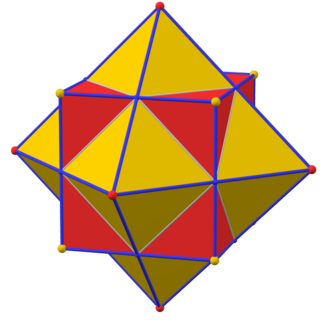
In geometry, every polyhedron is associated with a second dual structure, where the vertices of one correspond to the faces of the other, and the edges between pairs of vertices of one correspond to the edges between pairs of faces of the other. Such dual figures remain combinatorial or abstract polyhedra, but not all can also be constructed as geometric polyhedra. Starting with any given polyhedron, the dual of its dual is the original polyhedron.

In geometry, a polyhedron is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices.
ID or its variants may refer to:
Fold, folding or foldable may refer to:

Polyhedron was a magazine targeting consumers of role-playing games, and originally the official publication of the RPGA.

In geometry, a net of a polyhedron is an arrangement of non-overlapping edge-joined polygons in the plane which can be folded to become the faces of the polyhedron. Polyhedral nets are a useful aid to the study of polyhedra and solid geometry in general, as they allow for physical models of polyhedra to be constructed from material such as thin cardboard.
Toroidal describes something which resembles or relates to a torus or toroid:
Side or Sides may refer to:

In geometry, the midsphere or intersphere of a convex polyhedron is a sphere which is tangent to every edge of the polyhedron. Not every polyhedron has a midsphere, but the uniform polyhedra, including the regular, quasiregular and semiregular polyhedra and their duals all have midspheres. The radius of the midsphere is called the midradius. A polyhedron that has a midsphere is said to be midscribed about this sphere.
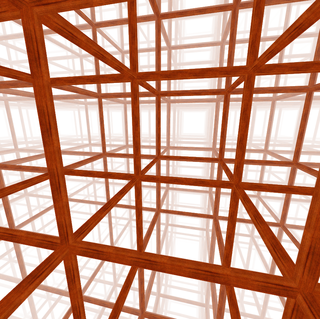
In geometry, a honeycomb is a space filling or close packing of polyhedral or higher-dimensional cells, so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical tiling or tessellation in any number of dimensions. Its dimension can be clarified as n-honeycomb for a honeycomb of n-dimensional space.
In geometry, a facet is a feature of a polyhedron, polytope, or related geometric structure, generally of dimension one less than the structure itself. More specifically:

In geometry, a flexible polyhedron is a polyhedral surface without any boundary edges, whose shape can be continuously changed while keeping the shapes of all of its faces unchanged. The Cauchy rigidity theorem shows that in dimension 3 such a polyhedron cannot be convex.
In geometry, a vertex is a point where two or more curves, lines, or edges meet or intersect. As a consequence of this definition, the point where two lines meet to form an angle and the corners of polygons and polyhedra are vertices.
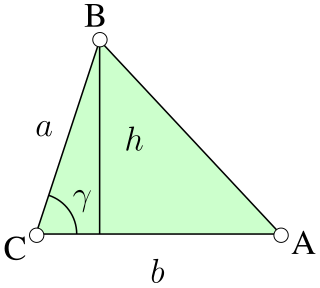
In geometry, an edge is a particular type of line segment joining two vertices in a polygon, polyhedron, or higher-dimensional polytope. In a polygon, an edge is a line segment on the boundary, and is often called a polygon side. In a polyhedron or more generally a polytope, an edge is a line segment where two faces meet. A segment joining two vertices while passing through the interior or exterior is not an edge but instead is called a diagonal.
In geometry and polyhedral combinatorics, the Kleetope of a polyhedron or higher-dimensional convex polytope P is another polyhedron or polytope PK formed by replacing each facet of P with a shallow pyramid. Kleetopes are named after Victor Klee.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.







