
The Douglas DC-3 is a fixed-wing propeller-driven airliner that revolutionized air transport in the 1930s and 1940s. Its lasting effect on the airline industry and World War II makes it one of the most significant transport aircraft ever produced. It has a cruise speed of 207 mph (333 km/h), capacity of 21 to 32 passengers or 6,000 lbs of cargo and a range of 1,500 mi (2,400 km).

The Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone is a twin-row, supercharged, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine with 18 cylinders displacing nearly 55 L. Power ranged from 2,200 to over 3,700 hp, depending on the model. Developed before World War II, the R-3350's design required a long time to mature before finally being used to power the Boeing B-29 Superfortress. After the war, the engine had matured sufficiently to become a major civilian airliner design, notably in its turbo-compound forms, and was used in the Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation airliners into the 1990s. The engine is now commonly used on Hawker Sea Fury and Grumman F8F Bearcat Unlimited Class Racers at the Reno Air Races. Its main rival was the Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major.

The Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major is an American 28-cylinder four-row radial piston aircraft engine designed and built during World War II, and the largest-displacement aviation piston engine to be mass-produced in the United States. It was the last of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp family, and the culmination of its maker's piston engine technology, but the war was over before it could power airplanes into combat. It did, however, power many of the last generation of large piston-engined aircraft before turbojets, and equivalent horsepower turboprops, supplanted it. Its main rival was the Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone.

The Pratt & Whitney Wasp was the civilian name of a family of air-cooled radial piston engines developed in the 1930s, 1940s, and 1950s.

The Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp is an American aircraft engine widely used in the 1930s and 1940s. Produced by Pratt & Whitney, it is a two-row, 14-cylinder, air-cooled radial design with seven cylinders on a row. It displaces 1,830 cu in (30.0 L) and its bore and stroke are both 5.5 in (140 mm). A total of 173,618 R-1830 engines were built, and from their use in two of the most-produced aircraft ever built, the four-engined B-24 heavy bomber and twin-engined DC-3 transport, more Twin Wasps may have been built than any other aviation piston engine in history. A "bored-out" version with a slightly higher power rating and other slight changes in detail design was produced as the R-2000. Mostly retired today, it is still used on Douglas DC-3 and various museum aircraft and warbirds seen at airshows. It is not manufactured anymore, but spares are still available and there exists a wide market for second-hand engines and parts.

The Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp is an aircraft engine of the reciprocating type that was widely used in American aircraft from the 1920s onward. It was the Pratt & Whitney aircraft company's first engine, and the first of the famed Wasp series. It was a single-row, nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial design, and displaced 1,344 cubic inches (22 L); bore and stroke were both 5.75 in (146 mm). A total of 34,966 engines were produced.

The Pratt & Whitney R-1535 Twin Wasp Junior was an engine used in American aircraft in the 1930s. The engine was first introduced in 1932 as a 14-cylinder version of the 9-cylinder R-985. It was a two-row, air-cooled radial design. Displacement was 1,535 in³ (25.2 L); bore and stroke were both 5-3/16 in (131.8 mm).

The Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Junior is a series of nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engines built by the Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Company from the 1930s to the 1950s. These engines have a displacement of 985 in3 (16 L); initial versions produced 300 hp (220 kW), while the most widely used versions produce 450 hp (340 kW).

The Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet was a widely used aircraft engine. Developed by Pratt & Whitney, 2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It first flew in 1927. It was a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. Displacement was 1,690 cubic inches. It was built under license in Italy as the Fiat A.59. In Germany, the BMW 132 was a developed version of this engine. The R-1860 Hornet B was an enlarged version produced from 1929.

The Douglas DC-4E was an American experimental airliner that was developed before World War II. The DC-4E never entered production due to being superseded by an entirely new design, the Douglas DC-4/C-54, which proved very successful. Many DC-4E design features found their way into the Japanese Nakajima G5N bomber.

The Saab 90 Scandia was a civil passenger aeroplane, manufactured by the Svenska Aeroplan Aktiebolaget (SAAB), in Linköping, Sweden. In 1944, as it was becoming clear that hostilities in Europe would soon be at an end, SAAB realised that the company had to diversify from purely military endeavours if it were to survive. The board therefore decided to put into action a plan to manufacture a twin-engined, short- to medium-haul passenger aircraft, as a successor for the Douglas DC-3.
The Pratt & Whitney Canada PW200 is a family of turbine engines developed specifically for helicopter applications. It entered service in the 1990s.
Twin Wasp may refer to one of three engines of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp series:

The Pratt & Whitney R-2000 Twin Wasp is a radial engine developed in the United States in 1942 to power military aircraft. It is one of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp series of radial engines.
The Cessna C-106 Loadmaster was a 1940s American twin-engined transport monoplane. Built of plywood it did not enter production due to a wartime shortage of material.
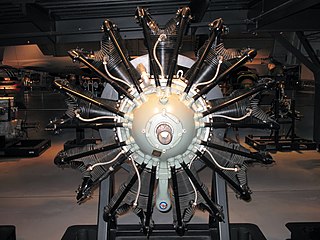
The Pratt & Whitney R-1860 Hornet B was a relatively uncommon aircraft engine. It was a development of Pratt & Whitney's earlier R-1690 Hornet and was basically similar, but enlarged in capacity from 1,690 to 1,860 cubic inches (30.5 L). Cylinder bore was increased by 1/8" and the crankshaft stroke by 3/8". Both engines were air-cooled radial engines, with a single row of nine cylinders.
The Pratt & Whitney R-2060 Yellow Jacket was a liquid-cooled aircraft engine project developed for the United States Army in the early 1930s. The engine had five banks of four in-line cylinders, and displaced 2,060 cubic inches. Designed to produce 1,000 hp, the engine produced 1,116 hp on its final run after 35 hours of testing. The engine was cancelled in favor of continuing development of Pratt & Whitney's air-cooled R-1830 Twin Wasp radial engine.













