| Look up run time , run-time , or runtime in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Run time, run-time, or runtime may refer to:
| Look up run time , run-time , or runtime in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Run time, run-time, or runtime may refer to:
In computer science, run time, runtime or execution time is the time during which a program is running (executing), in contrast to other program lifecycle phases such as compile time, link time and load time.
In computer programming, a runtime library (RTL) is a set of low-level routines used by a compiler to invoke some of the behaviors of a runtime environment, by inserting calls to the runtime library into compiled executable binary. The runtime environment implements the execution model, built-in functions, and other fundamental behaviors of a programming language. During execution of that computer program, execution of those calls to the runtime library cause communication between the executable binary and the runtime environment. A runtime library often includes built-in functions for memory management or exception handling. Therefore, a runtime library is always specific to the platform and compiler.
A runtime system, also called run-time system, runtime environment or run-time environment, primarily implements portions of an execution model. This is not to be confused with the runtime lifecycle phase of a program, during which the runtime system is in operation. Most languages have some form of runtime system that provides an environment in which programs run. This environment may address a number of issues including the layout of application memory, how the program accesses variables, mechanisms for passing parameters between procedures, interfacing with the operating system, and otherwise. The compiler makes assumptions depending on the specific runtime system to generate correct code. Typically the runtime system will have some responsibility for setting up and managing the stack and heap, and may include features such as garbage collection, threads or other dynamic features built into the language.

A film, also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, or photoplay, is a series of still images that, when shown on a screen, create the illusion of moving images.

Running Time is a 1997 independent crime thriller film written, produced & directed by Josh Becker. Principal cast members are Bruce Campbell, Jeremy Roberts and Anita Barone.
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Run time. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

A Java virtual machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs as well as programs written in other languages that are also compiled to Java bytecode. The JVM is detailed by a specification that formally describes what is required of a JVM implementation. Having a specification ensures interoperability of Java programs across different implementations so that program authors using the Java Development Kit (JDK) need not worry about idiosyncrasies of the underlying hardware platform.
In computing, cross-platform software is computer software that is implemented on multiple computing platforms. Cross-platform software may be divided into two types; one requires individual building or compilation for each platform that it supports, and the other one can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, e.g., software written in an interpreted language or pre-compiled portable bytecode for which the interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all platforms.
In computer science, program analysis is the process of automatically analyzing the behavior of computer programs regarding a property such as correctness, robustness, safety and liveness. Program analysis focuses on two major areas: program optimization and program correctness. The first focuses on improving the program’s performance while reducing the resource usage while the latter focuses on ensuring that the program does what it is supposed to do.
In computing, binary translation is a form of binary recompilation where sequences of instructions are translated from a source instruction set to the target instruction set. In some cases such as instruction set simulation, the target instruction set may be the same as the source instruction set, providing testing and debugging features such as instruction trace, conditional breakpoints and hot spot detection.
In computing, just-in-time (JIT) compilation is a way of executing computer code that involves compilation during execution of a program – at run time – rather than prior to execution. Most often, this consists of source code or more commonly bytecode translation to machine code, which is then executed directly. A system implementing a JIT compiler typically continuously analyses the code being executed and identifies parts of the code where the speedup gained from compilation or recompilation would outweigh the overhead of compiling that code.
In computer programming, an assertion is a statement that a predicate is always true at that point in code execution. It can help a programmer read the code, help a compiler compile it, or help the program detect its own defects.
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine executes the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a specific action to be carried out in order for a specific problem to be solved; as instructions of a program and therefore the actions they describe are being carried out by an executing machine, specific effects are produced in accordance to the semantics of the instructions being executed.
In software engineering, inversion of control (IoC) is a programming principle. IoC inverts the flow control as compared to traditional control flow. In IoC, custom-written portions of a computer program receive the flow of control from a generic framework. A software architecture with this design inverts control as compared to traditional procedural programming: in traditional programming, the custom code that expresses the purpose of the program calls into reusable libraries to take care of generic tasks, but with inversion of control, it is the framework that calls into the custom, or task-specific, code.
App or apps may refer to:
In software engineering, profiling is a form of dynamic program analysis that measures, for example, the space (memory) or time complexity of a program, the usage of particular instructions, or the frequency and duration of function calls. Most commonly, profiling information serves to aid program optimization.
Application virtualization software refers to both application virtual machines and software responsible for implementing them. Application virtual machines are typically used to allow application bytecode to run portably on many different computer architectures and operating systems. The application is usually run on the computer using an interpreter or just-in-time compilation (JIT). There are often several implementations of a given virtual machine, each covering a different set of functions.
Dynamic program analysis is the analysis of computer software that is performed by executing programs on a real or virtual processor. For dynamic program analysis to be effective, the target program must be executed with sufficient test inputs to produce interesting behavior. Use of software testing measures such as code coverage helps ensure that an adequate slice of the program's set of possible behaviors has been observed. Also, care must be taken to minimize the effect that instrumentation has on the execution of the target program. Dynamic analysis is in contrast to static program analysis. Unit tests, integration tests, system tests and acceptance tests use dynamic testing.
In computer science, ahead-of-time compilation is the act of compiling a higher-level programming language such as C or C++, or an intermediate representation such as Java bytecode or .NET Framework Common Intermediate Language (CIL) code, into a native (system-dependent) machine code so that the resulting binary file can execute natively.
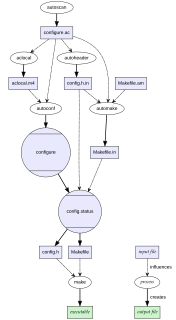
A configure script is an executable script designed to aid in developing a program to be run on a wide number of different computers. It matches the libraries on the user's computer, with those required by the program before compiling it from its source code.
Memory footprint refers to the amount of main memory that a program uses or references while running.
Tracing just-in-time compilation is a technique used by virtual machines to optimize the execution of a program at runtime. This is done by recording a linear sequence of frequently executed operations, compiling them to native machine code and executing them. This is opposed to traditional just-in-time (JIT) compilers that work on a per-method basis.
Program lifecycle phases are the stages a computer program undergoes, from initial creation to deployment and execution. The phases are edit time, compile time, link time, distribution time, installation time, load time, and run time.