
Photography is the art, application and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing, and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and mass communication.

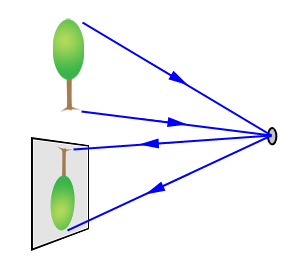
Camera obscura, also referred to as pinhole image, is the natural optical phenomenon that occurs when an image of a scene at the other side of a screen is projected through a small hole in that screen as a reversed and inverted image on a surface opposite to the opening. The surroundings of the projected image have to be relatively dark for the image to be clear, so many historical camera obscura experiments were performed in dark rooms.

A camera lens is an optical lens or assembly of lenses used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image chemically or electronically.
Panoramic photography is a technique of photography, using specialized equipment or software, that captures images with horizontally elongated fields of view. It is sometimes known as wide format photography. The term has also been applied to a photograph that is cropped to a relatively wide aspect ratio, like the familiar letterbox format in wide-screen video.

A vanishing point is a point on the image plane of a perspective drawing where the two-dimensional perspective projections of mutually parallel lines in three-dimensional space appear to converge. When the set of parallel lines is perpendicular to a picture plane, the construction is known as one-point perspective, and their vanishing point corresponds to the oculus, or "eye point", from which the image should be viewed for correct perspective geometry. Traditional linear drawings use objects with one to three sets of parallels, defining one to three vanishing points.

Computational photography refers to digital image capture and processing techniques that use digital computation instead of optical processes. Computational photography can improve the capabilities of a camera, or introduce features that were not possible at all with film based photography, or reduce the cost or size of camera elements. Examples of computational photography include in-camera computation of digital panoramas, high-dynamic-range images, and light field cameras. Light field cameras use novel optical elements to capture three dimensional scene information which can then be used to produce 3D images, enhanced depth-of-field, and selective de-focusing. Enhanced depth-of-field reduces the need for mechanical focusing systems. All of these features use computational imaging techniques.

Pinhole glasses, also known as stenopeic glasses, are eyeglasses with a series of pinhole-sized perforations filling an opaque sheet of plastic in place of each lens. Similar to the workings of a pinhole camera, each perforation allows only a very narrow beam of light to enter the eye which reduces the size of the circle of confusion on the retina and increases depth of field. In eyes with refractive error, the result is often a sharper image. However, a second effect may appear at the common bridge between each two adjacent holes, whereby two different rays of light coming from the same object are diffracted back toward the eye and onto different places on the retina. This leads to double vision around the rim of each hole the eye is not focussing on, which can make the overall image disturbing and tiring to look at for prolonged periods of time.
A pinhead mirror can be used to create a camera similar to a pinhole camera. Instead of passing through a tiny hole, the light to form the image is reflected by a small disc-shaped mirror. One advantage is that a pinhead mirror can be swivelled to scan a scene or project a scene to different locations.
Integral imaging is an autostereoscopic and multiscopic three-dimensional imaging technique that captures and reproduces a light field by using a two-dimensional array of microlenses, sometimes called a fly's-eye lens, normally without the aid of a larger overall objective or viewing lens. In capture mode, each microlens allows an image of the subject as seen from the viewpoint of that lens's location to be acquired. In reproduction mode, each microlens allows each observing eye to see only the area of the associated micro-image containing the portion of the subject that would have been visible through that space from that eye's location. The optical geometry can perhaps be visualized more easily by substituting pinholes for the microlenses, as has actually been done for some demonstrations and special applications.
Camera resectioning is the process of estimating the parameters of a pinhole camera model approximating the camera that produced a given photograph or video. Usually, the pinhole camera parameters are represented in a 3 × 4 matrix called the camera matrix.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to photography:

Epipolar geometry is the geometry of stereo vision. When two cameras view a 3D scene from two distinct positions, there are a number of geometric relations between the 3D points and their projections onto the 2D images that lead to constraints between the image points. These relations are derived based on the assumption that the cameras can be approximated by the pinhole camera model.

Redscale is a technique of shooting photographic film where the film is exposed from the wrong side, i.e. the emulsion is exposed through the base of the film. Normally, this is done by winding the film upside-down into an empty film canister. The name "redscale" comes because there is a strong color shift to red due to the red-sensitive layer of the film being exposed first, rather than last [the red layer is normally the bottom layer in C-41 film]. All layers are sensitive to blue light, so normally the blue layer is on top, followed by a filter. In this technique, blue light exposes the layers containing cyan and magenta dyes, but the layer containing yellow dye is left unexposed due to the filter. E-6 film has also been used for this technique.
"Tilted plane photography" is a method of employing focus as a descriptive, narrative or symbolic artistic device. It is distinct from the more simple uses of selective focus which highlight or emphasise a single point in an image, create an atmospheric bokeh, or miniaturise an obliquely-viewed landscape. In this method the photographer is consciously using the camera to focus on several points in the image at once while de-focussing others, thus making conceptual connections between these points.

Long-exposure, time-exposure, or slow-shutter photography involves using a long-duration shutter speed to sharply capture the stationary elements of images while blurring, smearing, or obscuring the moving elements. Long-exposure photography captures one element that conventional photography does not: an extended period of time.
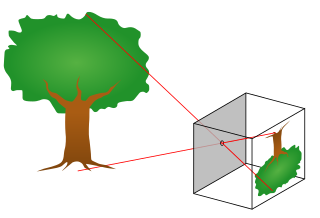
The pinhole camera model describes the mathematical relationship between the coordinates of a point in three-dimensional space and its projection onto the image plane of an ideal pinhole camera, where the camera aperture is described as a point and no lenses are used to focus light. The model does not include, for example, geometric distortions or blurring of unfocused objects caused by lenses and finite sized apertures. It also does not take into account that most practical cameras have only discrete image coordinates. This means that the pinhole camera model can only be used as a first order approximation of the mapping from a 3D scene to a 2D image. Its validity depends on the quality of the camera and, in general, decreases from the center of the image to the edges as lens distortion effects increase.

A pinhole is a small circular hole, as could be made with the point of a pin. In optics, pinholes with diameter between a few micrometers and a hundred micrometers are used as apertures in optical systems. Pinholes are commonly used to spatially filter a beam, where the small pinhole acts as a low-pass filter for spatial frequencies in the image plane of the beam.

A hole is an opening in or through a particular medium, usually a solid body. Holes occur through natural and artificial processes, and may be useful for various purposes, or may represent a problem needing to be addressed in many fields of engineering. Depending on the material and the placement, a hole may be an indentation in a surface, or may pass completely through that surface. In engineering, a hole may be blind or through if it is partial or complete depth.













