
The Three Kingdoms was the tripartite division of China between the states of Wei, Shu, and Wu. It started with the end of the Han dynasty and was followed by the Jin dynasty. The term "Three Kingdoms" is something of a misnomer, since each state was eventually headed not by a king, but by an emperor who claimed suzerainty over all China. Nevertheless, the term "Three Kingdoms" has become standard among English-speaking sinologists. To distinguish the three states from other historical Chinese states of the same names, historians have added a relevant character to the state's original name: the state that called itself Wei (魏) is also known as Cao Wei (曹魏), the state that called itself Han (漢) is also known as Shu Han (蜀漢) or just Shu (蜀), and the state that called itself Wu (吳) is also known as Eastern Wu or Sun Wu (孫吳).

劉 / 刘 is a Chinese surname. The Liu as transcribed in English can represent several different surnames written in different Chinese characters:

The Song dynasty, better known as the Liu Song dynasty, also known as Former Song (前宋) or Southern Song (南宋), was the first of the four Southern Dynasties in China, succeeding the Eastern Jin and followed by the Southern Qi.

Jiankang, or Jianye, as it was originally called, was the capital city of the Eastern Wu, the Jin dynasty and the Southern Dynasties. Its walls are extant ruins in the modern municipal region of Nanjing.

The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907-979) was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concurrent states were established elsewhere, mainly in South China. It was the last prolonged period of multiple political division in Chinese imperial history.

The Northern and Southern dynasties was a period in the history of China that lasted from 386 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Wu Hu states. It is sometimes considered as the latter part of a longer period known as the Six Dynasties. Though an age of civil war and political chaos, it was also a time of flourishing arts and culture, advancement in technology, and the spread of Mahayana Buddhism and Daoism. The period saw large-scale migration of Han Chinese to the lands south of the Yangtze. The period came to an end with the unification of all of China proper by Emperor Wen of the Sui Dynasty.
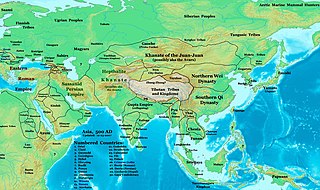
The Northern Wei or the Northern Wei Empire, also known as the Tuoba Wei (拓跋魏), Later Wei (後魏), or Yuan Wei (元魏), was a dynasty founded by the Tuoba clan of the Xianbei, which ruled northern China from 386 to 534 AD, during the period of the Southern and Northern Dynasties. Described as "part of an era of political turbulence and intense social and cultural change", the Northern Wei Dynasty is particularly noted for unifying northern China in 439: this was also a period of introduced foreign ideas, such as Buddhism, which became firmly established.

The Ten Kingdoms was a period in the history of Southern China that followed the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907. It lasted until the rise of the Song dynasty, which was founded in 960. Nine of the kingdoms were in the South and one small kingdom was in the far North. Many states were de facto independent long before the Tang Empire dissolved. The last of the Ten Kingdoms, the Northern Han, survived until 979.

The Northern Han kingdom was a state of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was founded by Liu Min (劉旻), formerly known as Liu Chong (劉崇), and lasted from 951 to 979.

The following is a chronology of the dynasties in the history of China from 21st century BC.

Wuyue, 907–978, was an independent coastal kingdom founded during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms (907–960) of Chinese history. It was ruled by the Qian family, whose family name remains widespread in the kingdom's former territory.

Southern Han, originally Great Yue, was one of the ten kingdoms that existed during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was located on China's southern coast, controlling modern Guangdong and Guangxi. The kingdom greatly expanded its capital Xingwang Fu (Chinese: 興王府; pinyin: Xìngwángfǔ,. It attempted but failed to annex the Tang province of Annam.

Taikang County, formerly known as Yangjia County or Yangxia County, is a county in the north of Zhoukou prefecture-level city, in the east of Henan province, China. It is divided into 23 townships and 766 villages. The county is home to 1.43 million Han Chinese and 25,000 Hui, with a population density of 581 people per kilometre squared.

The Later Han was founded in 947. It was the fourth of the Five Dynasties, and the third consecutive sinicized Shatuo ethnicity state, however, other sources indicate that the Later Han emperors claimed patrilineal Han Chinese ancestry. It was among the shortest-lived of all Chinese regimes, lasting for slightly under four years before it was overcome by a rebellion that resulted in the founding of the Later Zhou.
Fan Ye, courtesy name Weizong (蔚宗), was a Chinese historian and politician of the Liu Song dynasty during the Southern and Northern dynasties period. He was the compiler of the historical text Book of the Later Han. The son of Fan Tai (范泰), Fan Ye was born in present-day Shaoxing, Zhejiang, but his ancestral home was in Nanyang, Henan.

Liu Yu's expeditions were a series of successful campaigns mounted by Jin China from 409 AD to 416 AD against Southern Yan, Later Qin, Northern Wei and Xia that successfully recovered all of China's territory south of the Yellow River with the exception of the Chang'an area, which was taken by Xia. These victories were the basis of the prosperity of the Reign of Yuanjia.

The Sixteen Kingdoms, less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439, when the political order of northern China fractured into a series of short-lived sovereign states, most of which were founded by the "Five Barbarians," ethnic minority peoples who had settled in northern China during the preceding centuries and participated in the overthrow of the Western Jin dynasty in the early 4th century. The kingdoms founded by ethnic Xiongnu, Xianbei, Di, Jie, Qiang, as well as Han Chinese and other ethnicities, fought against each other and the Eastern Jin dynasty, which succeeded the Western Jin and ruled southern China. The period ended with the unification of northern China in the early 5th century by the Northern Wei, a dynasty that evolved from a kingdom founded by ethnic Xianbei.

Year 420 (CDXX) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Theodosius and Constantius. The denomination 420 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Liu Jiyuan (劉繼元), was the last ruler of China's Northern Han kingdom in its Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. He was the grandson of Liu Min. He ruled Northern Han from 968 until 979, when he surrendered to the Song forces under Emperor Taizong of Song.















