
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types other organs are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a drug class that reduce pain, decrease fever, prevent blood clots and, in higher doses, decrease inflammation. Side effects depend on the specific drug, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack and kidney disease.

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months.

Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, ectopic pregnancy, and for medical abortions. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, and osteosarcoma. Types of autoimmune diseases it is used for include psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It can be given by mouth or by injection.

Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is an estrogen medication which is mostly no longer used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications including pregnancy support for women with a history of recurrent miscarriage, hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency in women, treatment of prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women, and other uses. Today, it is only used in the treatment of prostate cancer and less commonly breast cancer. While most commonly taken by mouth, DES was available for use by other routes as well, for instance vaginal, topical, and by injection.

Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is a category of otherwise unrelated drugs defined by their use in rheumatoid arthritis to slow down disease progression. The term is often used in contrast to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and steroids.

Azathioprine (AZA), sold under the brand name Imuran among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used in rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and in kidney transplants to prevent rejection. It is taken by mouth or injected into a vein.

Psoriatic arthritis is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. This often happens in association with changes to the nails such as small depressions in the nail (pitting), thickening of the nails, and detachment of the nail from the nailbed. Skin changes consistent with psoriasis frequently occur before the onset of psoriatic arthritis but psoriatic arthritis can precede the rash in 15% of affected individuals. It is classified as a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
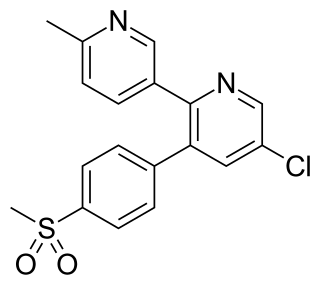
Etoricoxib (Arcoxia) is a selective COX-2 inhibitor from Merck & Co. Currently it is approved in more than 80 countries worldwide but not in the US, where the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required additional safety and efficacy data for etoricoxib before it will issue approval.

Penicillamine, sold under the trade names of Cuprimine among others, is a medication primarily used for the treatment of Wilson's disease. It is also used for people with kidney stones who have high urine cystine levels, rheumatoid arthritis, and various heavy metal poisonings. It is taken by mouth.

Erythema nodosum (EN), is an inflammatory condition characterized by inflammation of the fat cells under the skin, resulting in tender red nodules or lumps that are usually seen on both shins. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, and typically resolves spontaneously within 30 days. It is common in young people between 12–20 years of age.
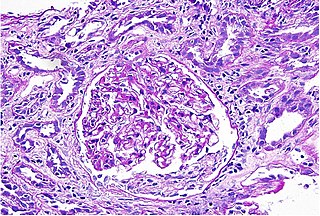
Interstitial nephritis, also known as tubulointerstitial nephritis, is inflammation of the area of the kidney known as the interstitium, which consists of a collection of cells, extracellular matrix, and fluid surrounding the renal tubules. In addition to providing a scaffolding support for the tubular architecture, the interstitium has been shown to participate in the fluid and electrolyte exchange as well as endocrine functions of the kidney. There are a variety of known factors that can provoke the inflammatory process within the renal interstitium, including pharmacologic, environmental, infectious and systemic disease contributors. The spectrum of disease presentation can range from an acute process to a chronic condition with progressive tubular cell damage and renal dysfunction.

Leflunomide is an immunosuppressive disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), used in active moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. It is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor that works by inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase.
Felty's syndrome, also called Felty syndrome, (FS) is rare autoimmune disease characterized by the triad of rheumatoid arthritis, enlargement of the spleen and too few neutrophils in the blood. The condition is more common in those aged 50–70 years, specifically more prevalent in females than males, and more so in Caucasians than those of African descent. It is a deforming disease that causes many complications for the individual.
Tocilizumab, also known as atlizumab, is an immunosuppressive drug, mainly for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, a severe form of arthritis in children. It is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R). Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is a cytokine that plays an important role in immune response and is implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, multiple myeloma and prostate cancer. It was developed by Hoffmann–La Roche and Chugai.

Chemotherapy-induced acral erythema is reddening, swelling, numbness and desquamation on palms of the hands and soles of the feet that can occur after chemotherapy in patients with cancer. Hand-foot syndrome is also rarely seen in sickle-cell disease. These skin changes usually are well demarcated. Acral erythema typically disappears within a few weeks after discontinuation of the offending drug.
Allen Caruthers Steere is a professor of rheumatology at Harvard University and previously at Tufts University and Yale University. Steere and his mentor, Stephen Malawista of Yale University, are credited with discovering and naming Lyme disease, and he has published almost 300 scholarly articles on Lyme disease during his more than 40 years of studies of this infection. At a ceremony in Hartford, Connecticut in 1998, Governor John G. Rowland declared September 24 to be "Allen C. Steere Day."

Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), also known simply as lupus, is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary between people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms.
Janus kinase inhibitors, also known as JAK inhibitors or jakinibs, are a type of medication that functions by inhibiting the activity of one or more of the Janus kinase family of enzymes, thereby interfering with the JAK-STAT signaling pathway.
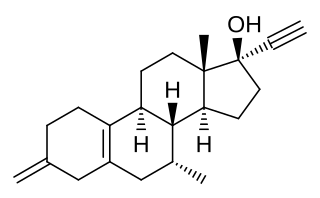
ERA-63, also known as ORG-37663, as well as 3-methylene-7α-methyl-17α-ethynylestra-5(10)-en-17β-ol, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and a selective agonist of the ERα that was under development for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis but was never marketed. The drug produced estrogenic effects but failed to show effectiveness for rheumatoid arthritis in a phase IIa clinical study. A large clinical trial also found that prinaberel (ERB-041), a selective ERβ agonist, was ineffective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in spite of activity in preclinical models.

















