
Artificial neural networks (ANN) or connectionist systems are computing systems vaguely inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. The neural network itself is not an algorithm, but rather a framework for many different machine learning algorithms to work together and process complex data inputs. Such systems "learn" to perform tasks by considering examples, generally without being programmed with any task-specific rules. For example, in image recognition, they might learn to identify images that contain cats by analyzing example images that have been manually labeled as "cat" or "no cat" and using the results to identify cats in other images. They do this without any prior knowledge about cats, for example, that they have fur, tails, whiskers and cat-like faces. Instead, they automatically generate identifying characteristics from the learning material that they process.
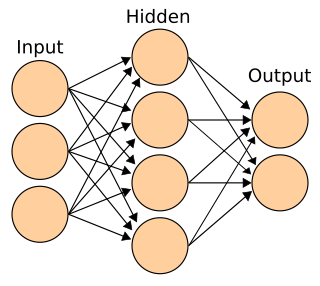
Connectionism is an approach in the fields of cognitive science, that hopes to explain mental phenomena using artificial neural networks (ANN).
In graph theory, a flow network is a directed graph where each edge has a capacity and each edge receives a flow. The amount of flow on an edge cannot exceed the capacity of the edge. Often in operations research, a directed graph is called a network, the vertices are called nodes and the edges are called arcs. A flow must satisfy the restriction that the amount of flow into a node equals the amount of flow out of it, unless it is a source, which has only outgoing flow, or sink, which has only incoming flow. A network can be used to model traffic in a computer network, circulation with demands, fluids in pipes, currents in an electrical circuit, or anything similar in which something travels through a network of nodes.

A recurrent neural network (RNN) is a class of artificial neural network where connections between nodes form a directed graph along a temporal sequence. This allows it to exhibit temporal dynamic behavior. Unlike feedforward neural networks, RNNs can use their internal state (memory) to process sequences of inputs. This makes them applicable to tasks such as unsegmented, connected handwriting recognition or speech recognition.

A feedforward neural network is an artificial neural network wherein connections between the nodes do not form a cycle. As such, it is different from recurrent neural networks.

A neural circuit is a population of neurons interconnected by synapses to carry out a specific function when activated. Neural circuits interconnect to one another to form large scale brain networks. Biological neural networks have inspired the design of artificial neural networks, but artificial neural networks are usually not strict copies of their biological counterparts

A neural network is a network or circuit of neurons, or in a modern sense, an artificial neural network, composed of artificial neurons or nodes. Thus a neural network is either a biological neural network, made up of real biological neurons, or an artificial neural network, for solving artificial intelligence (AI) problems. The connections of the biological neuron are modeled as weights. A positive weight reflects an excitatory connection, while negative values mean inhibitory connections. All inputs are modified by a weight and summed. This activity is referred as a linear combination. Finally, an activation function controls the amplitude of the output. For example, an acceptable range of output is usually between 0 and 1, or it could be −1 and 1.

Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to chordates of the group Cristozoa that arise from the embryonic ectoderm cell layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia.
Neural network software is used to simulate, research, develop, and apply artificial neural networks, software concepts adapted from biological neural networks, and in some cases, a wider array of adaptive systems such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Quantum neural networks (QNNs) are neural network models which are based on the principles of quantum mechanics. There are two different approaches to QNN research, one exploiting quantum information processing to improve existing neural network models, and the other one searching for potential quantum effects in the brain.

Spiking neural networks (SNNs) are artificial neural network models that more closely mimic natural neural networks. In addition to neuronal and synaptic state, SNNs also incorporate the concept of time into their operating model. The idea is that neurons in the SNN do not fire at each propagation cycle, but rather fire only when a membrane potential – an intrinsic quality of the neuron related to its membrane electrical charge – reaches a specific value. When a neuron fires, it generates a signal which travels to other neurons which, in turn, increase or decrease their potentials in accordance with this signal.

Long short-term memory (LSTM) is an artificial recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture used in the field of deep learning. Unlike standard feedforward neural networks, LSTM has feedback connections that make it a "general purpose computer". It can not only process single data points, but also entire sequences of data. For example, LSTM is applicable to tasks such as unsegmented, connected handwriting recognition or speech recognition.
Bloomberg Business Week wrote: "These powers make LSTM arguably the most commercial AI achievement, used for everything from predicting diseases to composing music."
Extension neural network is a pattern recognition method found by M. H. Wang and C. P. Hung in 2003 to classify instances of data sets. Extension neural network is composed of artificial neural network and extension theory concepts. It uses the fast and adaptive learning capability of neural network and correlation estimation property of extension theory by calculating extension distance.
ENN was used in:

Deep learning is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on the layers used in artificial neural networks. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.

The MNIST database is a large database of handwritten digits that is commonly used for training various image processing systems. The database is also widely used for training and testing in the field of machine learning. It was created by "re-mixing" the samples from NIST's original datasets. The creators felt that since NIST's training dataset was taken from American Census Bureau employees, while the testing dataset was taken from American high school students, it was not well-suited for machine learning experiments. Furthermore, the black and white images from NIST were normalized to fit into a 28x28 pixel bounding box and anti-aliased, which introduced grayscale levels.

In deep learning, a convolutional neural network is a class of deep neural networks, most commonly applied to analyzing visual imagery.

In machine learning, the vanishing gradient problem is a difficulty found in training artificial neural networks with gradient-based learning methods and backpropagation. In such methods, each of the neural network's weights receives an update proportional to the partial derivative of the error function with respect to the current weight in each iteration of training. The problem is that in some cases, the gradient will be vanishingly small, effectively preventing the weight from changing its value. In the worst case, this may completely stop the neural network from further training. As one example of the problem cause, traditional activation functions such as the hyperbolic tangent function have gradients in the range (0, 1), and backpropagation computes gradients by the chain rule. This has the effect of multiplying n of these small numbers to compute gradients of the "front" layers in an n-layer network, meaning that the gradient decreases exponentially with n while the front layers train very slowly.

DeepDream is a computer vision program created by Google engineer Alexander Mordvintsev which uses a convolutional neural network to find and enhance patterns in images via algorithmic pareidolia, thus creating a dream-like hallucinogenic appearance in the deliberately over-processed images.
An AI accelerator is a class of microprocessor or computer system designed as hardware acceleration for artificial intelligence applications, especially artificial neural networks, machine vision and machine learning. Typical applications include algorithms for robotics, internet of things and other data-intensive or sensor-driven tasks. They are often manycore designs and generally focus on low-precision arithmetic, novel dataflow architectures or in-memory computing capability. A number of vendor-specific terms exist for devices in this category, and it is an emerging technology without a dominant design. AI accelerators can be found in many devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers all around the world. See the heading titled ¨Examples" for more examples.










