This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
Sextus Pompeius Magnus Pius, in English Sextus Pompey, was a Roman general from the late Republic. He was the last focus of opposition to the Second Triumvirate. His father was Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus.
Gnaeus Pompeius, also known as Pompey the Younger, was a Roman politician and general from the late Republic.
Mucia Tertia was a Roman matrona who lived in the 1st century BC. She was the daughter of Quintus Mucius Scaevola, the pontifex maximus, consul in 95 BC. Her mother was a Licinia that divorced her father to marry Quintus Caecilius Metellus Nepos, in a scandal mentioned by several sources. Her name, Mucia Tertia, would suggest that she was a third daughter, according to the Roman naming convention for women, though it is believed that this was instead to differentiate her from her two aunts. Mucia had also two younger half-brothers from her mother's second marriage, Q. Metellus Celer, consul in 60 BC, and of Q. Metellus Nepos, consul in 57 BC.
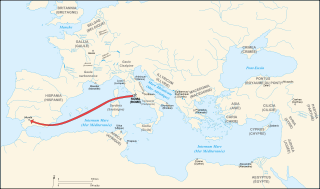
The Battle of Munda, in southern Hispania Ulterior, was the final battle of Caesar's civil war against the leaders of the Optimates. With the military victory at Munda, and the deaths of Titus Labienus and Gnaeus Pompeius, Caesar was politically able to return in triumph to Rome, and then govern as the elected Roman dictator. Subsequently, the assassination of Julius Caesar began the Republican decline that led to the Roman Empire, initiated with the reign of the Roman Emperor Augustus.
Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo was a Roman general and politician, who served as consul in 89 BC. He is often referred to in English as Pompey Strabo, to distinguish him from his son, the famous Pompey the Great, or from Strabo the geographer.

The gens Pompeia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, first appearing in history during the second century BC, and frequently occupying the highest offices of the Roman state from then until imperial times. The first of the Pompeii to obtain the consulship was Quintus Pompeius in 141 BC, but by far the most illustrious of the gens was Gnaeus Pompeius, surnamed Magnus, a distinguished general under the dictator Sulla, who became a member of the First Triumvirate, together with Caesar and Crassus. After the death of Crassus, the rivalry between Caesar and Pompeius led to the Civil War, one of the defining events of the final years of the Roman Republic.
Pompeia was a Roman woman. Pompeia was born and raised into a noble family in Picenum a rural district in Northern Italy, off the Adriatic Coast.
Pompeia was a Roman noblewoman of plebs status. Her mother was a Roman woman whose name is unknown and her father was the consul and general Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo. Pompeia’s brother was the triumvir Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus or Pompey the Great. She is the paternal aunt to Gnaeus Pompeius, Sextus Pompeius and Pompeia Magna, the children of her brother.
This article is about Sextus Pompeius, the paternal uncle of triumvir Pompey and the descendants from Pompey’s uncle. For Pompey’s son of the same name, see Sextus Pompey.
Pompeia Magna was the only daughter and second child born to Roman triumvir Pompey the Great from his third marriage, to Mucia Tertia. Her elder brother was Gnaeus Pompeius and her younger brother was Sextus Pompey.
Pompeia Magna was the daughter and only child of political rebel Sextus Pompey and Scribonia. Pompeia was the only child born to the sons of triumvir Pompey. Her paternal grandparents were Pompey and Mucia Tertia. Her maternal grandparents were consul of 34 BC, Lucius Scribonius Libo and an unnamed woman from the gens Sulpicius, the family that the Roman Emperor Galba descended from on his paternal side. Her parents are distantly related. Sextus was a great uncle to her maternal grandfather, which Libo was a son to Cornelia Sulla. Cornelia Sulla was a daughter to Pompeia Magna and Faustus Cornelius Sulla. Pompeia Magna and Sextus Pompeius were siblings.
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus was a noble Roman that lived during the 1st century; he is not to be confused with his namesake Pompey the Great. Pompeius was one among the sons of the consul of the year 27, Marcus Licinius Crassus Frugi and Scribonia.
Pompeia is the name of several ancient Roman women.
Gnaeus is a Latin praenomen, or personal name, which was common throughout the period of the Roman Republic, and well into imperial times. The feminine form is Gnaea. The praenomen was used by both patrician and plebeian families, and gave rise to the patronymic gens Naevia. The name was regularly abbreviated Cn., based on the archaic spelling, Cnaeus, dating from the period before the letters "C" and "G" were differentiated.
Sextus Pompeius may refer to:
Gnaeus Pompeius was a name of male members of the gens Pompeia, among the famous members were:


