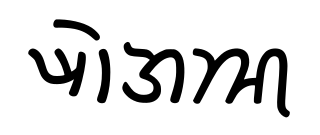Isma'ilism is a branch or sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (imām) to Ja'far al-Sadiq, wherein they differ from the Twelver Shia, who accept Musa al-Kadhim, the younger brother of Isma'il, as the true Imām.

Alamut is a mountain fortress at an altitude of 2163 meters at the central Alborz, in the Iranian stanza of Qazvin, about 100 kilometers from Tehran. In 1090 AD, the Alamut Castle, a mountain fortress in present-day Iran, came into the possession of Hassan-i Sabbah, a champion of the Nizari Ismaili cause. Until 1256, Alamut functioned as the headquarters of the Nizari Ismaili state, which included a series of strategic strongholds scattered throughout Persia and Syria, with each stronghold being surrounded by swathes of hostile territory.

Jamatkhana or Jamat Khana is an amalgamation derived from the Arabic word jama‘a (gathering) and the Persian word khana. It is a term used by some Muslim communities around the world, particularly sufi ones, to a place of gathering. Among some communities of Muslims, the term is often used interchangeably with the Arabic word musallah. The Nizārī Ismā'īlī community uses the term Jama'at Khana to denote their places of worship.
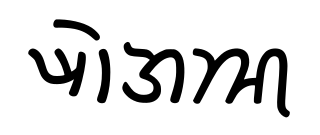
Khojkī, Khojakī, or Khwājā Sindhī, is a script used formerly and almost exclusively by the Khoja community of parts of the Indian subcontinent, including Sindh, Gujarat, and Punjab. However, this script also had a further reach and was used by members of Ismaili communities from Burma to East and South Africa. The Khojki script is one of the earliest forms of written Sindhi. The name "Khojki" is likely derived from the Persian word khoja, which means "master", or "lord".

The Khoja are a mainly Nizari Isma'ili Shia community of people from the western Indian subcontinent. Khojas predominantly reside in India, Pakistan and eastern Africa.
Ginans are devotional hymns or poems recited by Shia Ismaili Muslims.
Satpanth is a Sanskrit term used initially by Nizari Isma'ilis and Ismaili Sufis to identify their faith formed over 700 years ago by Pir Sadardin. Although the term is today used mainly by its subgroup formed in the 15th century by his grandson Pir Imam Shah which itself consists of various sub-sects, and differs from the mainstream Nizari Khojas in that they reject the Aga Khan as their leader and are known more commonly as Imamshahi. Uniquely, the term Satpanth has been historically used by Ismaili, as well as by adherents of subgroups. There are villages in Gujarat which are totally Satpanthi such as Pirana near Ahmedabad where Imam Shah is buried. Satpanthi dargahs are known to be venerated with a stark contrast in the devotees, with outward Muslims who may wear a hijab, and outward Hindus wearing traditional garb such as the sari.

Masyaf Castle is a medieval structure in the town of Masyaf in Hama Governorate, Syria, situated in the Orontes Valley, approximately 40.03 kilometres to the west of Hama. It served to protect the approach to other Ismaili castles in the Syrian Coastal Mountain Range at a site controlling the trade routes to cities further inland such as Banyas. The castle itself stands on a platform about 20 metres above the surrounding plain. It became famous as the stronghold from which Rashid ad-Din Sinan, known as the Old Man of the Mountain, ruled from 1166-1193. He was a leader of the Syrian branch of the Shia Nizari Isma'ili sect, also known as the Assassins, and a figure in the history of the Crusades.
Rukn al-Dīn al-Hasan ibn Muhammad Khurshāh (1230–1256) was the son of ‘Alā’ ad-Dīn Muḥammad III and the 27th Isma'ili Imam. He was also the fifth and final Nizari Isma'ili Imam who ruled at Alamut. The Imam was the eldest son of Imam ʿAla al-Din Muhammad and succeeded his murdered father to the Imamate in 1255. Imam Rukn al-Din engaged in a long series of negotiations with the invading Mongols, and under whose leadership Alamut Castle was surrendered to the Mongol Empire marking the end of the Nizari state in Persia.

Ḥasan ʿAlā Zikrihi's-Salām or Hassan II was the hereditary Imam of the Nizari Isma'ilis of the Alamut Period from 1162 until 1166. From his capital of Alamut he ruled parts of Persia and Syria. His chief subordinate in Syria was Rashid ad-Din Sinan, the Old Man of the Mountain.

The Nizari state was a Nizari Isma'ili Shia state founded by Hassan-i Sabbah after he took control of the Alamut Castle in 1090 AD, which marked the beginning of an era of Ismailism known as the "Alamut period". Their people were also known as the Assassins or Hashashins.
Nūram Mubīn is a Gujarati Nizari Ismaili text written by Ali Muhammad Jan Muhammad Chunara (1881–1966) and first published in 1936. It tells of the lives of the Ismaili Imams from the seventh to the twentieth centuries, and is notable for being the first authorized Ismaili history written in an Indian vernacular language.
Nūr al-Dīn Muḥammad II or ʾAʿlā Muḥammad was the Nizari Isma'ili Imām of Alamūt who reigned the longest period out of any lord (Khudawand) of Alamut, forty-four years. He affirmed the policies of his father, Hassan Ala Dhikrihi's Salam, who had been stabbed to death a year after proclaiming Qiyāma, or Resurrection.
The Aga Khan Case was an 1866 court decision in the High Court of Bombay by Justice Sir Joseph Arnould that established the authority of the first Aga Khan, Hasan Ali Shah, as the head of the Khoja community of Bombay.

ʿAlāʾ ad-Dīn Muḥammad III, more commonly known as ʿAlāʾ ad-Dīn (علاءالدین), son of Jalāl al-Dīn Ḥasan III, was the 26th Nizāri Isma'ilism Imām. He ruled the Nizari Ismaili state from 1221 to 1255. By some accounts, he was considered a respected scholar and the spiritual and worldly leader of the Nizari Ismailis. The intellectual life of Persia has been described as having flourished during his 34-year reign. Allegedly, he was known for his tolerance and pluralism. His reign witnessed the beginnings of the Mongol conquests of Persia and the eastern Muslim world. He was assassinated by an unknown perpetrator on 1 December 1255, and was succeeded by his eldest son, Rukn al-Din Khurshah, in 1255.
Shams al-Dīn Muḥammad was the 28th imam of the Nizari Isma'ili community. Little is known about his life. He was the first imam to rule after the destruction of the Nizari state by the Mongol Empire, and spent his life hiding his true identity.
By the late 11th century, the Shi'a sub-sect of Ismailism had found many adherents in Persia, although the region was occupied by the Sunni Seljuk Empire. The hostile tendencies of the Abbasid–Seljuk order triggered a revolt by Ismailis in Persia under Hassan-i Sabbah.
Haji Bibi v. His Highness Sir Sultan Mohamed Shah, the Aga Khan, often referred to as the Haji Bibi Case, was a 1908 court case in the Bombay High Court heard by Justice Russell. The case was fundamentally a dispute over the inheritance of the estate of Hasan Ali Shah, a Persian nobleman with the title Aga Khan I and the hereditary leader of the Nizari Ismailis. A number of the properties and other monetary assets had been passed down to Aqa Ali Shah, Aga Khan II and then to his grandson, Sir Sultan Muhammad Shah, Aga Khan III. The plaintiffs included Haji Bibi who was a widowed granddaughter of Aga Khan I and a few other members of the family that all claimed rights to the wealth. The decision is notable as it confirmed the Aga Khan III's exclusive rights to the assets of his grandfather and to the continued religious offerings by his followers, including some Khojas, as the 48th Imam of the Nizaris.
The Mongol campaign against the Nizaris of the Alamut period began in 1253 after the Mongol invasion of the Khwarazmian Empire and a series of Nizari–Mongol conflicts. The campaign was ordered by the Great Khan Möngke and was led by his brother, Hülegü. The campaign against the Nizaris and later the Abbasid Caliphate was intended to establish a new khanate in the region—the Ilkhanate.
Abū ʿAlī Ḥasan, or ʿAlī, surnamed Al-Hādī was the 20th Ismaili Nizari Imam. Born in Cairo, he was about 17 years old when his predecessor, Imam al-Mustansir, died, and 20 years old during the assumption of his Imamate in 490 AH/1097 CE. Henceforward, the seat of Ismaili Imamate was transferred from Egypt to Persia owing to the division among the Ismailis, where Hasan bin Sabbah had founded the Nizari Ismaili state.