
The San Luis Valley is a region in south-central Colorado with a small portion overlapping into New Mexico. It is the headwaters of the Rio Grande. It contains 6 counties and portions of 3 others. The valley was ceded to the United States by Mexico following the Mexican–American War. Hispanic settlers began moving north and settling in the valley after the United States made a treaty with the Utes and established a fort. Prior to the Mexican war the Spanish and Mexican governments had reserved the valley to the Utes, their allies. During the 19th century Anglo settlers settled in the valley and engaged in mining, ranching, and irrigated agriculture. Today the valley has a diverse Anglo and Hispanic population.

The Entrada Sandstone is a formation in the San Rafael Group that is found in the U.S. states of Wyoming, Colorado, northwest New Mexico, northeast Arizona and southeast Utah. Part of the Colorado Plateau, this formation was deposited during the Jurassic period sometime between 180 and 140 million years ago in various environments, including tidal mudflats, beaches and sand dunes. The Middle Jurassic San Rafael Group was dominantly deposited as ergs in a desert environment around the shallow Sundance Sea.

Kritosaurus is an incompletely known genus of hadrosaurid (duck-billed) dinosaur. It lived about 74.5-66 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous of North America. The name means "separated lizard", but is often mistranslated as "noble lizard" in reference to the presumed "Roman nose".

The Cutler Formation or Cutler Group is a rock unit that is spread across the U.S. states of Arizona, northwest New Mexico, southeast Utah and southwest Colorado. It was laid down in the Early Permian during the Wolfcampian stage. Its subunits, therefore, are variously called formations or members depending on the publication.
Members :

The Chinle Formation is an Upper Triassic continental geologic formation of fluvial, lacustrine, and palustrine to eolian deposits spread across the U.S. states of Nevada, Utah, northern Arizona, western New Mexico, and western Colorado. The Chinle is controversially considered to be synonymous to the Dockum Group of eastern Colorado and New Mexico, western Texas, the Oklahoma panhandle, and southwestern Kansas. The Chinle is sometimes colloquially named as a formation within the Dockum Group in New Mexico and in Texas. The Chinle Formation is part of the Colorado Plateau, Basin and Range, and the southern section of the Interior Plains.

A structural basin is a large-scale structural formation of rock strata formed by tectonic warping of previously flat-lying strata. Structural basins are geological depressions, and are the inverse of domes. Some elongated structural basins are also known as synclines. Structural basins may also be sedimentary basins, which are aggregations of sediment that filled up a depression or accumulated in an area; however, many structural basins were formed by tectonic events long after the sedimentary layers were deposited.
The Fruitland Formation is a sedimentary geological formation containing layers of sandstone, shale, and coal. It was laid down in marshy delta conditions, with poor drainage and frequent flooding, under a warm, humid and seasonal climate. It is found in the San Juan Basin in the states of New Mexico and Colorado, in the United States of America. The Fruitland Formation contains beds of bituminous coal that are mined in places along the outcrop. Since the 1980s, the coal beds of the Fruitland Formation have yielded large quantities of coalbed methane. The productive area for coalbed methane straddles the Colorado-New Mexico state line, and is one of the most productive areas for coalbed methane in the United States.
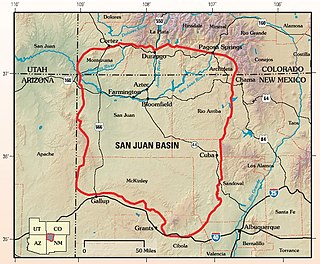
The San Juan Basin is a geologic structural basin located near the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. The basin covers 7,500 square miles and resides in northwestern New Mexico, southwestern Colorado, and parts of Utah and Arizona. Specifically, the basin occupies space in the San Juan, Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and McKinley counties in New Mexico, and La Plata and Archuleta counties in Colorado. The basin extends roughly 100 miles N-S and 90 miles E-W.

The Nacimiento Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in the San Juan Basin of western New Mexico and named for the Nacimiento Mountains. It is a heterogeneous nonmarine formation composed of shale, siltstone, and sandstone, deposited in floodplain, fluvial and lacustrine settings, and made up of sediment shed from the San Juan uplift to the north and the Brazos-Sangre de Cristo uplift to the east. It was deposited mostly between ~64.5 and ~61 million years ago, during the early and middle Paleocene. The climate was humid and warm to hot. This unit interbeds with the underlying Ojo Alamo Formation but is separated by an unconformity from the overlying San Jose Formation.
Navajosuchus is an extinct genus of alligatorine crocodylian. Its fossils have been found in the Paleocene-age Nacimiento Formation of the San Juan Basin, New Mexico. It was named in 1942 by Charles C. Mook, and the original type species was N. novomexicanus. N. novomexicanus was based on AMNH 5186, a partial skull collected in 1913. Later research showed that Navajosuchus novomexicanus was the same as the earlier-named Allognathosuchus mooki. However, A. mooki may or may not belong to the genus Allognathosuchus, and if it does not, the name of the crocodilian would become Navajosuchus mooki. Under whichever name is used, this animal would have been a generalized predator of the Nacimiento floodplains. It was the most common Nacimiento Formation crocodilian, found in both the Puercan and Torrejonian faunal assemblages.

Brachychampsa is an extinct genus of alligatoroid. Specimens have been found from New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, North and South Dakota, New Jersey, and Saskatchewan. One specimen has been found from the Darbasa Formation of Kazakhstan, although the species status is indeterminant for the fossil. The genus first appeared during the late Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous and became extinct during the early Danian stage of the Paleocene, a few million years after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Brachychampsa is distinguished by an enlarged fourth maxillary tooth in the upper jaw.
Denazinosuchus is a genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Its fossils have been recovered from the Upper Cretaceous Fruitland Formation and Kirtland Formation of the San Juan Basin, New Mexico. It is the most abundant and readily identifiable mesoeucrocodylian of the San Juan Basin, mostly due to its distinctive subrectangular, flattened, and sparsely pitted bony armor. It was first described in 1932 by Carl Wiman on the basis of a skull as a species of Goniopholis, G. kirtlandicus. Spencer G. Lucas and Robert M. Sullivan redescribed the species in 2003 and gave it its own genus, Denazinosuchus. To date, Denazinosuchus is only known from skull material, armor, and a thigh bone.

The Sierra de las Quijadas National Park is a national park located in the northwestern part of the Argentine province of San Luis. It was established on December 10, 1991, to protect the natural features, representative of the Semiarid Chaco and the Argentine Low Monte ecoregions.

The Point Lookout Sandstone is a Cretaceous bedrock formation occurring in New Mexico and Colorado.

The Ojo Alamo Formation is a geologic formation spanning the Mesozoic/Cenozoic boundary. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, though all dinosaur remains come from the lowest part of the formation, the Naashoibito member (sometimes considered part of the Kirtland Formation, which dates to the late Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous period.

The La Cruz Formation is an Aptian geologic formation in Argentina. Pterosaur fossils of Pterodaustro guinazui have been recovered from the formation. The formation, the uppermost unit of the El Gigante Group, overlies the El Toscal Formation, and is overlain by the Lagarcito Formation. The unit comprises sandstones and conglomerates, deposited in an alluvial plain to fluvial environment.
The Burro Canyon Formation is an Early Cretaceous Period sedimentary geologic formation, found in western Colorado, the Chama Basin and eastern San Juan Basin of northern New Mexico, and in eastern Utah.

Choiyoi Group is a Permian and Triassic-aged group of volcano-sedimentary formations in Argentina and Chile. The group bears evidence of bimodal-style volcanism related to an ancient subduction zone that existed along the western margin of the supercontinent Gondwana.
Colorado Formation may refer to:













