
Beowulf is an Old English epic poem consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is arguably one of the most important works of Old English literature. The date of composition is a matter of contention among scholars; the only certain dating pertains to the manuscript, which was produced between 975 and 1025. The author was an anonymous Anglo-Saxon poet, referred to by scholars as the "Beowulf poet".
A spark plug is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air mixture by an electric spark, while containing combustion pressure within the engine. A spark plug has a metal threaded shell, electrically isolated from a central electrode by a porcelain insulator. The central electrode, which may contain a resistor, is connected by a heavily insulated wire to the output terminal of an ignition coil or magneto. The spark plug's metal shell is screwed into the engine's cylinder head and thus electrically grounded. The central electrode protrudes through the porcelain insulator into the combustion chamber, forming one or more spark gaps between the inner end of the central electrode and usually one or more protuberances or structures attached to the inner end of the threaded shell and designated the side, earth, or ground electrode(s).

An electrical connector is an electro-mechanical device used to join electrical terminations and create an electrical circuit. Electrical connectors consist of plugs (male-ended) and jacks (female-ended). The connection may be temporary, as for portable equipment, require a tool for assembly and removal, or serve as a permanent electrical joint between two wires or devices. An adapter can be used to effectively bring together dissimilar connectors.

An RCA connector, sometimes called a phono connector or Cinch connector, is a type of electrical connector commonly used to carry audio and video signals. The name RCA derives from the Radio Corporation of America, which introduced the design by the early 1940s for internal connection of the pickup to the chassis in home radio-phonograph consoles. It was originally a low-cost, simple design, intended only for mating and disconnection when servicing the console. Refinement came with later designs, although they remained compatible.
Hot swapping is replacing or adding components without stopping or shutting down the system. With the appropriate software installed on the computer, a user can plug and unplug such components without rebooting. Specifically, hot swapping describes inserting and/or removing components without interruption to the system. A well-known example of this hot swap functionality is the Universal Serial Bus (USB) that allows users to add or remove peripheral components such as a mouse, keyboard, printer, or portable hard drive; depending upon the supplier such devices are characterized as hot-swappable or hot-pluggable.

Anglo-Saxon architecture was a period in the history of architecture in England, and parts of Wales, from the mid-5th century until the Norman Conquest of 1066. Anglo-Saxon secular buildings in Britain were generally simple, constructed mainly using timber with thatch for roofing. No universally accepted example survives above ground.

A banana connector is a single-wire electrical connector used for joining wires to equipment. The term 4 mm connector is also used, especially in Europe, although not all banana connectors will mate with 4 mm parts, and 2 mm banana connectors exist. Various styles of banana plug contacts exist, all based on the concept of spring metal applying outward force into the unsprung cylindrical jack to produce a snug fit with good electrical conductivity. Common types include: a solid pin split lengthwise and splayed slightly, a tip of four leaf springs, a cylinder with a single leaf spring on one side, a bundle of stiff wire, a central pin surrounded by a multiply-slit cylinder with a central bulge, or simple sheet spring metal rolled into a nearly complete cylinder. The plugs are frequently used to terminate patch cords for electronic test equipment, while sheathed banana plugs are common on multimeter probe leads.

A bung, stopper or cork is a truncated cylindrical or conical closure to seal a container, such as a bottle, tube or barrel. Unlike a lid, which encloses a container from the outside without displacing the inner volume, a bung is partially inserted inside the container to act as a seal.

An extension cord, power extender, drop cord, or extension lead is a length of flexible electrical power cable (flex) with a plug on one end and one or more sockets on the other end. The term usually refers to mains extensions but is also used to refer to extensions for other types of cabling. If the plug and power outlet are of different types, the term "adapter cord" may be used. Most extension cords range from around two to thirty feet in length although they are made up to 300 feet in length.

A patch cable, patch cord or patch lead is an electrical or optical cable used to connect one electronic or optical device to another for signal routing. Devices of different types are connected with patch cords. Patch cords are usually produced in many different colors so as to be easily distinguishable, and are relatively short, perhaps no longer than two metres. Types of patch cords include microphone cables, headphone extension cables, XLR connector, Tiny Telephone (TT) connector, RCA connector and ¼" TRS phone connector cables, and thicker, hose-like cords used to carry video or amplified signals. However, patch cords typically refer only to short cords used with patch panels.

A silo is a structure for storing bulk materials. Silos are used in agriculture to store grain or fermented feed known as silage. Silos are more commonly used for bulk storage of grain, coal, cement, carbon black, woodchips, food products and sawdust. Three types of silos are in widespread use today: tower silos, bunker silos, and bag silos.

Rock fishing is fishing from rocky outcrops into the sea. It is a popular pastime in Australia and New Zealand. It can be a dangerous pastime and claims many lives each year, although this may improve as more fishermen are beginning to wear life jackets.
A stopcock is a form of valve used to control the flow of a liquid or gas. The term is not precise and is applied to many different types of valve. The only consistent attribute is that the valve is designed to completely stop the flow when closed fully.

A flat tire is a deflated pneumatic tire, which can cause the rim of the wheel to ride on the tire tread or the ground potentially resulting in loss of control of the vehicle or irreparable damage to the tire. The most common cause of a flat tire is puncturing of the tire by a sharp object, such as a nail, letting air escape. Depending on the size of the puncture, the tire may deflate slowly or rapidly.
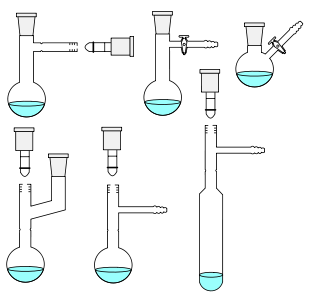
A Schlenk flask, or Schlenk tube is a reaction vessel typically used in air-sensitive chemistry, invented by Wilhelm Schlenk. It has a side arm fitted with a PTFE or ground glass stopcock, which allows the vessel to be evacuated or filled with gases. These flasks are often connected to Schlenk lines, which allow both operations to be done easily.
The Bomb, ground, 6 lb was a British World War II grenade containing about 2 pints of mustard gas. It was intended to be used to contaminate trenches, dug-outs, rooms, observation posts and small enclosures, and on cross-roads, narrow defiles, obstacles and debris of demolition.
Tube drawing is a process to size a tube by shrinking a large diameter tube into a smaller one, by drawing the tube through a die. This process produces high-quality tubing with precise dimensions, good surface finish, and the added strength of cold working. For this reason this process is established for many materials, mainly metalworking but also glass. Because it is so versatile, tube drawing is suitable for both large- and small-scale production. The large-scale production of glass typically uses a one step process where glass is directly drawn into a tube from a melting tank.

The Lava River Cave near Bend, Oregon, is part of the Newberry National Volcanic Monument, which is managed by the United States Forest Service. At 5,211 feet (1,588 m) in length, the northwest section of the cave is the longest continuous lava tube in Oregon. While the cave’s discovery in 1889 was officially credited to a pioneer hunter, the presence of obsidian flakes near the cave has led archaeologists to conclude that Native Americans knew about the cave long before settlers arrived in central Oregon.

The first reflecting telescope built by Sir Isaac Newton in 1668 is a landmark in the history of telescopes, being the first known successful reflecting telescope. It was the prototype for a design that later came to be called a newtonian telescope.

Waytemore Castle is a ruined castle in the town of Bishop's Stortford in Hertfordshire, United Kingdom.. The remains are a Grade I listed structure.