
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a period of time, often annually. GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation rates of the countries; therefore using a basis of GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) is arguably more useful when comparing differences in living standards between nations.
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. For households and individuals, "income is the sum of all the wages, salaries, profits, interest payments, rents, and other forms of earnings received in a given period of time."
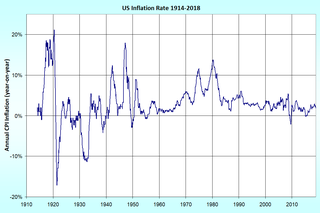
In economics, inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation reflects a reduction in the purchasing power per unit of money – a loss of real value in the medium of exchange and unit of account within the economy. The measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index, usually the consumer price index, over time. The opposite of inflation is deflation.
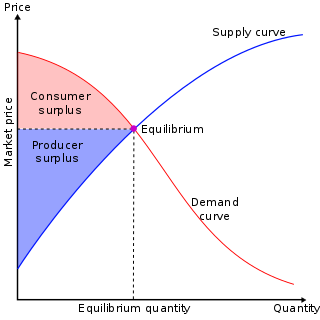
In mainstream economics, economic surplus, also known as total welfare or Marshallian surplus, refers to two related quantities. Consumer surplus or consumers' surplus is the monetary gain obtained by consumers because they are able to purchase a product for a price that is less than the highest price that they would be willing to pay. Producer surplus or producers' surplus is the amount that producers benefit by selling at a market price that is higher than the least that they would be willing to sell for; this is roughly equal to profit.
This aims to be a complete article list of economics topics:

A Consumer Price Index measures changes in the price level of market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households.
Trade can be a key factor in economic development. The prudent use of trade can boost a country's development and create absolute gains for the trading partners involved. Trade has been touted as an important tool in the path to development by prominent economists. However trade may not be a panacea for development as important questions surrounding how free trade really is and the harm trade can cause domestic infant industries to come into play.
A free price system or free price mechanism is a mechanism of resource allocation that relies upon monetary prices set by the interchange of supply and demand. The resulting prices serve as signals communicated between producers and consumers which serve to guide the production and distribution of resources. Through the free price system, supplies are rationed, income is distributed, and resources are allocated.

iDE, formerly International Development Enterprises, is an international nonprofit organization that promotes a business approach to increasing income and creating livelihood opportunities for poor rural households. iDE was founded in 1982 by Paul Polak, a Denver, Colorado psychiatrist who promoted the concept of helping poor people become entrepreneurs instead of simply giving them handouts. Originally, iDE was devoted to the manufacture, marketing, and distribution of affordable, scalable micro-irrigation and low-cost water recovery systems throughout the developing world. iDE facilitates local manufacture and distribution of these products through local supply chains that sell to farmers at an affordable price which they can repay in one growing season. This strategy allows farmers to grow higher value and surplus crops, and in turn links them to high-value crop markets where they can realize profits from their higher yields. Recently, their success is in the promotion of sanitation products to decrease the practice of open defecation leading to diarrheal disease.
Production is a process of combining various material inputs and immaterial inputs in order to make something for consumption. It is the act of creating an output, a good or service which has value and contributes to the utility of individuals.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to economics:

In United States federal agriculture legislation, the Agricultural Adjustment Act Amendment of 1935 made several important and lasting changes to the Agricultural Adjustment Act of 1933. Franklin D. Roosevelt signed the Act into law on August 24, 1935.
In United States agricultural policy, gross farm income refers to the monetary and non-monetary income received by farm operators. Its main components include cash receipts from the sale of farm products, government payments, other farm income, value of food and fuel produced and consumed on the same farm, rental value of farm dwellings, and change in value of year-end inventories of crops and livestock.
The General Services Support Estimate (GSSE) is an Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) indicator of the annual monetary value of gross transfers of general services provided to agriculture collectively, arising from policy measures that support agriculture, regardless of their nature, objectives and impacts on farm production, income, or consumption of farm products. Examples include research and development, education, infrastructure, and marketing and promotion programs. The GSSE can be expressed in monetary terms or as a percentage of the total support to agriculture.

The annual United Kingdom National Accounts records and describes economic activity in the United Kingdom and as such is used by government, banks, academics and industries to formulate the economic and social policies and monitor the economic progress of the United Kingdom. It also allows international comparisons to be made. The Blue Book is published by the UK Office for National Statistics alongside the United Kingdom Balance of Payments – The Pink Book.
This glossary of economics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in economics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.







