
The Apache License is a permissive free software license written by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF). The Apache License, Version 2.0 requires preservation of the copyright notice and disclaimer. Like other free software licenses, the license allows the user of the software the freedom to use the software for any purpose, to distribute it, to modify it, and to distribute modified versions of the software, under the terms of the license, without concern for royalties. This makes the Apache License a FRAND-RF license. The ASF and its projects release the software they produce under the Apache License. The license is also used by many non-ASF projects.

DragonFly BSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system forked from FreeBSD 4.8. Matthew Dillon, an Amiga developer in the late 1980s and early 1990s and FreeBSD developer between 1994 and 2003, began working on DragonFly BSD in June 2003 and announced it on the FreeBSD mailing lists on 16 July 2003.
tmpfs is a common name for a temporary file storage facility on many Unix-like operating systems. It is intended to appear as a mounted file system, but stored in volatile memory instead of a persistent storage device. A similar construction is a RAM disk, which appears as a virtual disk drive and hosts a disk file system.
UNIX System V is one of the first commercial versions of the Unix operating system. It was originally developed by AT&T and first released in 1983. Four major versions of System V were released, numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4. System V Release 4, or SVR4, was commercially the most successful version, being the result of an effort, marketed as "Unix System Unification", which solicited the collaboration of the major Unix vendors. It was the source of several common commercial Unix features. System V is sometimes abbreviated to SysV.
These tables provide a comparison of operating systems, of computer devices, as listing general and technical information for a number of widely used and currently available PC or handheld operating systems. The article "Usage share of operating systems" provides a broader, and more general, comparison of operating systems that includes servers, mainframes and supercomputers.
Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE) is a software interface for Unix-like computer operating systems that lets non-privileged users create their own file systems without editing kernel code. This is achieved by running file system code in user space while the FUSE module provides only a "bridge" to the actual kernel interfaces.
The file command is a standard program of Unix and Unix-like operating systems for recognizing the type of data contained in a computer file.

TrueOS is a Unix-like, server-oriented operating system built upon the most recent releases of FreeBSD-CURRENT. It aims to be easy to install by using a graphical installation program, and easy and ready-to-use immediately by providing KDE SC, Lumina, LXDE, MATE, or Xfce as the desktop environment. It provides official binary Nvidia and Intel drivers for hardware acceleration and an optional 3D desktop interface through KWin, and Wine is ready-to-use for running Microsoft Windows software. TrueOS is able to run Linux software, in addition to FreeBSD Ports collection, and it has its own .txz package manager. TrueOS supports OpenZFS, and the installer offers disk encryption with geli.
Data scrubbing is an error correction technique that uses a background task to periodically inspect main memory or storage for errors, then correct detected errors using redundant data in the form of different checksums or copies of data. Data scrubbing reduces the likelihood that single correctable errors will accumulate, leading to reduced risks of uncorrectable errors.
In computing, a dynamic linker is the part of an operating system that loads and links the shared libraries needed by an executable when it is executed, by copying the content of libraries from persistent storage to RAM, and filling jump tables and relocating pointers. The specific operating system and executable format determine how the dynamic linker functions and how it is implemented.
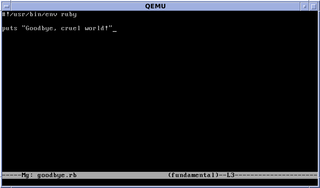
mg, originally called MicroGnuEmacs, is a public-domain text editor that runs on Unix-like operating systems. It is based on MicroEMACS, but intended to more closely resemble GNU Emacs while still maintaining a small memory footprint and fast speed. An expanded version of the original is included as part of OpenBSD, where it is maintained, and snapshots of the OpenBSD version are available in the native package management trees of many other systems, including MacPorts, FreeBSD Ports, pkgsrc and Debian.

NTFS-3G is an open-source cross-platform implementation of the Microsoft Windows NTFS file system with read-write support. NTFS-3G often uses the FUSE file system interface, so it can run unmodified on many different operating systems. It is runnable on Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenSolaris, illumos, BeOS, QNX, WinCE, Nucleus, VxWorks, Haiku, MorphOS, Minix, macOS and OpenBSD. It is licensed under either the GNU General Public License or a proprietary license. It is a partial fork of ntfsprogs and is under active maintenance and development.
The Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) was an operating system based on Research Unix, developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Berkeley. Today, "BSD" often refers to its descendants, such as FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, or DragonFly BSD.

OpenBSD is a free and open-source, security-focused, Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution. Theo de Raadt created OpenBSD in 1995 by forking NetBSD. According to de Raadt, OpenBSD is a research operating system for developing security mitigations.
Write Ahead Physical Block Logging (WAPBL) provides meta data journaling for file systems in conjunction with Fast File System (FFS) to accomplish rapid filesystem consistency after an unclean shutdown of the filesystem and better general use performance over regular FFS. With the journal, fsck is no longer required at system boot; instead, the system can replay the journal in order to correct any inconsistencies in the filesystem if the system has been shutdown in an unclean fashion.
HAMMER is a high-availability 64-bit file system developed by Matthew Dillon for DragonFly BSD using B+ trees. Its major features include infinite NFS-exportable snapshots, master-multislave operation, configurable history retention, fsckless-mount, and checksums to deal with data corruption. HAMMER also supports data block deduplication, meaning that identical data blocks will be stored only once on a file system. A successor, HAMMER2, was announced in 2011 and became the default in Dragonfly 5.2.

NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was forked. It continues to be actively developed and is available for many platforms, including servers, desktops, handheld devices, and embedded systems.








