
Captain George Vancouver was a British officer of the Royal Navy best known for his 1791–95 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what are now the American states of Alaska, Washington, and Oregon, as well as the province of British Columbia in Canada. He also explored the Hawaiian Islands and the southwest coast of Australia.

The Chatham Islands form an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about 800 kilometres (500 mi) east of the South Island of New Zealand. It consists of about ten islands within a 40-kilometre (25 mi) radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island. Some of these islands, once cleared for farming, are now preserved as nature reserves to conserve some of the unique flora and fauna.
The resident population is 600. The local economy is largely dependent on conservation, tourism, farming, and fishing.

Nathaniel Pitt Langford (1832–1911) was an explorer, businessman, bureaucrat, vigilante and historian from Saint Paul, Minnesota who played an important role in the early years of the Montana gold fields, territorial government and the creation of Yellowstone National Park.

Pitt Island is the second largest island in the Chatham Archipelago, New Zealand. It is called Rangiauria in Māori and Rangiaotea in Moriori.
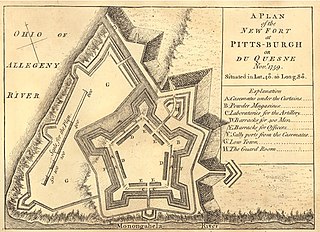
Fort Pitt was a fort built by British forces between 1759 and 1761 during the French and Indian War at the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers, where the Ohio River is formed in western Pennsylvania. It was near the site of Fort Duquesne, a French colonial fort built in 1754 as tensions increased between Great Britain and France in both Europe and North America. The French destroyed Fort Duquesne in 1758 when they retreated under British attack.

Point State Park is a Pennsylvania state park on 36 acres (150,000 m2) in Downtown Pittsburgh, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, USA, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers, forming the Ohio River.
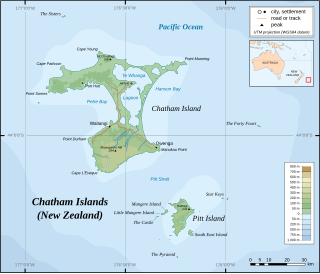
South East Island is the third largest island in the Chatham Islands archipelago, and covers an area of 218 hectares. It lies 800 kilometres (497 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island off the south-east coast of Pitt Island, 55 kilometres (34 mi) south-east of the main settlement, Waitangi, on Chatham Island.

Inca Gold is a novel written by Clive Cussler. First published in 1994, it is the twelfth book in Cussler's Dirk Pitt series.

The Clue of the Black Keys is the twenty-eighth volume in the Nancy Drew mystery series. It was first published in 1951 under the pseudonym Carolyn Keene. The actual authors were ghostwriters Wilhelmina Rankin and Harriet Stratemeyer Adams.

Fort Pitt Museum is an indoor/outdoor museum that is administered by the Senator John Heinz History Center in downtown Pittsburgh, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania in the United States. It is at the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny Rivers, where the Ohio River is formed. Fort Pitt Museum is surrounded by Point State Park, a Pennsylvania state park named for the geographically and historically significant point that is between the rivers. This piece of land was key to controlling the upper reaches of the Ohio River Valley and western Pennsylvania, before, during and after the French and Indian War as well as the American Revolution.

Expedition to the Demonweb Pits is a super-adventure module for the 3.5 edition of the Dungeons & Dragons roleplaying game. The adventure is designed for characters of levels 9–12. It involves the machinations of the demon lords Lolth and Graz'zt, and was heavily influenced by the 1980 adventure module, Queen of the Demonweb Pits.

Lieutenant-Colonel the Hon Albert Pitt was a 19th-century New Zealand politician, and a cabinet minister. In 1914, eight years after his death, The Albert Pitt Memorial Gates were erected in the Queen's Gardens, Nelson.
The 1970 Pittsburgh Steelers season was the franchise's 38th in the National Football League. They improved from a league-worst 1–13 record the previous year, finishing with a 5–9 record and third place in the newly formed AFC Central. The Steelers began the decade in a new conference and a new stadium with a new quarterback. After nearly 40 years in the NFL they shifted to the AFC, to complete the merger between the NFL and AFL. It was the NFL's weakest division that season, as the Steelers finished three games behind the division-winning Cincinnati Bengals—a team that was only in its third year of existence that season.
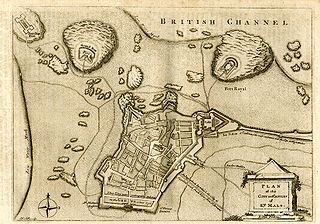
The Raid on St Malo took place in June 1758 when an amphibious British naval expedition landed close to the French port of St Malo in Brittany. While the town itself was not attacked, as had been initially planned, the British destroyed large amounts of shipping before re-embarking a week later. The naval forces were under the command of Richard Howe while the army was led by the Duke of Marlborough and Lord Sackville.
Francis was a 41 tons (bm) colonial schooner that was partially constructed at the Deptford Dockyard, England, and sent in frame aboard the Pitt to Australia to be put together for the purposes of exploration. The vessel had originally been designed for George Vancouver’s discovery voyage of the west coast of North America.
The California Indian Wars were a series of massacres, wars, and battles between the United States Army, and the Indigenous peoples of California. The wars lasted from 1850, immediately after the acquisition of Alta California during the Mexican–American War became the state of California, to 1880 when the last minor military operation on the Colorado River that ended the Calloway Affair of 1880.
Fort Crook was a U. S. Army post, first established as Camp Hollenbush in 1857, in Shasta County, California, northeast of Fall River Mills, California.















