In business and engineering, new product development (NPD) covers the complete process of bringing a new product to market. A central aspect of NPD is product design, along with various business considerations. New product development is described broadly as the transformation of a market opportunity into a product available for sale. The product can be tangible or intangible, though sometimes services and other processes are distinguished from "products." NPD requires an understanding of customer needs and wants, the competitive environment, and the nature of the market.
Cost, time and quality are the main variables that drive customer needs. Aiming at these three variables, innovative companies develop continuous practices and strategies to better satisfy customer requirements and to increase their own market share by a regular development of new products. There are many uncertainties and challenges which companies must face throughout the process. The use of best practices and the elimination of barriers to communication are the main concerns for the management of the NPD.
In the field of management, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of the major goals and initiatives taken by an organization's top management on behalf of owners, based on consideration of resources and an assessment of the internal and external environments in which the organization operates.
Product management is an organisational lifecycle function within a company dealing with the planning, forecasting, and production, or marketing of a product or products at all stages of the product lifecycle. Similarly, product lifecycle management (PLM) integrates people, data, processes and business systems. It provides product information for companies and their extended supply chain enterprise.

Product life-cycle management (PLM) is the succession of strategies by business management as a product goes through its life-cycle. The conditions in which a product is sold changes over time and must be managed as it moves through its succession of stages.
Market research is an organized effort to gather information about target markets or customers. It is a very important component of business strategy. The term is commonly interchanged with marketing research; however, expert practitioners may wish to draw a distinction, in that marketing research is concerned specifically about marketing processes, while market research is concerned specifically with markets.
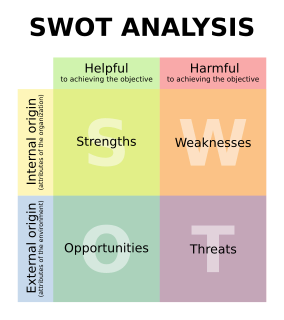
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique used to help a person or organization identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to business competition or project planning. It is intended to specify the objectives of the business venture or project and identify the internal and external factors that are favorable and unfavorable to achieving those objectives. Users of a SWOT analysis often ask and answer questions to generate meaningful information for each category to make the tool useful and identify their competitive advantage. SWOT has been described as the tried-and-true tool of strategic analysis.
Marketing strategy is a long-term, forward-looking approach to planning with the fundamental goal of achieving a sustainable competitive advantage. Strategic planning involves an analysis of the company's strategic initial situation prior to the formulation, evaluation and selection of market-oriented competitive position that contributes to the company's goals and marketing objectives.
Competitive intelligence (CI) is the action of defining, gathering, analyzing, and distributing intelligence about products, customers, competitors, and any aspect of the environment needed to support executives and managers in strategic decision making for an organization.
In management literature, gap analysis involves the comparison of actual performance with potential or desired performance. If an organization does not make the best use of current resources, or forgoes investment in capital or technology, it may produce or perform below an idealized potential. This concept is similar to an economy's production being below the production possibilities frontier.
Business development entails tasks and processes to develop and implement growth opportunities within and between organizations. It is a subset of the fields of business, commerce and organizational theory. Business development is the creation of long-term value for an organization from customers, markets, and relationships. Business development can be taken to mean any activity by either a small or large organization, non-profit or for-profit enterprise which serves the purpose of ‘developing’ the business in some way. In addition, business development activities can be done internally or externally by a business development consultant. External business development can be facilitated through Planning Systems, which are put in place by governments to help small businesses. In addition, reputation building has also proven to help facilitate business development.
A target audience is the intended audience or readership of a publication, advertisement, or other message. In marketing and advertising, it is a particular group of consumers within the predetermined target market, identified as the targets or recipients for a particular advertisement or message. Businesses that have a wide target market will focus on a specific target audience for certain messages to send, such as The Body Shops Mother's Day advertisements, which were aimed at the children and spouses of women, rather than the whole market which would have included the women themselves.
Diversification is a corporate strategy to enter into a new market or industry in which the business doesn't currently operate, while also creating a new product for that new market. This is the most risky section of the Ansoff Matrix, as the business has no experience in the new market and does not know if the product is going to be successful
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to marketing:
A target market is a group of customers within a business's serviceable available market at which a business aims its marketing efforts and resources. A target market is a subset of the total market for a product or service. The target market typically consists of consumers who exhibit similar characteristics and are considered most likely to buy a business's market offerings or are likely to be the most profitable segments for the business to service.
Sales intelligence refers to technologies, applications, and practices for the collection, integration, analysis, and presentation of information to help salespeople find, monitor and understand data that provides insights into prospects’ and existing clients’ daily business. The data used in SI solutions is based on either internal data, behavioral data or open data. Companies use sales intelligence software to improve the quality and quantity of sales leads by using data to find new opportunities and provide salespeople with the information they need to take advantage of them. Many of these
A phase-gate process, is a project management technique in which an initiative or project is divided into distinct stages or phases, separated by decision points.
The SIUE School of Business is an academic unit of Southern Illinois University Edwardsville (SIUE) located in Edwardsville, Illinois, United States.


