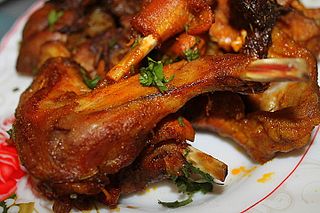Lancashire hotpot is a stew originating from Lancashire in the North West of England. It consists of lamb or mutton and onion, topped with sliced potatoes and baked in a heavy pot on a low heat.

Goulash is a stew of meat and vegetables usually seasoned with paprika and other spices. Originating from medieval Hungary, goulash is a popular meal predominantly eaten in Central Europe but also in other parts of Europe. It is one of the national dishes of Hungary and a symbol of the country.

Polish cuisine is a style of cooking and food preparation originating in or widely popular in Poland. Polish cuisine has evolved over the centuries to become very eclectic due to Poland's history and it shares many similarities with other West Slavic countries like neighbouring Czech and Slovak. It has also been widely influenced by other Central European cuisines, namely German, Austrian and Hungarian as well as Jewish, French, Turkish and Italian culinary traditions. Polish-styled cooking in other cultures is often referred to as à la polonaise.
Romanian cuisine is a diverse blend of different dishes from several traditions with which it has come into contact, but it also maintains its own character. It has been mainly influenced by a series of European cuisines such as the Austrian cuisine, German cuisine, Greek cuisine, or Hungarian cuisine, yet it also includes culinary elements stemming from the cuisines of the Slavic-speaking countries of Eastern and Central Europe, most notably Serbian and Bulgarian as well as Polish, Ukrainian, and Russian.

Sancocho is a traditional soup in several Latin American cuisines. Variations represent popular national dishes in the Puerto Rico, Honduras, Ecuador, Colombia, Cuba, Panama, Dominican Republic, and Venezuela. It usually consists of large pieces of meat, tubers and vegetables served in a broth.

Czech cuisine has both influenced and been influenced by the cuisines of surrounding countries. Many of the cakes and pastries that are popular in Central Europe originated within the Czech lands. Contemporary Czech cuisine is more meat-based than in previous periods; the current abundance of farmable meat has enriched its presence in regional cuisine. Traditionally, meat has been reserved for once-weekly consumption, typically on weekends. The body of Czech meals typically consists of two or more courses; the first course is traditionally soup, the second course is the main dish, and the third course can include supplementary courses, such as dessert or compote. In the Czech cuisine, thick soups and many kinds of sauces, both based on stewed or cooked vegetables and meats, often with cream, as well as baked meats with natural sauces (gravies), are popular dishes.

Sopa de mondongo is a soup made from diced tripe slow-cooked with vegetables such as bell peppers, onions, carrots, cabbage, celery, tomatoes, cilantro (coriander), garlic or root vegetables. The dish is generally prepared in former Spanish colonies in Latin America, Caribbean, and in the Philippines.

Eintopf is a traditional type of German stew which can consist of a great number of ingredients. Technically, the term refers to a way of cooking the ingredients in one pot, not to any specific recipe.
L'oille is a French potée or soup believed to be the forerunner of pot-au-feu composed of various meats and vegetables.
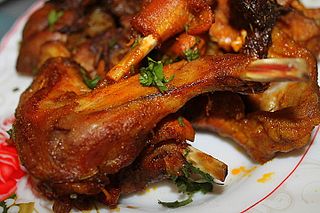
The cuisine of Algeria is influenced by Algeria's interactions and exchanges with other cultures and nations over the centuries. It is characterized by a wealth derived from both land and sea products. Conquests or demographic movement towards the Algerian territory were two of the main factors of exchanges between the different peoples and cultures. This cuisine is a Mediterranean and North African cuisine with Berber roots.

Cocido (Spanish) or cozido (Portuguese) is a traditional stew eaten as a main dish in Spain, Portugal, Brazil and other Hispanophone and Lusophone countries.

Puchero is a type of stew originally from Spain, prepared in Yucatán, Mexico, Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay, Perú, south of Brazil, the Philippines, and Spain, specifically the autonomous communities of Andalusia and the Canary Islands. The name comes from the Spanish word "puchero" which means "stewpot".

A stew is a combination of solid food ingredients that have been cooked in liquid and served in the resultant gravy. Ingredients in a stew can include any combination of vegetables and may include meat, especially tougher meats suitable for slow-cooking, such as beef. Poultry, sausages, and seafood are also used. While water can be used as the stew-cooking liquid, stock is also common. Seasoning and flavourings may also be added. Stews are typically cooked at a relatively low temperature, allowing flavours to mingle.

Cabbage stew is a stew prepared using cabbage as a primary ingredient. Basic preparations of the dish use cabbage, various vegetables such as onion, carrot and celery, and vegetable stock. Additional ingredients can include meats such as pork, sausage and beef, potatoes, noodles, diced apples, apple juice, chicken broth, herbs and spices, salt and pepper.