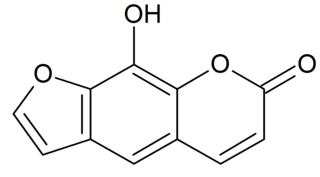This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Hypermethioninemia is an excess of the amino acid methionine, in the blood. This condition can occur when methionine is not broken down properly in the body.
In enzymology, a 12-hydroxydihydrochelirubine 12-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-hydroxyanthranilate 4-C-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an amine N-methyltransferase is an enzyme that is ubiquitously present in non-neural tissues and that catalyzes the N-methylation of tryptamine and structurally related compounds.
In enzymology, a cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a hexaprenyldihydroxybenzoate methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nicotinate N-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phenol O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a putrescine N-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-coclaurine-N-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a xanthotoxol O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [methionine synthase] reductase (EC 1.16.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a S-adenosylhomocysteine deaminase (EC 3.5.4.28) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
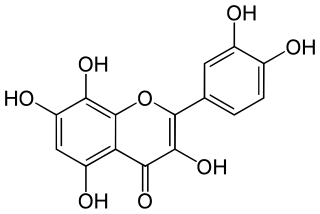
Gossypetin, also known as 3,5,7,8,3',4'-hexahydroxyflavone, is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It has been isolated from the flowers and the calyx of Hibiscus sabdariffa (roselle) and exhibits a strong antibacterial activity. The compound has also been found to act as an antagonist of TrkB. Recently it was shown that gossypetin has radioprotective activity.

Isorhamnetin is an O-methylated flavon-ol from the class of flavonoids. A common food source of this 3'-methoxylated derivative of quercetin and its glucoside conjugates are pungent yellow or red onions, in which it is a minor pigment, quercetin-3,4'-diglucoside and quercetin-4'-glucoside and the aglycone quercetin being the major pigments. Another source is the spice, herbal medicinal and psychoactive Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida), which is described as accumulating isorhamnetin and its 7-O-glucoside derivate.

Ayanin is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is the 3,7,4'-tri-O-methylated derivative of quercetin.
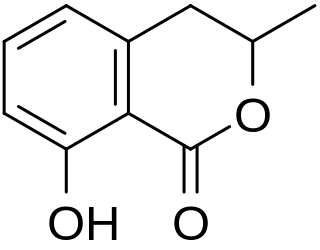
Mellein is a dihydroisocoumarin, a phenolic compound produced by the mold species Aspergillus ochraceus.
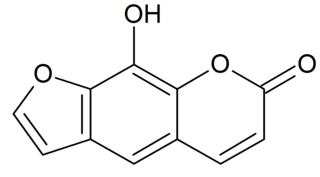
Xanthotoxol is a furanocoumarin. It is one of the major active ingredients in Cnidium monnieri.