
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships came into practical usage during the early 1800s; however, there were exceptions that came before. Steamships usually use the prefix designations of "PS" for paddle steamer or "SS" for screw steamer. As paddle steamers became less common, "SS" is assumed by many to stand for "steam ship". Ships powered by internal combustion engines use a prefix such as "MV" for motor vessel, so it is not correct to use "SS" for most modern vessels.

The Victory ship was a class of cargo ship produced in large numbers by North American shipyards during World War II to replace losses caused by German submarines. They were a more modern design compared to the earlier Liberty ship, were slightly larger and had more powerful steam turbine engines giving higher speed to allow participation in high speed convoys and make them more difficult targets for German U-boats. A total of 531 Victory ships were built.

SS Deutschland was a 21,046 gross registered ton (GRT) German HAPAG ocean liner which was sunk in a British air attack on May 3, 1945 when it was in the process of being converted as a hospital ship. All people on-board the Deutschland survived the attack, though two accompanying vessels sank with great loss of life.

SS American Victory is a Victory ship which saw brief service in the Pacific Theater of Operations during the waning months of World War II, Korean War from 1951-1954, and Vietnam War from 1967-1969. Built in June 1945, she carried ammunition and other cargo from U.S. West Coast ports to Southeast Asia, then ferried cargo, equipment and troops back to the U.S. after the war ended. She survived two typhoons, and one hurricane. She sailed around the world twice.
A ship's hold or cargo hold is a space for carrying cargo.

USS Kenton (APA-122) was a Haskell-class attack transport of the US Navy. She was built and used during World War II. She was of the VC2-S-AP5 Victory ship design type. She was named for Kenton County, Kentucky.

SS Clan Alpine was a British cargo steamer owned by Clan Line Steamers Ltd. Launched in 1918 she was the third ship to carry this name. She was torpedoed and sunk in the Second World War whilst carrying materiel to aid the British campaigns in Africa.
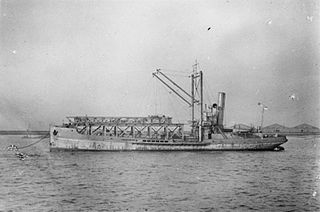
HMS Slinger was an experimental catapult ship operated by the Royal Navy during the First World War. After Royal Navy service from 1917 to 1919, she operated as a commercial cargo ship under the names SS Niki and SS Lingfield from 1920 until she sank in 1941.

Short Brothers Limited was a British shipbuilding company formed in 1850 and based at Pallion, Sunderland since 1869. The company closed in 1964 when it failed to invest to build bigger ships.
USS West Gambo (ID-3220) was a steel-hulled, single-screw cargo ship that served in the United States Navy from 1918 to 1919. She later saw commercial service as SS West Gambo and SS Empire Hartebeeste, and under the latter name was sunk during World War II.

SS Corinthic was a British passenger ship, built in 1902 by Harland & Wolff and launched for the British shipping companies White Star Line and Shaw, Savill & Albion Line. She was the second of the Athenic-class ocean liners built for passenger and cargo service between Britain and New Zealand. Her sister ships were SS Athenic (1902) and SS Ionic (1903). In 1931 Corinthic was decommissioned and scrapped.
A number of ships were named Uganda, including -

SS Gallic was a cargo steamship built in 1918. During her career, she had six different owners and sailed under the flags of the United Kingdom, Panama and Indonesia. In spite of prevailing maritime superstition that it is unlucky to change a ship's name, she underwent seven name changes and survived a 37-year career unscathed. She was scrapped at Hong Kong in 1956, the last surviving White Star Line cargo ship.

The SS Georgic was a steam ship built by Harland and Wolff for the White Star Line to replace the SS Naronic which was lost at sea. Georgic was a cargo ship designed principally to carry livestock, at the time of entering service in 1895 she was the largest cargo ship in the world with a deadweight tonnage of 12,000 tons.

SS Cape Gibson (AK-5051) is a Cape G Class Break bulk cargo ship of the United States Maritime Administration, last used as a training ship at Texas A&M University at Galveston. Currently she later mothballed in the Beaumont Reserve Fleet.

SS Russian was a British Cargo ship, of the Victorian class of 1895, that was torpedoed and sunk by UB-43 210 miles East of Malta in the Mediterranean Sea, while she was travelling from Salonica, Greece, to Newport, United Kingdom, in ballast. The ship was 156.2 metres long, with a beam of 18.1 metres. The ship was assessed at 8,825 GRT. She had a 1 x 3 cyl. triple expansion engine, single shaft driving a single screw propeller.

The SS Clarksdale Victory was the 80th Victory ship built during World War II. She was launched by the California Shipbuilding Company on January 27, 1945, and completed on February 26, 1945. The ship’s United States Maritime Commission designation was VC2-S-AP3, hull number 80. She was built in just 86 days under the Emergency Shipbuilding program. SS Clarksdale Victory served in the Pacific Ocean during WW2. SS Clarksdale Victory was 80th of the new 10,500-ton class ship known as Victory ships. Victory ships were designed to replace the earlier Liberty Ships. Liberty ships were designed to be used just for WW2. Victory ships were designed to last longer and serve the US Navy after the war. The Victory ship differed from a Liberty ship in that they were: faster, longer and wider, taller, a thinner stack set farther toward the superstructure and had a long raised forecastle.
The following index is provided as an overview of and topical guide to recreational dive sites:












