Region B may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Region B. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Region B may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Region B. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
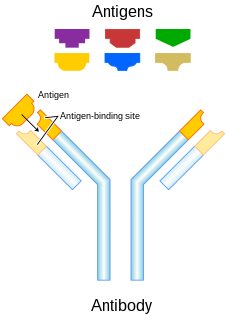
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to neutralize pathogens such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen, via the fragment antigen-binding (Fab) variable region. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize its target directly. Depending on the antigen, the binding may impede the biological process causing the disease or may activate macrophages to destroy the foreign substance. The ability of an antibody to communicate with the other components of the immune system is mediated via its Fc region, which contains a conserved glycosylation site involved in these interactions. The production of antibodies is the main function of the humoral immune system.
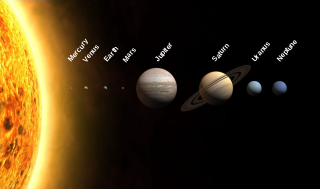
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound planetary system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of the objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the eight planets, with the remainder being smaller objects, such as the five dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that orbit the Sun indirectly—the moons—two are larger than the smallest planet, Mercury.

Voltage, electric potential difference, electric pressure or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points. The difference in electric potential between two points in a static electric field is defined as the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage is named volt. In SI units, work per unit charge is expressed as joules per coulomb, where 1 volt = 1 joule per 1 coulomb. The official SI definition for volt uses power and current, where 1 volt = 1 watt per 1 ampere. This definition is equivalent to the more commonly used 'joules per coulomb'. Voltage or electric potential difference is denoted symbolically by ∆V, but more often simply as V, for instance in the context of Ohm's or Kirchhoff's circuit laws.

South East England is the most populous of the nine official regions of England at the first level of NUTS for statistical purposes. It consists of Berkshire, Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Surrey and West Sussex. As with the other regions of England, apart from Greater London, the south east has no elected government.

The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of NUTS for statistical purposes. It consists of Derbyshire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire, Northamptonshire, Nottinghamshire and Rutland. The region has an area of 15,627 km2 (6,034 sq mi), with a population over 4.5 million in 2011. There are five main urban centres, Derby, Leicester, Lincoln, Northampton and Nottingham. Others include Boston, Skegness, Chesterfield, Corby, Grantham, Hinckley, Kettering, Loughborough, Mansfield, Newark-on-Trent and Wellingborough.
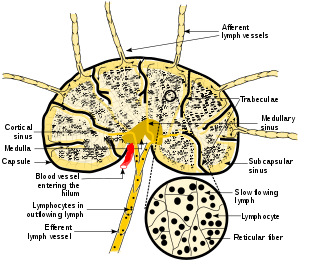
A lymph node or lymph gland is an ovoid or kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system, and of the adaptive immune system, that is widely present throughout the body. They are linked by the lymphatic vessels as a part of the circulatory system. Lymph nodes are major sites of B and T lymphocytes, and other white blood cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles and cancer cells. Lymph nodes do not have a detoxification function, which is primarily dealt with by the liver and kidneys.
A regional lockout is a class of digital rights management preventing the use of a certain product or service, such as multimedia or a hardware device, outside a certain region or territory. A regional lockout may be enforced through physical means, through technological means such as detecting the user's IP address or using an identifying code, or through unintentional means introduced by devices only supporting certain regional technologies.

The West Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of NUTS for statistical purposes. It covers the western half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It contains Birmingham and the larger West Midlands conurbation, which is the third most populous in the United Kingdom. The City of Coventry is also located within the West Midlands county, but is separated from the conurbation to the west by several miles of green belt. The region also contains 6 shire counties which stretch from the Welsh Border to the East Midlands.
The International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities is an Intergovernmental organization founded in 1957 to collect and provide nautical expertise and advice.

A sea mark, also seamark and navigation mark, is a form of aid to navigation and pilotage that identifies the approximate position of a maritime channel, hazard, or administrative area to allow boats, ships, and seaplanes to navigate safely.
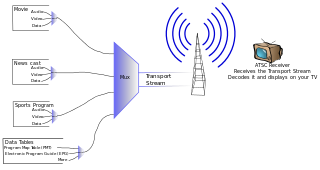
The Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) is the MPEG and privately defined program-specific information originally defined by General Instrument for the DigiCipher 2 system and later extended for the ATSC digital television system for carrying metadata about each channel in the broadcast MPEG transport stream of a television station and for publishing information about television programs so that viewers can select what to watch by title and description.

DVD region codes are a digital rights management technique designed to allow rights holders to control the international distribution of a DVD release, including its content, release date, and price, all according to the appropriate region.

The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian Government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a National Reserve System.
Clifton Court Forebay is a reservoir in the San Joaquin River Delta region of eastern Contra Costa County, California, 17 mi (27 km) southwest of Stockton. The estuary region the forebay is located in is only 1m to 3m above mean sea level.

Two-dimensional space is a geometric setting in which two values are required to determine the position of an element. In mathematics, it is commonly represented by the symbol ℝ2. For a generalization of the concept, see dimension.

Attica Region is an administrative region of Greece, that encompasses the entire metropolitan area of Athens, the country's capital and largest city. The region is coextensive with the former Attica Prefecture of Central Greece, but covers a greater area than the historical region of Attica.
The Jats of Kutch are a cattle breeding nomadic Muslim community, found in the Kutch region of Gujarat in India. They are one of a number of communities of Maldhari pastoral nomads found in the Banni region of Kutch.