
Dehydroalanine is a dehydroamino acid. It does not exist in its free form, but it occurs naturally as a residue found in peptides of microbial origin. As an amino acid residue, it is unusual because it has an unsaturated backbone.
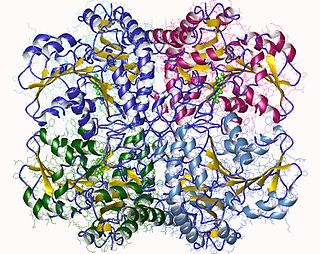
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate (α-ketobutyrate), and ammonia:

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.

In enzymology, an alliin lyase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 3-chloro-D-alanine dehydrochlorinase (EC 4.5.1.2) catalyzes the reaction

Cystathionine beta-lyase, also commonly referred to as CBL or β-cystathionase, is an enzyme that primarily catalyzes the following α,β-elimination reaction
The enzyme cysteine-S-conjugate β-lyase (EC 4.4.1.13) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme D-cysteine desulfhydrase (EC 4.4.1.15) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme D-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.18), with systematic name D-serine ammonia-lyase (pyruvate-forming), catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme L-cysteate sulfo-lyase (EC 4.4.1.25) catalyzes the reaction
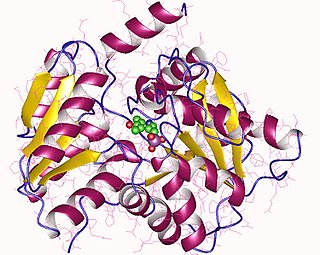
The enzyme L-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme methionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.11, MGL) is in the γ-family of PLP-dependent enzymes. It degrades sulfur-containing amino acids to α-keto acids, ammonia, and thiols:

The enzyme ornithine cyclodeaminase catalyzes the chemical reaction
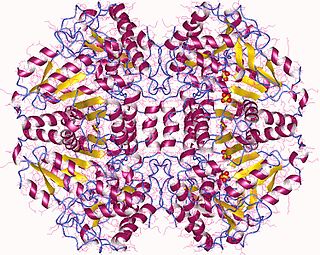
The enzyme tryptophanase (EC 4.1.99.1) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme tyrosine phenol-lyase (EC 4.1.99.2) catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a cystathionine gamma-synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cystathionine from cysteine and an activated derivative of homoserine, e.g.:
In enzymology, a cysteine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an O-acetylhomoserine aminocarboxypropyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
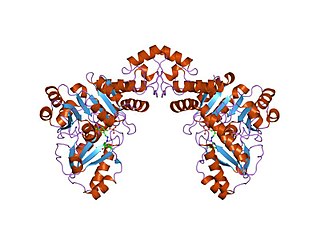
In molecular biology, the Cys/Met metabolism PLP-dependent enzyme family is a family of proteins including enzymes involved in cysteine and methionine metabolism which use PLP (pyridoxal-5'-phosphate) as a cofactor.
S-alkyl-L-cysteine sulfoxide lyase may refer to:











