An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two main functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing.

In computer networking, IP address spoofing or IP spoofing is the creation of Internet Protocol (IP) packets with a false source IP address, for the purpose of impersonating another computing system.

A judge is a person who presides over court proceedings, either alone or as a part of a panel of judges. The powers, functions, method of appointment, discipline, and training of judges vary widely across different jurisdictions. The judge is supposed to conduct the trial impartially and, typically, in an open court. The judge hears all the witnesses and any other evidence presented by the barristers or solicitors of the case, assesses the credibility and arguments of the parties, and then issues a ruling on the matter at hand based on his or her interpretation of the law and his or her own personal judgment. In some jurisdictions, the judge's powers may be shared with a jury. In inquisitorial systems of criminal investigation, a judge might also be an examining magistrate.

Network address translation (NAT) is a method of remapping one IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. The technique was originally used as a shortcut to avoid the need to readdress every host when a network was moved. It has become a popular and essential tool in conserving global address space in the face of IPv4 address exhaustion. One Internet-routable IP address of a NAT gateway can be used for an entire private network.

In computer networks, a proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server and the proxy server evaluates the request as a way to simplify and control its complexity. Proxies were invented to add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems.
Whitelisting is the practice of explicitly allowing some identified entities access to a particular privilege, service, mobility, access or recognition. It is the reverse of blacklisting.

A dead letter office (DLO) is a facility within a postal system where undeliverable mail is processed. Mail is considered to be undeliverable when the address is invalid so it cannot be delivered to addressee, and there is no return address so it cannot be returned to the sender.
In computer science, a reference is a value that enables a program to indirectly access a particular datum, such as a variable's value or a record, in the computer's memory or in some other storage device. The reference is said to refer to the datum, and accessing the datum is called dereferencing the reference.
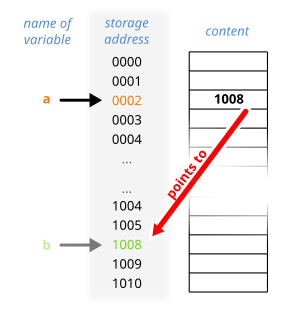
In computer science, a pointer is a programming language object that stores the memory address of another value located in computer memory. A pointer references a location in memory, and obtaining the value stored at that location is known as dereferencing the pointer. As an analogy, a page number in a book's index could be considered a pointer to the corresponding page; dereferencing such a pointer would be done by flipping to the page with the given page number and reading the text found on that page. The actual format and content of a pointer variable is dependent on the underlying computer architecture.
Mrs. or Mrs is a commonly used English honorific used for women, usually for those who are married and who do not instead use another title, such as Dr, Professor, President, Dame, etc. In most Commonwealth countries, a full stop (period) is usually not used with the title. In the United States and Canada a period is usually used.

A standing ovation is a form of applause where members of a seated audience stand up while applauding after extraordinary performances of particularly high acclaim. In Ancient Rome returning military commanders whose victories did not quite meet the requirements of a triumph but which were still praiseworthy were celebrated with an ovation instead, from the Latin ovo, "I rejoice". The word's use in English to refer to sustained applause dates from at least 1831.
An honorific is a title that conveys esteem, courtesy, or respect for position or rank when used in addressing or referring to a person. Sometimes, the term "honorific" is used in a more specific sense to refer to an honorary academic title. It is also often conflated with systems of honorific speech in linguistics, which are grammatical or morphological ways of encoding the relative social status of speakers.
Disposable email addressing, also known as DEA or dark mail, refers to an approach where a unique email address is used for every contact or entity. The benefit is that if anyone compromises the address or utilises it in connection with email abuse, the address owner can easily cancel it without affecting any of their other contacts.
In computer science, a call stack is a stack data structure that stores information about the active subroutines of a computer program. This kind of stack is also known as an execution stack, program stack, control stack, run-time stack, or machine stack, and is often shortened to just "the stack". Although maintenance of the call stack is important for the proper functioning of most software, the details are normally hidden and automatic in high-level programming languages. Many computer instruction sets provide special instructions for manipulating stacks.
The Japanese language makes use of honorific suffixes when referring to others in a conversation. These suffixes are attached to the end of names, and are often gender-neutral. Honorific suffixes also indicate the level of the speaker and referred individual's relationship and are often used alongside other components of Japanese honorific speech, called keigo (敬語).
In C++ computer programming, copy elision refers to a compiler optimization technique that eliminates unnecessary copying of objects. The C++ language standard generally allows implementations to perform any optimization, provided the resulting program's observable behavior is the same as if, i.e. pretending, the program were executed exactly as mandated by the standard.
In computer programming, a subroutine is a sequence of program instructions that performs a specific task, packaged as a unit. This unit can then be used in programs wherever that particular task should be performed.
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), although many people use the two terms interchangeably. Thus http://www.example.com is a URL, while www.example.com is not.</ref> URLs occur most commonly to reference web pages (http), but are also used for file transfer (ftp), email (mailto), database access (JDBC), and many other applications.
The prefix The Honourable or The Honorable is an honorific style that is used before the names of certain classes of people.







