This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
In computing, a file server is a computer attached to a network that provides a location for shared disk access, i.e. shared storage of computer files that can be accessed by the workstations that are able to reach the computer that shares the access through a computer network. The term server highlights the role of the machine in the client–server scheme, where the clients are the workstations using the storage. It is common that a file server does not perform computational tasks, and does not run programs on behalf of its clients.
It is designed primarily to enable the storage and retrieval of data while the computation is carried out by the workstations.

Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. NAS is specialized for serving files either by its hardware, software, or configuration. It is often manufactured as a computer appliance – a purpose-built specialized computer. NAS systems are networked appliances which contain one or more storage drives, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID. Network-attached storage removes the responsibility of file serving from other servers on the network. They typically provide access to files using network file sharing protocols such as NFS, SMB, or AFP. From the mid-1990s, NAS devices began gaining popularity as a convenient method of sharing files among multiple computers. Potential benefits of dedicated network-attached storage, compared to general-purpose servers also serving files, include faster data access, easier administration, and simple configuration.
In computer data storage, data striping is the technique of segmenting logically sequential data, such as a file, so that consecutive segments are stored on different physical storage devices.
A disk array controller is a device which manages the physical disk drives and presents them to the computer as logical units. It almost always implements hardware RAID, thus it is sometimes referred to as RAID controller. It also often provides additional disk cache.
Serial Storage Architecture (SSA) was a serial transport protocol used to attach disk drives to server computers.

Clariion is a discontinued SAN disk array manufactured and sold by EMC Corporation, it occupied the entry-level and mid-range of EMC's SAN disk array products. In 2011, EMC introduced the EMC VNX Series, designed to replace both the Clariion and Celerra products.
Is a computer storage product by NetApp running ONTAP operation system; terms ONTAP, AFF, FAS often used as synonyms, also filer is a synonyms though it is not an official name. There are two types of FAS systems, Hybrid and All-Flash:
- NetApp proprietary custom-build hardware appliances with HDD or SSD drives called hybrid Fabric-Attached Storage
- NetApp proprietary custom-build hardware appliances with only SSD drives and optimized ONTAP for low latency called ALL-Flash FAS.
Vinum, is a logical volume manager, also called software RAID, allowing implementations of the RAID-0, RAID-1 and RAID-5 models, both individually and in combination. The original Vinum was part of the base distribution of the FreeBSD operating system since 3.0, as well as descendants, including DragonFly BSD; in more recent versions of FreeBSD, it has been replaced with gvinum, which was first introduced around FreeBSD 6. Vinum source code is maintained in the FreeBSD and DragonFly source trees. Vinum supports RAID levels 0, 1, 5, and JBOD.
mdadm is a Linux utility used to manage and monitor software RAID devices. It is used in modern GNU/Linux distributions in place of older software RAID utilities such as raidtools2 or raidtools.
A logical disk, logical volume or virtual disk is a virtual device that provides an area of usable storage capacity on one or more physical disk drive(s) in a computer system. The disk is described as logical or virtual because it does not actually exist as a single physical entity in its own right. The goal of the logical disk is to provide computer software with what seems a contiguous storage area, sparing them the burden of dealing with the intricacies of storing files on multiple physical units. Most modern operating systems provide some form of logical volume management.
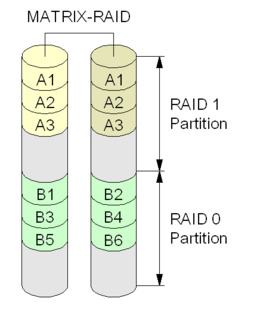
In computer data storage, Rapid Storage Technology (RST), until 2010 called Matrix RAID, is a firmware, hardware and software RAID system. This software monitors essential parts of the RAID function, including the S.M.A.R.T. parameters of connected/supported data devices. It gives an OK/NOK state of devices and RAID. Chipset and BIOS revision must match to the RST revision, and older revisions will endanger SMART monitoring. Supported Intel chipsets may change with each revision of RST.
Within a storage network, encryption of data may occur at different hardware levels. Array controller based encryption describes the encryption of data occurring at the disk array controller before being sent to the disk drives. This article will provide an overview of different implementation techniques to array controller based encryption. For cryptographic and encryption theory, see disk encryption theory.

A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a Computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to enhance accessibility of storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries, to servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as locally-attached devices. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN) by other devices, thereby preventing interference of LAN traffic in data transfer.
The most widespread standard for configuring multiple hard disk drives is RAID, which comes in a number of standard configurations and non-standard configurations. Non-RAID drive architectures also exist, and are referred to by acronyms with similarity to RAID, several tongue-in-cheek
A Redundant Array of Inexpensive Servers (RAIS) or Redundant Array of Independent Nodes (RAIN) is the use of multiple servers to provide the same service in such a way that service will still be available if the servers fails. The term may imply some kind of load balancing between the servers.




