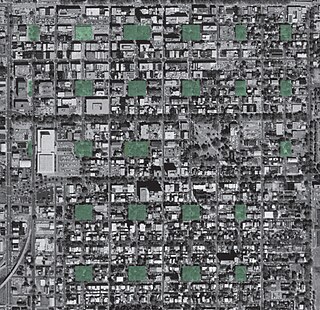
The city of Savannah, Province of Georgia, was laid out in 1733, in what was colonial America, around four open squares, each surrounded by four residential ("tything") blocks and four civic ("trust") blocks. The layout of a square and eight surrounding blocks was known as a "ward." The original plan was part of a larger regional plan that included gardens, farms, and "out-lying villages." Once the four wards were developed in the mid-1730s, two additional wards were laid. Oglethorpe's agrarian balance was abandoned after the Georgia Trustee period. Additional squares were added during the late 18th and 19th centuries, and by 1851 there were 24 squares in the city. In the 20th century, three of the squares were demolished or altered beyond recognition, leaving 21. In 2010, one of the three "lost" squares, Ellis, was reclaimed, bringing the total to today's 22.

The Oglethorpe Plan is an urban planning idea that was most notably used in Savannah, Georgia, one of the Thirteen Colonies, in the 18th century. The plan uses a distinctive street network with repeating squares of residential blocks, commercial blocks, and small green parks to create integrated, walkable neighborhoods.

Bull Street is a major street in Savannah, Georgia, United States. Named for Colonel William Bull (1683–1755), it runs from Bay Street in the north to Derenne Avenue in the south. It is around 3.40 miles in length, not including the section interrupted by Forsyth Park. It is the center of a National Historic Landmark District.

John Dorsett House is a historic building in Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located at 536 East State Street, in the northeastern tything of Greene Square, and was built in 1845 for New York City-born shipbuilder John W. Dorsett by Dix Fletcher. The city's smallest free-standing house, it was moved from 422 Hull Street, in Savannah's Crawford Ward, in the mid-20th century. The structure is part of Savannah's Historic District.

Greene Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is the easternmost square in the second row of the city's five rows of squares. The square is located on Houston Street and East President Street, and is south of Washington Square, east of Columbia Square and north of Crawford Square. The oldest buildings on the square are at 510 East York Street, 509 East President Street and 503 East President Street, each in the southwestern trust/civic block, which are believed to have been built at the same time as the square itself (1799).

Columbia Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the second row of the city's five rows of squares, on Habersham Street and East President Street. It is south of Warren Square and between Oglethorpe Square to the west and Greene Square to the east. The oldest building on the square is at 307 East President Street, today's 17 Hundred 90 Inn, which, as its name suggests, dates to the 18th century.

Franklin Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the northernmost row of the city's five rows of squares, at Montgomery Street and West St. Julian Street. It is west of Ellis Square in the northwestern corner of the city's grid of squares. The square now anchors the western end of the City Market retail area.

Johnson Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. Located in the northernmost row of the city's five rows of squares, it was the first of the squares to be laid out, in 1733, and remains the largest of the 22. It is east of Ellis Square, west of Reynolds Square and north of Wright Square. Situated on Bull Street and St. Julian Street, it is named for Robert Johnson, colonial governor of South Carolina and a friend of General James Oglethorpe. The oldest building on the square is the Ann Hamilton House, at 26 East Bryan Street, which dates to 1824.

Reynolds Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the northernmost row of the city's five rows of squares, on Abercorn Street and East St. Julian Street. It is east of Johnson Square, west of Warren Square and north of Oglethorpe Square. The oldest building on the square is The Olde Pink House, which dates to 1771.

Telfair Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the second row of the city's five rows of squares, on Barnard Street and West President Street, and was laid out in 1733 as one of the first four squares. It is south of Ellis Square, west of Wright Square and north of Orleans Square. Liberty Square formerly stood to its west but was later paved over. The oldest building on the square is Telfair Academy, at 121 Barnard Street, which dates to 1818–1820.

Wright Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the second row of the city's five rows of squares, on Bull Street and President Street, and was laid out in 1733 as one of the first four squares. It is south of Johnson Square, west of Oglethorpe Square, north of Chippewa Square and east of Telfair Square. The oldest building on the square is the William Waring Property, at 12 West State Street, which dates to 1825.

Oglethorpe Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the second row of the city's five rows of squares, on Abercorn Street and East President Street, and was laid out in 1742. It is south of Reynolds Square, west of Columbia Square, north of Colonial Park Cemetery and east of Wright Square. The oldest building on the square is the Owens–Thomas House, at 124 Abercorn Street, which dates 1819.

Orleans Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the middle row of the city's five rows of squares, on Barnard Street and West McDonough Street, and was laid out in 1815, shortly after the event it commemorates: General Andrew Jackson's victory at the Battle of New Orleans that January. It is south of Telfair Square, west of Chippewa Square and north of Pulaski Square. The oldest building on the square is the John Ash House, at 114–116 West Hull Street, which dates to 1817.

Chippewa Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the middle row of the city's five rows of squares, on Bull Street and McDonough Street, and was laid out in 1815. It is south of Wright Square, west of Colonial Park Cemetery, north of Madison Square and east of Orleans Square. The oldest building on the square is The Savannah Theatre, at 222 Bull Street, which dates to 1818.

Crawford Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the middle row of the city's five rows of squares, on Houston Street and East McDonough Street, and was laid out in 1841. It is south of Greene Square and east of Colonial Park Cemetery on the eastern edge of the Savannah Historic District. The oldest building on the square is at 224 Houston Street, which dates to 1850.

Pulaski Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the fourth row of the city's five rows of squares, on Barnard Street and West Macon Street, and was laid out in 1837. It is south of Orleans Square, west of Madison Square and north of Chatham Square. It is known for its live oaks. The oldest buildings on the square are the Theodosius Bartow House and the Bernard Constantine House, which date to 1839.

Madison Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the fourth row of the city's five rows of squares, on Bull Street and Macon Street, and was laid out in 1837. It is south of Chippewa Square, west of Lafayette Square, north of Monterey Square and east of Pulaski Square. The square is named for James Madison, fourth president of the United States. The oldest building on the square is the Sorrel–Weed House, at 6 West Harris Street, which dates to 1840.

Lafayette Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the fourth row of the city's five rows of squares, on Abercorn Street and East Macon Street, and was laid out in 1837. It is south of Colonial Park Cemetery, west of Troup Square, north of Calhoun Square and east of Madison Square. The square is named for Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de Lafayette, the French hero of the American Revolution who visited Savannah in 1825. The oldest building on the square is the Andrew Low Carriage House, at 329 Abercorn Street, which dates to 1849.

Troup Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the fourth row of the city's five rows of squares, on Habersham Street and East Macon Street, and was laid out in 1837. It is south of Colonial Park Cemetery, east of Lafayette Square and north of Whitefield Square. The square is named for George Troup, the former Georgia governor, Congressman and senator. It is one of only two Savannah squares named for a person living at the time.

Whitefield Square is one of the 22 squares of Savannah, Georgia, United States. It is located in the southernmost row of the city's five rows of squares, on Habersham Street and East Wayne Street, and was the final square laid out, in 1851. It is south of Troup Square and east of Calhoun Square in the southeastern corner of Savannah's grid of squares. The oldest building on the square is at 412–414 East Taylor Street, which dates to 1855.






















