
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as 1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.

The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates from the use of this surface for placing and then sniffing powdered tobacco, or "snuff." It is sometimes referred to by its French name tabatière.
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus.

The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew.

The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The radius is shorter and smaller than the ulna. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.

A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The wrist may be deformed. The ulna bone may also be broken.
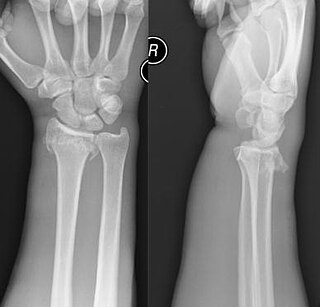
A Smith's fracture, also sometimes known as a reverse Colles' fracture or Goyrand-Smith's, is a fracture of the distal radius. It is caused by a direct blow to the dorsal forearm or falling onto flexed wrists, as opposed to a Colles' fracture which occurs as a result of falling onto wrists in extension. Smith's fractures are less common than Colles' fractures.
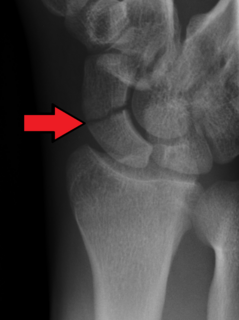
A scaphoid fracture is a break of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. Symptoms generally includes pain at the base of the thumb which is worse with use of the hand. The anatomic snuffbox is generally tender and swelling may occur. Complications may include nonunion of the fracture, avascular necrosis, and arthritis.

A humerus fracture is a break of the humerus bone in the upper arm. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and bruising. There may be a decreased ability to move the arm and the person may present holding there elbow. Complications may include injury to an artery or nerve, and compartment syndrome.

An accessory bone or supernumerary bone is a bone that is not normally present in the body, but can be found as a variant in a significant number of people. They pose a risk of being misdiagnosed as bone fractures on radiography.
The Essex-Lopresti fracture is a fracture of the radial head with concomitant dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint and disruption of the interosseous membrane. The injury is named after Peter Essex-Lopresti who described it in 1951.
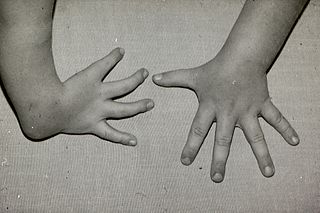
Radial dysplasia, also known as radial club hand or radial longitudinal deficiency, is a congenital difference occurring in a longitudinal direction resulting in radial deviation of the wrist and shortening of the forearm. It can occur in different ways, from a minor anomaly to complete absence of the radius, radial side of the carpal bones and thumb. Hypoplasia of the distal humerus may be present as well and can lead to stiffness of the elbow. Radial deviation of the wrist is caused by lack of support to the carpus, radial deviation may be reinforced if forearm muscles are functioning poorly or have abnormal insertions. Although radial longitudinal deficiency is often bilateral, the extent of involvement is most often asymmetric.

Olecranon fracture is a fracture of the bony portion of the elbow. The injury is fairly common and often occurs following a fall or direct trauma to the elbow. The olecranon is the proximal extremity of the ulna which is articulated with the humerus bone and constitutes a part of the elbow articulation. Its location makes it vulnerable to direct trauma.

Wrist arthroscopy can be used to look inside the joint of the wrist. It is a minimally invasive technique which can be utilized for diagnostic purposes as well as for therapeutic interventions. Wrist arthroscopy has been used for diagnostic purposes since it was first introduced in 1979. However, it only became accepted as diagnostic tool around the mid-1980s. At that time, arthroscopy of the wrist was an innovative technique to determine whether a problem could be found in the wrist. A few years later, wrist arthroscopy could also be used as a therapeutic tool. The term is from the Greek άρθρωση, arthros "joint" and σκοπεῖν, skopein "to look or see".
Nissen-Lie classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Nissen-Lie classification system there are seven types of fractures. The classification system was first published in 1939.
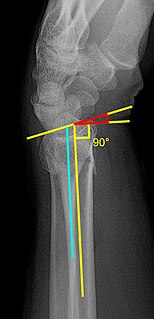
There are a number of ways to classify distal radius fractures. Classifications systems are devised to describe patterns of injury which will behave in predictable ways, to distinguish between conditions which have different outcomes or which need different treatments. Most wrist fracture systems have failed to accomplish any of these goals and there is no consensus about the most useful one.













