Red clover is a species of clover native to Europe, Western Asia, and northwest Africa.

Trifolium pratense, the red clover, is a herbaceous species of flowering plant in the bean family Fabaceae, native to Europe, Western Asia, and northwest Africa, but planted and naturalised in many other regions.
Red clover may also refer to:
- Red clover vein mosaic virus, a plant pathogenic virus.
- Red clover necrotic mosaic virus translation enhancer elements
- Red Clover Creek, a stream in Plumas County, California
- Red clover diseases, a list of diseases that affect red clover
- Red Clover (film), a 2012 horror film starring Billy Zane
Red clover vein mosaic virus (RCVMV) is a plant pathogenic virus.

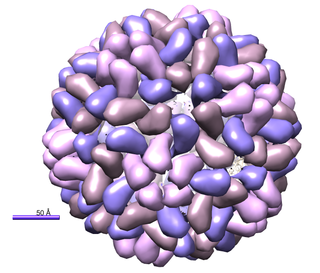
Red clover necrotic mosaic virus (RCNMV) contains several structural elements present within the 3' and 5' untranslated regions (UTR) of the genome that enhance translation. In eukaryotes transcription is a prerequisite for translation. During transcription the pre-mRNA transcript is processes where a 5' cap is attached onto mRNA and this 5' cap allows for ribosome assembly onto the mRNA as it acts as a binding site for the eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4F. Once eIF4F is bound to the mRNA this protein complex interacts with the poly(A) binding protein which is present within the 3' UTR and results in mRNA circularization. This multiprotein-mRNA complex then recruits the ribosome subunits and scans the mRNA until it reaches the start codon. Transcription of viral genomes differs from eukaryotes as viral genomes produce mRNA transcripts that lack a 5’ cap site. Despite lacking a cap site viral genes contain a structural element within the 5’ UTR known as an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). IRES is a structural element that recruits the 40s ribosome subunit to the mRNA within close proximity of the start codon.
Red Clover Creek is a northwestward-flowing stream originating on Horton Ridge east of the Sierra Nevada crest in Plumas County, California, United States. It courses 27 miles (43 km) through Dotta Canyon and the Red Clover Valley, culminating in Last Chance Creek, which flows in turn, into Indian Creek in the Genesee Valley, and from there to the East Branch North Fork Feather River. The Red Clover Valley sits at an elevation of about 5,400 feet (1,600 m) and is located on the east side of the Sierra Nevada crest, approximately 60 miles (97 km) north of Truckee and 30 miles (48 km) southeast of Quincy. This region of the northern Sierra Nevada is known as the Diamond Mountains.
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Red clover. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |