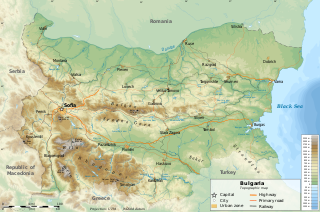
Bulgaria is a country situated in Southeast Europe, bordering Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. The northern border with Romania follows the river Danube until the city of Silistra. The land area of Bulgaria is 110,879 square kilometres (42,811 sq mi), slightly larger than that of Iceland or the U.S. state of Tennessee. Considering its relatively small size, Bulgaria has a great variety of topographical features. Even within small parts of the country, the land may be divided into plains, plateaus, hills, mountains, basins, gorges, and deep river valleys. The geographic center of Bulgaria is located in Uzana.
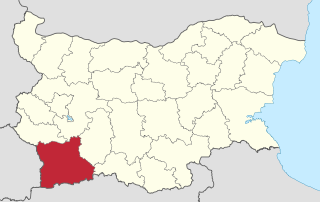
Blagoevgrad Province, also known as Pirin Macedonia is a province (oblast) of southwestern Bulgaria. It borders four other Bulgarian provinces to the north and east, to the Greek region of Macedonia to the south, and North Macedonia to the west. The province has 14 municipalities with 12 towns. Its principal city is Blagoevgrad, while other significant towns include Bansko, Gotse Delchev, Melnik, Petrich, Razlog, Sandanski, and Simitli.

Pirin National Park, originally named Vihren National Park, encompasses the larger part of the Pirin Mountains in southwestern Bulgaria, spanning an area of 403.56 km2 (155.82 sq mi). It is one of the three national parks in the country, the others being Rila National Park and Central Balkan National Park. The park was established in 1962 and its territory was expanded several times since then. Pirin National Park was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1983. The altitude varies from 950 m to 2,914 m at Vihren, Bulgaria's second highest summit and the Balkans' third.

The Central Balkan National Park lies in the heart of Bulgaria, nestled in the central and higher portions of the Balkan Mountains. Its altitude varies from 550 m. near the town of Karlovo to 2376 m. at Botev Peak, the highest summit in the mountain range. It was established on 31 October 1991. The Central Balkan National Park is the third largest protected territory in Bulgaria, spanning an area of 716.69 km² with total length of 85 km from the west to the east and an average width of 10 km. It occupies territory from 5 of the 28 provinces of the country: Lovech, Gabrovo, Sofia, Plovdiv and Stara Zagora. The national park includes nine nature reserves covering 28% of its territory: Boatin, Tsarichina, Kozya Stena, Steneto, Severen Dzhendem, Peeshti Skali, Sokolna, Dzhendema and Stara Reka.

Silkosia is a nature reserve in Strandzha Nature Park, located in the homonymous mountain, southeastern Bulgaria. Its territory close to the villages Kosti and Balgari. Silkosia is the oldest reserve in the country, declared on 23 July 1931 in order to protect the evergreen bushes unique for Europe. It encompasses part of the Veleka river catchment area with a territory of 389.6 ha or 3.896 km2. The terrain is various, in the lower parts there are predominantly swamp areas with typical Central European flora. The reserve encompasses territory between 100 and 250 m altitude and is thus among the lowest-lying nature reserves in the country.

Belasitsa Nature Park covers the northern slopes of Belasitsa Mountain in the Southwest Region of Bulgaria. The total area of the park is 117 km². Belasitsa is part of the European ecological network NATURA 2000 and is managed by the Belasitsa Nature Park Directorate which is a legal entity under the authority of the Executive Forest Agency of Ministry of Agriculture and Food. The Directorate office is located in the village of Kolarovo.

The Rodope montane mixed forests constitute a terrestrial ecoregion of Europe defined by the WWF. It belongs in the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests Biome and the Palearctic ecozone. There are three national parks in the ecoregion, all of them situated in Bulgaria: Central Balkan National Park, Pirin National Park, a UNESCO world heritage site, and Rila National Park.

Rila Monastery Nature Park is among the largest nature parks in Bulgaria spanning a territory of 252.535 km2 in the western part of the Rila mountain range at an altitude between 750 and 2713 meters. It is situated in Rila Municipality, Kyustendil Province and includes forests, mountain meadows, alpine areas and 28 glacial lakes. With a little more than 1 million visitors, it is the second most visited nature park in the country, after Vitosha Nature Park.

Teberda Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' located on the northern slopes of the western section of the Caucasus Mountains. It is the most visited nature reserve in the Russian Federation, with over 200,000 recorded in 2010. Included in the reserve are a popular tourist complex ("Dombay") and resorts in the surrounding areas. The terrain show extremes in variation: 31.7% forests, 20% meadows, 8.5% glaciers, 38.4% rock and scree, 0.7% - water. The reserve is divided into two sections - the Tebardinsky to the east, and the Arkhyz to the west. The two sections were connected in 2010 by a "biosphere polygon", the Caucasus State Nature Reserve. The two sectors are situated in the Karachayevsky District of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic. It is part of a UNESCO World Biosphere Reserve. The reserve was created in 1936, and covers an area of 84,996 ha (328.17 sq mi).

Uzunbodzhak, also transliterated as Ouzounboudjak is an UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, one of the five nature reserves in Strandzha Nature Park in south-eastern Bulgaria. The reserve is sometimes called Lopushna. Uzunbodzhak was established on 13 December 1956 and was included in the UNESCO network of biosphere reserves in March 1977. It covers an area of 2529.6 hectares, or 25.296 km2. All economic activities are prohibited on the territory of the reserve.

Stara Reka is one of the nine nature reserves in the Central Balkan National Park in central Bulgaria. Stara Reka was established on 19 March 1981 to protect the unique ecosystems of the Balkan Mountains. It spans an area of 1974.7 hectares, or 19.747km2.

Paril is a mountain saddle (pass) in western Bulgaria between the mountain ranges of Pirin to the north and Slavyanka to the south. It is situated on the territory of the Sandanski and Hadzhidimovo municipalities in Blagoevgrad Province.

Bayuvi Dupki–Dzhindzhiritsa, also spelled Doupki–Djindjiritza, is a nature reserve in Pirin National Park, located in the homonymous mountain range in south-western Bulgaria. It is situated in Razlog Municipality, Blagoevgrad Province. Bayuvi Dupki–Dzhindzhiritsa is among the nation's oldest reserves, declared in 1934 to protect the forests of Macedonian pine and Bosnian pine, both Balkan endemic species. Its territory was further expanded in 1976 and 1980 and spans an area of 2873 ha or 28,73 km2. It was declared a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in 1977. The reserve encompasses territory between 1200 and 2907 m altitude. Geologically it is dominated by Proterozoic marbles and has extensive karst terrain with numerous caves and karst formations.

Yulen is a nature reserve in Pirin National Park, located in the homonymous mountain range in south-western Bulgaria. It is situated in Bansko Municipality, Blagoevgrad Province. Yulen was declared on 26 August 1994 to monitor the growth of alpine plant species without human influence, as well as to protect rare plant and animal species. It spans a territory of 3156 ha or 31.56 km2.

Ali Botush, also spelled Alibotoush, is a nature reserve in the small mountain range of Slavyanka, located on the border between Bulgaria and Greece. The reserve occupies the northern section of the mountain which lies within the territory of Bulgaria and takes its name from the old name of Slavyanka. It is situated in the municipalities of Sandanski and Hadzhidimovo, Blagoevgrad Province. It was declared in 1951 to protect the largest forests of the endemic Bosnian pine in the Balkan Peninsula. Its territory was further expanded several times and spans an area of 1638 ha or 16,38 km2. It was declared a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in 1977.

Tisata is a nature reserve in south-western Bulgaria. It is situated in Kresna Municipality, Blagoevgrad Province. The reserve is managed by the administration of Pirin National Park despite the fact it lies outside the limits of the park.

Orelyak, also known as Orelek or Orlovi skali, is a peak in the Pirin mountain range, south-western Bulgaria. Reaching height of 2,099 m, it is the highest summit of Central Pirin, the second-highest subdivision of the mountain range. Orelayk is situated on Pirin's main ridge to the north of the Baba Peak and to the north-west of the Chala Peak. It has the shape of a triangular dome. The western slopes descend steeply, at places vertically, to the valley of the Pirinska Bistritsa river. Orelayk is built up of karstificated marbles. Near its highest point is located a 96 m-high radio and television repeater. The lower part of the northern slopes falls within the territory of the Orelyak Reserve, created to protect the old growth beech forests of Central Pirin.

The Melnik Earth Pyramids are rock formations, known as hoodoos, situated at the foothills of the Pirin mountain range in south-western Bulgaria. They span an area of 17 km2 near the town of Melnik, Blagoevgrad Province. Reaching a height of up to 100 m these sandstone pyramids are shaped in forms, resembling giant mushrooms, ancient towers and obelisks. They were formed primarily due to erosion from rainfall and bedrock wear. The Melnik Earth Pyramids are a geological phenomenon of global importance and were declared a natural landmark in 1960. The rock formations are home to rich flora and fauna heavily influenced by the Mediterranean climate. They are a tourist destination due to the natural environment of the area, the cultural sights of Melnik and the Rozhen Monastery.

The Stob Earth Pyramids are rock formations, known as hoodoos, situated at the foothills of the Rila mountain range in south-western Bulgaria. They span an area of 0.7 km2 near the village of Stob, Kyustendil Province. The rock formations are up to 12 m high and up to 40 m thick at the base. Their shape is mostly conical to mushroomlike. Some of the columns are topped by flat stones.





























