This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
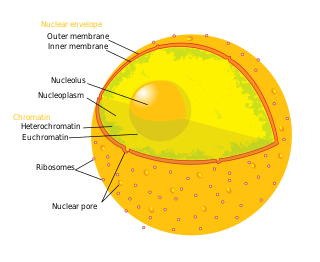
The nucleolus is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis. Nucleoli also participate in the formation of signal recognition particles and play a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy.

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with lipids, proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.
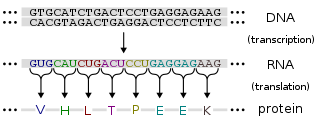
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.
OpenEXR is a high dynamic range raster file format, released as an open standard along with a set of software tools created by Industrial Light & Magic (ILM), under a free software license similar to the BSD license.
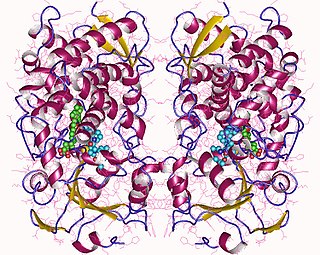
Cytochrome P450 3A4 is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body.

Quark, Strangeness and Charm is the seventh studio album by the English space rock group Hawkwind, released in 1977. It spent 6 weeks on the UK albums chart peaking at #30.

Live Seventy Nine is a 1980 live album by Hawkwind recorded on their Winter 1979 tour. It reached #15 on the UK album chart.
The retinoid X receptor (RXR) is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by 9-cis retinoic acid, which is discussed controversially to be of endogenous relevance, and 9-cis-13,14-dihydroretinoic acid, which is likely to be the major endogenous mammalian RXR-selective agonist.
High Rise, High-Rise or Highrise may refer to:
Repeat Performance were a series of budget compilation albums issued by Charisma Records in 1980. The first of the series was a various artists compilation, subsequent albums showcased an artist on the label. BG004, claimed to be a compilation of Genesis, was unissued.

Spirit of the Age is a 1988 compilation album by the British space rock group Hawkwind covering their Charisma Records period 1976–1979. It was issued by Virgin Records after they had acquired the Charisma catalogue, to test whether there was a viable market for the Hawkwind albums included in the deal. There was, and the company then re-issued each of the four albums the following year as part of the Compact price series.

Spacebrock is the 23rd studio album by Hawkwind, released in 2000, although the lack of contributors and title has prompted suggestions that it is a de facto Dave Brock solo album.
Sonic Assassins were a UK band formed in 1977, composed of members from Hawkwind and local Devon band Ark.
Simon King is an English drummer most noted for his work with Hawkwind. He was described in 1985 by British rock magazine Sounds as the 'definitive rock drummer.'

Spirit of the Age and The Dream Goes On are two triple CD anthologies released in 2008 covering the periods 1976-84 and 1985-97 of the British rock group Hawkwind.
A xenobiotic-sensing receptor is a receptor that binds xenobiotics. They include the following nuclear receptors:













