Central Europe is the region comprising the central part of Europe. It is said to occupy continuous territory that are otherwise conventionally Western Europe, Southern Europe, and Eastern Europe. The concept of Central Europe is based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. Central Europe is going through a phase of "strategic awakening", with initiatives such as the CEI, Centrope and the Visegrád Four. While the region's economy shows high disparities with regard to income, all Central European countries are listed by the Human Development Index as very highly developed.

Czechoslovakia, or Czecho-Slovakia, was a sovereign state in Central Europe that existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until its peaceful dissolution into the Czech Republic and Slovakia on 1 January 1993.

The Central Powers, consisting of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria—hence also known as the Quadruple Alliance —was one of the two main coalitions that fought World War I (1914–18).

Frankfurt is a metropolis and the largest city of the German federal state of Hesse, and its 746,878 (2017) inhabitants make it the fifth-largest city of Germany after Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, and Cologne. On the River Main, it forms a continuous conurbation with the neighbouring city of Offenbach am Main, and its urban area has a population of 2.3 million. The city is at the centre of the larger Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region, which has a population of 5.5 million and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr Region. Since the enlargement of the European Union in 2013, the geographic centre of the EU is about 40 km (25 mi) to the east of Frankfurt's central business district. Like France and Franconia, the city is named after the Franks. Frankfurt is the largest city in the Rhine Franconian dialect area.

Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central and Western Europe, lying between the Baltic and North Seas to the north, and the Alps to the south. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France to the southwest, and Luxembourg, Belgium and the Netherlands to the west.
The High German languages or High German dialects comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and Uerdingen isoglosses in central and southern Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, and Luxembourg, as well as in neighboring portions of France, Italy, the Czech Republic (Bohemia), and Poland. They are also spoken in diaspora in Romania, Russia, the United States, Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Chile, and Namibia.

Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a small landlocked country in western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital, Luxembourg City, together with Brussels and Strasbourg, is one of the three official capitals of the European Union and the seat of the European Court of Justice, the highest judicial authority in the EU. Its culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its neighbours, making it essentially a mixture of French and German cultures, as evident by the nation's three official languages: French, German, and the national language, Luxembourgish. The repeated invasions by Germany, especially in World War II, resulted in the country's strong will for mediation between France and Germany and, among other things, led to the foundation of the European Union.

The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a peace treaty signed on March 3, 1918 between the new Bolshevik government of Russia and the Central Powers, that ended Russia's participation in World War I. The treaty was signed at German-controlled Brest-Litovsk, after two months of negotiations. The treaty was agreed upon by the Russians to stop further invasion. According to the treaty, Soviet Russia defaulted on all of Imperial Russia's commitments to the Allies and eleven nations became independent in Eastern Europe and western Asia.

World War II, also known as the Second World War, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The vast majority of the world's countries—including all the great powers—eventually formed two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. A state of total war emerged, directly involving more than 100 million people from over 30 countries. The major participants threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. World War II was the deadliest conflict in human history, marked by 50 to 85 million fatalities, most of whom were civilians in the Soviet Union and China. It included massacres, the genocide of the Holocaust, strategic bombing, premeditated death from starvation and disease, and the only use of nuclear weapons in war.

Eastern Europe is the eastern part of the European continent. There is no consensus on the precise area it covers, partly because the term has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, cultural, and socioeconomic connotations. There are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region". A related United Nations paper adds that "every assessment of spatial identities is essentially a social and cultural construct".

The Socialist Unity Party of Germany, established in April 1946, was the governing Marxist–Leninist political party of the German Democratic Republic from the country's foundation in October 1949 until its dissolution after the Peaceful Revolution in 1989.

A federation is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governing status of the component states, as well as the division of power between them and the central government, is typically constitutionally entrenched and may not be altered by a unilateral decision of either party, the states or the federal political body. Alternatively, federation is a form of government in which sovereign power is formally divided between a central authority and a number of constituent regions so that each region retains some degree of control over its internal affairs. It is often argued that federal states where the central government has the constitutional authority to suspend a constituent state's government by invoking gross mismanagement or civil unrest, or to adopt national legislation that overrides or infringe on the constituent states' powers by invoking the central government's constitutional authority to ensure "peace and good government" or to implement obligations contracted under an international treaty, are not truly federal states.

The Deutsche Bundesbank is the central bank of the Federal Republic of Germany and as such part of the European System of Central Banks (ESCB). Due to its strength and former size, the Bundesbank is the most influential member of the ESCB. Both the Bundesbank and the European Central Bank (ECB) are located in Frankfurt, Germany. It is sometimes referred to as "Buba" for Bundesbank, while its official abbreviation is BBk.

Prussia was a historically prominent German state that originated in 1525 with a duchy centred on the region of Prussia on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It was de facto dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and de jure by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organised and effective army. Prussia, with its capital in Königsberg and from 1701 in Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany.
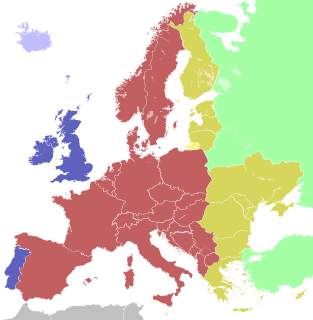
Central European Time (CET), used in most parts of Europe and a few North African countries, is a standard time which is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time offset from UTC can be written as UTC+01:00. The same standard time, UTC+01:00, is also known as Middle European Time and under other names like Berlin Time, Warsaw Time and Romance Standard Time (RST), Paris Time or Rome Time.

World War I, also known as the First World War or the Great War, was a global war originating in Europe that lasted from 28 July 1914 to 11 November 1918. Contemporaneously described as "the war to end all wars", it led to the mobilisation of more than 70 million military personnel, including 60 million Europeans, making it one of the largest wars in history. It is also one of the deadliest conflicts in history, with an estimated nine million combatants and seven million civilian deaths as a direct result of the war, while resulting genocides and the 1918 influenza pandemic caused another 50 to 100 million deaths worldwide.

Viacom International Media Networks (VIMN) is the international division of Viacom. The company oversees the production, broadcasting and promotion of key Viacom brands outside of the United States. These brands include MTV, VH1, Nickelodeon, Comedy Central, BET, VIVA, Colors and Game One.

Austria, officially the Republic of Austria, is a country of nearly 9 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Hungary and Slovakia to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The territory of Austria covers 83,879 km2 (32,386 sq mi). The terrain is highly mountainous, lying within the Alps; only 32% of the country is below 500 m (1,640 ft), and its highest point is 3,798 m (12,461 ft). The majority of the population speaks local Bavarian dialects as their native language, and German in its standard form is the country's official language. Other local official languages are Hungarian, Burgenland Croatian, and Slovene.