces free neutrons and gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay.

Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the nature of the particles that constitute matter and radiation. Although the word particle can refer to various types of very small objects, particle physics usually investigates the irreducibly smallest detectable particles and the fundamental interactions necessary to explain their behaviour. By our current understanding, these elementary particles are excitations of the quantum fields that also govern their interactions. The currently dominant theory explaining these fundamental particles and fields, along with their dynamics, is called the Standard Model. Thus, modern particle physics generally investigates the Standard Model and its various possible extensions, e.g. to the newest "known" particle, the Higgs boson, or even to the oldest known force field, gravity.

In particle physics, the strong interaction is the mechanism responsible for the strong nuclear force (also called the strong force, nuclear strong force, or colour force), and is one of the four known fundamental interactions, with the others being electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and gravitation. At the range of 10−15 m (1 femtometer), the strong force is approximately 137 times as strong as electromagnetism, a million times as strong as the weak interaction, and 1038 times as strong as gravitation. The strong nuclear force holds most ordinary matter together because it confines quarks into hadron particles such as the proton and neutron. In addition, the strong force binds neutrons and protons to create atomic nuclei. Most of the mass of a common proton or neutron is the result of the strong force field energy; the individual quarks provide only about 1% of the mass of a proton.
Nuclear engineering is the branch of engineering concerned with the application of breaking down atomic nuclei (fission) or of combining atomic nuclei (fusion), or with the application of other sub-atomic processes based on the principles of nuclear physics. In the sub-field of nuclear fission, it particularly includes the design, interaction, and maintenance of systems and components like nuclear reactors, nuclear power plants, or nuclear weapons. The field also includes the study of medical and other applications of radiation, particularly Ionizing radiation, nuclear safety, heat/thermodynamics transport, nuclear fuel, or other related technology and the problems of nuclear proliferation.
The Mössbauer effect, or recoilless nuclear resonance fluorescence, is a physical phenomenon discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1958. It involves the resonant and recoil-free emission and absorption of gamma radiation by atomic nuclei bound in a solid. Its main application is in Mössbauer spectroscopy.

In physics, binding energy is the minimum energy required to disassemble a system of particles into separate parts. This energy is equal to the mass defect minus the amount of energy, or mass, that is released when a bound system is created, and is what keeps the system together.
Engineering physics or engineering science refers to the study of the combined disciplines of physics, mathematics and engineering, particularly computer, nuclear, electrical, electronic, materials or mechanical engineering. By focusing on the scientific method as a rigorous basis, it seeks ways to apply, design, and develop new solutions in engineering.

Raja Ramanna was an Indian physicist who is best known for his role in India's nuclear program during its early stages.
The Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, in Dubna, Moscow Oblast, Russia, is an international research center for nuclear sciences, with 5500 staff members, 1200 researchers including 1000 Ph.Ds from eighteen states, members of the institution. Most scientists, however, are eminent Russian scientists.

The nuclear force is a force that acts between the protons and neutrons of atoms. Neutrons and protons, both nucleons, are affected by the nuclear force almost identically. Since protons have charge +1 e, they experience an electric force that tends to push them apart, but at short range the attractive nuclear force is strong enough to overcome the electromagnetic force. The nuclear force binds nucleons into atomic nuclei.
Astatine (85At) has 39 known isotopes, all of which are radioactive; the range of their mass numbers is from 191 to 229. There also exist 23 metastable excited states. The longest-lived isotope is 210At, which has a half-life of 8.1 hours; the longest-lived isotope existing in naturally occurring decay chains is 219At with a half-life of 56 seconds.

The Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics (SINP) is an institution of basic research and training in physical and biophysical sciences located in Bidhannagar, Kolkata, India. The institute is named after the famous Indian physicist Meghnad Saha.

Nuclear astrophysics is an interdisciplinary branch of physics involving close collaboration among researchers in various subfields of nuclear physics and astrophysics: notably stellar modeling; measurement and theoretical estimation of nuclear reaction rates; physical cosmology and cosmochemistry; gamma ray, optical and X-ray astronomy; and extending our knowledge about nuclear lifetimes and masses. In general terms, nuclear astrophysics aims to understand the origin of the chemical elements and the energy generation in stars.

Rajagopala Chidambaram is an Indian Physicist who is known for his integral role in India's nuclear weapons program; he coordinated test preparation for the Pokhran-I (1975) and Pokhran-II (1998).
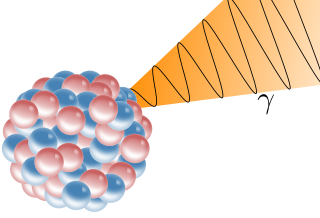
A gamma ray or gamma radiation, is a penetrating electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves and so imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation gamma rays based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; he had previously discovered two less penetrating types of decay radiation, which he named alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power.
Physics Letters was a scientific journal published from 1962 to 1966, when it split in two series now published by Elsevier:









