
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs for immediate use in the computer. The term memory is often synonymous with the term primary storage or main memory. An archaic synonym for memory is store.

Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other electrically charged particles. Electronics is a subfield of electrical engineering, but it differs from it in that it focuses on using active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog to digital. Electronics also encompasses the fields of microelectronics, nanoelectronics, optoelectronics, and quantum electronics, which deal with the fabrication and application of electronic devices at microscopic, nanoscopic, optical, and quantum scales.

An integrated circuit is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of miniaturized transistors and other electronic components are integrated together on the chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete components, allowing a large transistor count.

Robert Norton Noyce, nicknamed "the Mayor of Silicon Valley", was an American physicist and entrepreneur who co-founded Fairchild Semiconductor in 1957 and Intel Corporation in 1968. He was also credited with the realization of the first monolithic integrated circuit or microchip, which fueled the personal computer revolution and gave Silicon Valley its name.
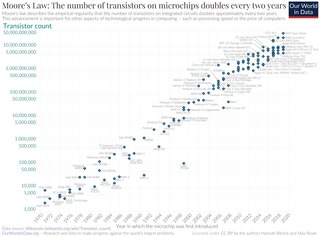
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship linked to gains from experience in production.

Jack St. Clair Kilby was an American electrical engineer who took part in the realization of the first integrated circuit while working at Texas Instruments (TI) in 1958. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics on December 10, 2000. Kilby was also the co-inventor of the handheld calculator and the thermal printer, for which he had the patents. He also had patents for seven other inventions.
Semiconductor memory is a digital electronic semiconductor device used for digital data storage, such as computer memory. It typically refers to devices in which data is stored within metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) memory cells on a silicon integrated circuit memory chip. There are numerous different types using different semiconductor technologies. The two main types of random-access memory (RAM) are static RAM (SRAM), which uses several transistors per memory cell, and dynamic RAM (DRAM), which uses a transistor and a MOS capacitor per cell. Non-volatile memory uses floating-gate memory cells, which consist of a single floating-gate transistor per cell.

In integrated circuits, depletion-load NMOS is a form of digital logic family that uses only a single power supply voltage, unlike earlier NMOS logic families that needed more than one different power supply voltage. Although manufacturing these integrated circuits required additional processing steps, improved switching speed and the elimination of the extra power supply made this logic family the preferred choice for many microprocessors and other logic elements.
This article details the history of electrical engineering. The first substantial practical use of electricity was electromagnetism.
The 1 μm process is a level of MOSFET semiconductor process technology that was commercialized around the 1984–1986 timeframe, by leading semiconductor companies like NTT, NEC, Intel and IBM. It was the first process where CMOS was common.
A transistor is a semiconductor device with at least three terminals for connection to an electric circuit. In the common case, the third terminal controls the flow of current between the other two terminals. This can be used for amplification, as in the case of a radio receiver, or for rapid switching, as in the case of digital circuits. The transistor replaced the vacuum-tube triode, also called a (thermionic) valve, which was much larger in size and used significantly more power to operate. The first transistor was successfully demonstrated on December 23, 1947, at Bell Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey. Bell Labs was the research arm of American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T). The three individuals credited with the invention of the transistor were William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain. The introduction of the transistor is often considered one of the most important inventions in history.

Fujio Masuoka is a Japanese engineer, who has worked for Toshiba and Tohoku University, and is currently chief technical officer (CTO) of Unisantis Electronics. He is best known as the inventor of flash memory, including the development of both the NOR flash and NAND flash types in the 1980s. He also invented the first gate-all-around (GAA) MOSFET (GAAFET) transistor, an early non-planar 3D transistor, in 1988.
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each other. This process is especially prominent in systems such as those of DC or AC rotating electrical machines which can be designed and operated to generate power from a mechanical process (generator) or used to power a mechanical effect (motor). Electrical engineering in this context also encompasses electronics engineering.
The first planar monolithic integrated circuit (IC) chip was demonstrated in 1960. The idea of integrating electronic circuits into a single device was born when the German physicist and engineer Werner Jacobi developed and patented the first known integrated transistor amplifier in 1949 and the British radio engineer Geoffrey Dummer proposed to integrate a variety of standard electronic components in a monolithic semiconductor crystal in 1952. A year later, Harwick Johnson filed a patent for a prototype IC. Between 1953 and 1957, Sidney Darlington and Yasuo Tarui proposed similar chip designs where several transistors could share a common active area, but there was no electrical isolation to separate them from each other.
Dawon Kahng was a Korean-American electrical engineer and inventor, known for his work in solid-state electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET, along with his colleague Mohamed Atalla, in 1959. Kahng and Atalla developed both the PMOS and NMOS processes for MOSFET semiconductor device fabrication. The MOSFET is the most widely used type of transistor, and the basic element in most modern electronic equipment.
In semiconductor electronics, Dennard scaling, also known as MOSFET scaling, is a scaling law which states roughly that, as transistors get smaller, their power density stays constant, so that the power use stays in proportion with area; both voltage and current scale (downward) with length. The law, originally formulated for MOSFETs, is based on a 1974 paper co-authored by Robert H. Dennard, after whom it is named.

The memory cell is the fundamental building block of computer memory. The memory cell is an electronic circuit that stores one bit of binary information and it must be set to store a logic 1 and reset to store a logic 0. Its value is maintained/stored until it is changed by the set/reset process. The value in the memory cell can be accessed by reading it.
Bijan Davari is an Iranian-American engineer. He is an IBM Fellow and Vice President at IBM Thomas J Watson Research Center, Yorktown Hts, NY. His pioneering work in the miniaturization of semiconductor devices changed the world of computing. His research led to the first generation of voltage-scaled deep-submicron CMOS with sufficient performance to totally replace bipolar technology in IBM mainframes and enable new high-performance UNIX servers. As head of IBM’s Semiconductor Research Center (SRDC), he led IBM into the use of Copper interconnect, silicon on insulator (SOI), and Embedded DRAM before its rivals. He is a member of the U.S. National Academy of Engineering and is known for his seminal contributions to the field of CMOS technology. He is an IEEE Fellow, recipient of the J J Ebers Award in 2005 and IEEE Andrew S. Grove Award in 2010. At the present time, he leads the Next Generation Systems Area of research.











