
Grodno Region or Grodno Oblast or Hrodna Voblasts is one of the regions of Belarus. It is located in the western part of the country.

Volyn Oblast is an oblast (province) in northwestern Ukraine. Its administrative centre is Lutsk. Kovel is the westernmost town and the last station in Ukraine on the rail line running from Kyiv to Warsaw. The population is 1,021,356
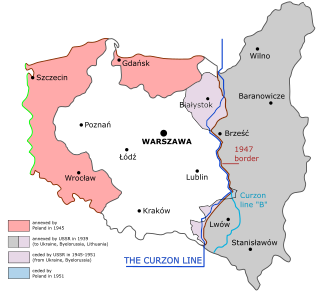
The Curzon Line was a proposed demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and the Soviet Union, two new states emerging after World War I. It was first proposed by The 1st Earl Curzon of Kedleston, the British Foreign Secretary, to the Supreme War Council in 1919 as a diplomatic basis for a future border agreement.

Spiš is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland. Spiš is an informal designation of the territory, but it is also the name of one of the 21 official tourism regions of Slovakia. The region is not an administrative division in its own right, but between the late 11th century and 1920 it was an administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary,.
The Polish minority in the Soviet Union are Polish diaspora who used to reside near or within the borders of the Soviet Union before its dissolution. Some of them continued to live in the post-Soviet states, most notably in Lithuania, Belarus, and Ukraine, the areas historically associated with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, as well as in Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan among others.

Red Ruthenia, or Red Rus' (Latin: Ruthenia Rubra; Russia Rubra; Ukrainian: Червона Русь, romanized: Chervona Rus'; Polish: Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; Russian: Червонная Русь, romanized: Chervonnaya Rus'; Romanian: Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages for the south-western principalities of the Kievan Rus', namely the Principality of Peremyshl and the Principality of Belz. Nowadays the region comprises parts of western Ukraine and adjoining parts of south-eastern Poland. It has also sometimes included parts of Lesser Poland, Podolia, Right-bank Ukraine and Volhynia. Centred on Przemyśl (Peremyshl) and Belz, it has included major cities such as: Chełm, Zamość, Rzeszów, Krosno and Sanok, as well as Lviv and Ternopil.
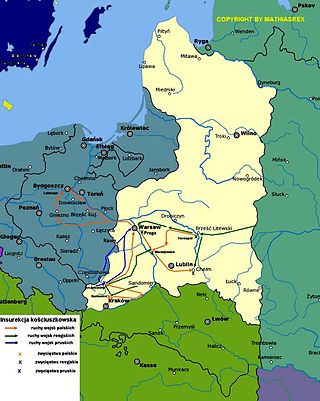
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation.

Lemkos are an ethnic group inhabiting the Lemko Region of Carpathian Rus', an ethnographic region in the Carpathian Mountains and foothills spanning Ukraine, Slovakia and Poland.

The Polish diaspora comprises Poles and people of Polish heritage or origin who live outside Poland. The Polish diaspora is also known in modern Polish as Polonia, the name for Poland in Latin and many Romance languages.

Poles in Germany are the second largest Polish diaspora (Polonia) in the world and the biggest in Europe. Estimates of the number of Poles living in Germany vary from 2 million to about 3 million people living that might be of Polish descent. Their number has quickly decreased over the years, and according to the latest census, there are approximately 866.690 Poles in Germany. The main Polonia organisations in Germany are the Union of Poles in Germany and Congress of Polonia in Germany. Polish surnames are relatively common in Germany, especially in the Ruhr area.

Western Belorussia or Western Belarus is a historical region of modern-day Belarus which belonged to the Second Polish Republic during the interwar period. For twenty years before the 1939 invasion of Poland, it was the northern part of the Polish Kresy macroregion. Following the end of World War II in Europe, most of Western Belorussia was ceded to the Soviet Union by the Allies, while some of it, including Białystok, was given to the Polish People's Republic. Until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Western Belorussia formed the western part of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR). Today, it constitutes the west of modern Belarus.

The Poles in Lithuania, also called Lithuanian Poles, estimated at 183,000 people in the Lithuanian census of 2021 or 6.5% of Lithuania's total population, are the country's largest ethnic minority.
The Belarusian minority in Poland is composed of 47,000 people according to the Polish census of 2011. This number decreased in the last decades from over 300,000 due to an active process of assimilation. Most of them live in the Podlaskie Voivodeship.

The Polish minority in Belarus numbers officially 288,000 according to 2019 census. However, according to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Poland the number is as high as 1,100,000. It forms the second largest ethnic minority in the country after the Russians, at around 3.1% of the total population. An estimated 205,200 Belarusian Poles live in large agglomerations and 82,493 in smaller settlements, with the number of women exceeding the number of men by 33,905. Some estimates by Polish non-governmental sources in the U.S. are higher, citing the previous poll held in 1989 under the Soviet authorities with 413,000 Poles recorded.

The Polish population transfers in 1944–1946 from the eastern half of prewar Poland, were the forced migrations of Poles toward the end and in the aftermath of World War II. These were the result of a Soviet Union policy that had been ratified by the main Allies of World War II. Similarly, the Soviet Union had enforced policies between 1939 and 1941 which targeted and expelled ethnic Poles residing in the Soviet zone of occupation following the Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland. The second wave of expulsions resulted from the retaking of Poland from the Wehrmacht by the Red Army. The USSR took over territory for its western republics.
Following centuries of relative ethnic diversity, the population of modern Poland has become nearly completely ethnically homogeneous Polish as a result of the radically altered borders as well as both the Nazi German and Soviet Russian or Polish Communist campaigns of genocide, expulsion and deportation during and after World War II in the country, in addition to the earlier long processes of Polonization. Nevertheless, multiple ethnic minorities of various origin remain in Poland today, including some newly arrived or grown in size in recent decades.

The Republic of Poland and the Republic of Belarus established diplomatic relations on 2 March 1992. Poland was one of the first countries to recognise Belarusian independence. Both countries share a border and have shared histories, for they have been part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and later, the Russian Empire. They joined the United Nations together in October 1945 as original members. The two countries are currently engaged in a border crisis.
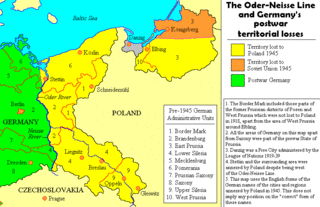
The Oder–Neisse line is the basis of most of the international border between Germany and Poland. It runs mainly along the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers and meets the Baltic Sea in the north, just west of the ports of Szczecin and Świnoujście.

The demographics of Poland constitute all demographic features of the population of Poland, including population density, ethnicity, education level, the health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.

Zakerzonia is an informal name for the territories of Poland to the west of the Curzon Line which used to have sizeable Ukrainian populations, including significant Lemko, Boyko populations, before the invasion of Poland by the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany in 1939, and were claimed as ethnically Ukrainian territories by Ukrainian nationalists in the aftermath of World War II. However, before 1939, the areas of Zakerzonia were mostly inhabited by Poles, who constituted about 70% of the population of this area. Ukrainians lived in a minority in Zakerzonia, constituting about 20% of the area's population.
















