
The New York Shipbuilding Corporation was an American shipbuilding company that operated from 1899 to 1968, ultimately completing more than 500 vessels for the U.S. Navy, the United States Merchant Marine, the United States Coast Guard, and other maritime concerns. At its peak during World War II, NYSB was the largest and most productive shipyard in the world. Its best-known vessels include the destroyer USS Reuben James (DD-245), the cruiser USS Indianapolis (CA-35), the aircraft carrier USS Kitty Hawk (CV-63), the nuclear-powered cargo ship NS Savannah, and a quartet of cargo-passenger liners nicknamed the Four Aces.
New York most commonly refers to:

The Plunger class was an early class of United States Navy submarines, used primarily as training and experimental vessels for the newly formed "silent service" to familiarize naval personnel with the performance and operations of such craft. They were known as the "A-class" after being renamed to A-type designations on 17 November 1911. All except Plunger ended up being stationed in the Philippines, an American possession, prior to the outbreak of World War I. They were shipped there on colliers. In some instances, this class of submarines is referred to as the Adder-class submarine, as USS Adder was the first boat of the class to be completed.
USS Moray (SS-300), a Balao-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy named for the moray, a family of large eels found in crevices of coral reefs in tropical and subtropical oceans.

USS Becuna (SS/AGSS-319), a Balao-class submarine, is a former ship of the United States Navy named for the becuna, a pike-like fish of Europe. She was designated a National Historic Landmark for her service in World War II, for which she earned four battle stars. She presently serves as a museum ship at the Independence Seaport Museum in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
American Export-Isbrandtsen Lines, New York, was the leading US-flag shipping company between the U.S. east coast and the Mediterranean from 1919 to 1977, offering both cargo ship services and passenger ship services, until it declared bankruptcy and was acquired by Farrell Lines, New York.

The B-class submarines were three United States Navy submarines built by the Fore River Shipbuilding Company in Quincy, Massachusetts, under a subcontract from the Electric Boat Company. They were eventually stationed in the Philippines, an American possession, beginning in 1912–15. They were shipped there on colliers. All three were stricken and expended as targets 1919–22.

The C-class submarines were five United States Navy submarines built by the Fore River Shipbuilding Company in Quincy, Massachusetts, under a subcontract from the Electric Boat Company. Built between 1906 and 1909, and in commission from 1908 to 1919, all five were subsequently sold for scrap in 1920. They were considerably larger than the preceding B class at 275 tons submerged vs. 173 tons submerged, and were the first United States submarines with two-shaft propulsion, doubling the machinery of the B class.

SS Traffic was a tender of the White Star Line, and the fleetmate to the SS Nomadic. She was built for the White Star Line by Harland and Wolff, at Belfast, to serve the Olympic-class ocean liners. SS Traffic ferried some of the third class passengers to RMS Titanic for her maiden voyage. She served as a tender for White Star, as a minesweeper for the French Navy between 1917 and 1919, and supported troop ships at the end of the First World War. After the war she was sold to Société Cherbourgeoise Transbordement, and later renamed Ingénieur Reibell. She was scuttled by the French as the Germans invaded in 1940, but was salvaged and used by the Germans as an armed coastal vessel until being scrapped in 1941.

SS Prinz Friedrich Wilhelm was an ocean liner for North German Lloyd (NDL) from her launch in 1907 until the end of World War I. After the war, she briefly served as USS Prinz Friedrich Wilhelm (ID-4063) for the United States Navy returning American troops from France. The vessel was first chartered—and later purchased outright—by Canadian Pacific Steamships (CP) and operated under the names Empress of China, Empress of India, Montlaurier, Monteith, and Montnairn. She was scrapped in 1929.

SS Zeeland was a British and Belgian ocean liner of the International Mercantile Marine Co. (IMM). She was a sister ship to Vaderland and a near sister ship to Kroonland and Finland of the same company. Although her name was Dutch, it was changed during World War I to the less German-sounding SS Northland. She served for a time as a British troop ship under the name HMT Northland. Reverting to Zeeland after the war, the ship was renamed SS Minnesota late in her career. Zeeland sailed primarily for IMM's Red Star Line for most of her early career, but also sailed under charter for the White Star Line, the International Navigation Company, the American Line, and the Atlantic Transport Line, all IMM subsidiary lines.

USS Shoshone (ID-1760) was a transport that served in the United States Navy in 1919. Shoshone (ID-1760), the first United States Navy ship of the name, was built in 1911 by Bremer Vulkan at Vegesack, Germany, and operated as a passenger-cargo ship by the Hamburg-America Line as SS Wasgenwald. Wasgenwald was chartered for World War I service by the United States Army on 26 October 1917 from the Custom House, New York, and used as a depot collier with the name SS Shoshone.

Panama Pacific Line was a subsidiary of International Mercantile Marine (IMM) established to carry passengers and freight between the US East and West Coasts via the Panama Canal.

USS Carrillo (ID-1406) was a United States Navy cargo ship in commission from 1918 to 1919.

USS General G. W. Goethals (ID-1443) was a United States Navy cargo ship and troop transport in commission in 1919.

USS Mexican (ID-1655) was a United States Navy cargo ship and animal transport in commission from 1917 to 1919. She operated as the commercial steamship SS Mexican from 107 to 1917 and from 1919 to 1948.
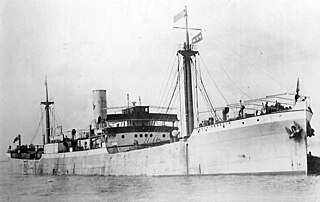
USS Santa Rosalia (ID-1503) was a United States Navy cargo ship in commission from 1918 to 1919.

The wooden-hulled excursion steamer Westport was built in 1911 by William McKie of East Boston, MA., and owned by the Eastern Steamship Lines, Inc., of Boston India Wharf at the start of World War I. The Navy inspected the ship in the 1st Naval District on 1 February 1918 for possible use as a passenger and freight carrier, and she was taken over on 14 November 1918. Five days later, her name was changed to Adrian-to avoid confusion with the Naval Overseas Transportation Service (NOTS) freighter Westport - and, given the classification Id. No. 2362, was initially assigned to the 1st Naval District.

SS Erinpura was a passenger liner built for the British-India Steam Navigation Company in 1911. She was the first British India ship built for Eastern service to be fitted with radio. She was sunk in the Mediterranean during World War II.

SS Princess Mary was a passenger vessel in the coastal service fleet of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) during the first half of the 20th century.















