In mathematics, the associative property is a property of some binary operations. In propositional logic, associativity is a valid rule of replacement for expressions in logical proofs.

A circle is a simple closed shape. It is the set of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre; equivalently it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is constant. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius. This article is about circles in Euclidean geometry, and, in particular, the Euclidean plane, except where otherwise noted.
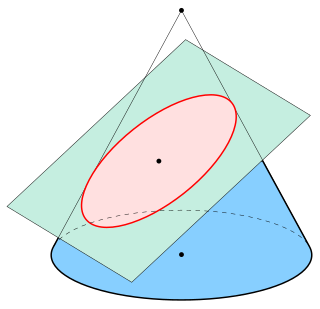
In mathematics, an ellipse is a curve in a plane surrounding two focal points such that the sum of the distances to the two focal points is constant for every point on the curve. As such, it is a generalization of a circle, which is a special type of an ellipse having both focal points at the same location. The elongation of an ellipse is represented by its eccentricity, which for an ellipse can be any number from 0 to arbitrarily close to but less than 1.
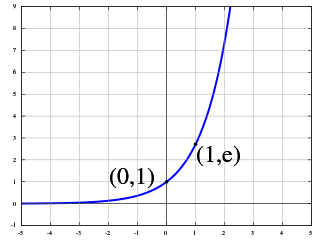
In mathematics, an exponential function is a function of the form

In mathematics, a linear equation is an equation that may be put in the form

In mathematics, the trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in all sciences that are related to geometry, such as navigation, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, geodesy, and many others. They are among the simplest periodic functions, and as such are also widely used for studying periodic phenomena, through Fourier analysis.

In mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point.

In probability theory and statistics, Bayes' theorem describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event. For example, if cancer is related to age, then, using Bayes' theorem, a person's age can be used to more accurately assess the probability that they have cancer, compared to the assessment of the probability of cancer made without knowledge of the person's age.

In machine learning, support-vector machines are supervised learning models with associated learning algorithms that analyze data used for classification and regression analysis. Given a set of training examples, each marked as belonging to one or the other of two categories, an SVM training algorithm builds a model that assigns new examples to one category or the other, making it a non-probabilistic binary linear classifier. An SVM model is a representation of the examples as points in space, mapped so that the examples of the separate categories are divided by a clear gap that is as wide as possible. New examples are then mapped into that same space and predicted to belong to a category based on which side of the gap they fall.

In mathematics, two varying quantities are said to be in a relation of proportionality, if they are multiplicatively connected to a constant, that is, when either their ratio or their product yields a constant. The value of this constant is called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant.

In mathematics, a plane is a flat, two-dimensional surface that extends infinitely far. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point, a line and three-dimensional space. Planes can arise as subspaces of some higher-dimensional space, as with a room's walls extended infinitely far, or they may enjoy an independent existence in their own right, as in the setting of Euclidean geometry.

In mathematics, an inequality is a relation that holds between two values when they are different.

In mathematics, a function was originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a function of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable. The concept of function was formalized at the end of the 19th century in terms of set theory, and this greatly enlarged the domains of application of the concept.
Juan Bautista Diamante, minor Spanish dramatist of the school of Calderón, was the son of a Portuguese mother and a Sicilian merchant of Greek parentage who came to Madrid some time before 1631. He began writing for the stage in the early 1650s, gained favour at the courts of Philip IV and Charles II, and became a knight of St. John in 1660. It has been suggested that Juan Bautista may have been of Jewish stock, and that the Diamante family, including the playwright's half-brothers Pablo and Francisco Diamante who also achieved success in their different spheres, falsified public records of marriage, baptism, etc. in order to obscure their marrano origins.
Bernardino Lanini or Lanino was an Italian painter of the Renaissance period, active mainly in Milan.
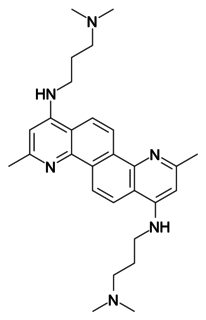
FGI-106 is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug developed as a potential treatment for enveloped RNA viruses, in particular viral hemorrhagic fevers from the bunyavirus, flavivirus and filovirus families. It acts as an inhibitor which blocks viral entry into host cells. In animal tests FGI-106 shows both prophylactic and curative action against a range of deadly viruses for which few existing treatments are available, including the bunyaviruses hantavirus, Rift Valley fever virus and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, the flavivirus dengue virus, and the filoviruses Ebola virus and Marburg virus.
Eric Lanini is an Italian footballer who currently plays as a striker for Imolese on loan from Juventus.
Lanini is an Italian surname. Notable people with the surname include:
Stefano Lanini is an Italian football player. He plays for Giana Erminio.














