The muscular system is an organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates blood throughout the body. The muscular systems in vertebrates are controlled through the nervous system although some muscles can be completely autonomous. Together with the skeletal system in the human, it forms the musculoskeletal system, which is responsible for the movement of the body.
Putrefaction is the fifth stage of death, following pallor mortis, livor mortis, algor mortis, and rigor mortis. This process references the breaking down of a body of an animal post-mortem. In broad terms, it can be viewed as the decomposition of proteins, and the eventual breakdown of the cohesiveness between tissues, and the liquefaction of most organs. This is caused by the decomposition of organic matter by bacterial or fungal digestion, which causes the release of gases that infiltrate the body's tissues, and leads to the deterioration of the tissues and organs. The approximate time it takes putrefaction to occur is dependent on various factors. Internal factors that affect the rate of putrefaction include the age at which death has occurred, the overall structure and condition of the body, the cause of death, and external injuries arising before or after death. External factors include environmental temperature, moisture and air exposure, clothing, burial factors, and light exposure. Body farms are facilities that study the way various factors affect the putrefaction process.

Smooth(soft) muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations. It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium.

Skeletal muscles are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres.

Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) in (via the gut) and out (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and between body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and bone. Bone acts as a calcium storage center for deposits and withdrawals as needed by the blood via continual bone remodeling.

A myofibril is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2 micrometres. They are created during embryonic development in a process known as myogenesis.

A sarcomere is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells which are formed during embryonic myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes. The costamere is a different component that connects the sarcomere to the sarcolemma.

The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells that is similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in other cells. The main function of the SR is to store calcium ions (Ca2+). Calcium ion levels are kept relatively constant, with the concentration of calcium ions within a cell being 10,000 times smaller than the concentration of calcium ions outside the cell. This means that small increases in calcium ions within the cell are easily detected and can bring about important cellular changes (the calcium is said to be a second messenger). Calcium is used to make calcium carbonate (found in chalk) and calcium phosphate, two compounds that the body uses to make teeth and bones. This means that too much calcium within the cells can lead to hardening (calcification) of certain intracellular structures, including the mitochondria, leading to cell death. Therefore, it is vital that calcium ion levels are controlled tightly, and can be released into the cell when necessary and then removed from the cell.

Cardiac muscle is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall and the inner layer, with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix.
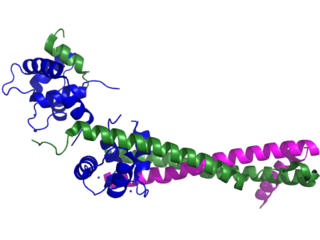
Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-specific troponins I and T are extensively used as diagnostic and prognostic indicators in the management of myocardial infarction and acute coronary syndrome. Blood troponin levels may be used as a diagnostic marker for stroke or other myocardial injury that is ongoing, although the sensitivity of this measurement is low.

The post-mortem interval (PMI) is the time that has elapsed since an individual's death. When the time of death is not known, the interval may be estimated, and so an approximate time of death established. Postmortem interval estimations can range from hours, to days or even years depending on the type of evidence present. There are standard medical and scientific techniques supporting such an estimation.

Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state.
Myocardial contractility represents the innate ability of the heart muscle (cardiac muscle or myocardium) to contract. The ability to produce changes in force during contraction result from incremental degrees of binding between different types of tissue, that is, between filaments of myosin (thick) and actin (thin) tissue. The degree of binding depends upon the concentration of calcium ions in the cell. Within an in vivo intact heart, the action/response of the sympathetic nervous system is driven by precisely timed releases of a catecholamine, which is a process that determines the concentration of calcium ions in the cytosol of cardiac muscle cells. The factors causing an increase in contractility work by causing an increase in intracellular calcium ions (Ca++) during contraction.

Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the contractile proteins and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act together in muscle contraction, and in order of size are a thick one of mostly myosin, a thin one of mostly actin, and a very thin one of mostly titin.

Myosin light-chain kinase also known as MYLK or MLCK is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that phosphorylates a specific myosin light chain, namely, the regulatory light chain of myosin II.
Cadaveric spasm, also known as postmortem spasm, instantaneous rigor mortis, cataleptic rigidity, or instantaneous rigidity, is a rare form of muscular stiffening that occurs at the moment of death and persists into the period of rigor mortis. Cadaveric spasm can be distinguished from rigor mortis as the former is a stronger stiffening of the muscles that cannot be easily undone, while rigor mortis can.

In the histology of skeletal muscle, a triad is the structure formed by a T tubule with a sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) known as the terminal cisterna on either side. Each skeletal muscle fiber has many thousands of triads, visible in muscle fibers that have been sectioned longitudinally. In mammals, triads are typically located at the A-I junction; that is, the junction between the A and I bands of the sarcomere, which is the smallest unit of a muscle fiber.

Metabolic myopathies are myopathies that result from defects in biochemical metabolism that primarily affect muscle. They are generally genetic defects that interfere with muscle's ability to create energy, causing a low ATP reservoir within the muscle cell.
Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling (CardiacEC coupling) describes the series of events, from the production of an electrical impulse (action potential) to the contraction of muscles in the heart. This process is of vital importance as it allows for the heart to beat in a controlled manner, without the need for conscious input. EC coupling results in the sequential contraction of the heart muscles that allows blood to be pumped, first to the lungs (pulmonary circulation) and then around the rest of the body (systemic circulation) at a rate between 60 and 100 beats every minute, when the body is at rest. This rate can be altered, however, by nerves that work to either increase heart rate (sympathetic nerves) or decrease it (parasympathetic nerves), as the body's oxygen demands change. Ultimately, muscle contraction revolves around a charged atom (ion), calcium (Ca2+), which is responsible for converting the electrical energy of the action potential into mechanical energy (contraction) of the muscle. This is achieved in a region of the muscle cell, called the transverse tubule during a process known as calcium induced calcium release.
The stages of death of a human being have medical, biochemical and legal aspects. The term taphonomy from palaeontology applies to the fate of all kinds of remains of organisms. Forensic taphonomy is concerned with remains of the human body.












