This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
Soda or SODA may refer to:
Middleware in the context of distributed applications is software that provides services beyond those provided by the operating system to enable the various components of a distributed system to communicate and manage data. Middleware supports and simplifies complex distributed applications. It includes web servers, application servers, messaging and similar tools that support application development and delivery. Middleware is especially integral to modern information technology based on XML, SOAP, Web services, and service-oriented architecture.
An application server is a software framework that provides both facilities to create web applications and a server environment to run them.

BEA Systems, Inc. was a company specialized in enterprise infrastructure software products which was wholly acquired by Oracle Corporation on April 29, 2008.
Founded in 1969, Software AG is an enterprise software company with over 10,000 enterprise customers in over 70 countries. The company is the second largest software vendor in Germany, and the seventh largest in Europe. Software AG is traded on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange under the symbol “SOW” and part of the technology index TecDAX.
Java Business Integration (JBI) is a specification developed under the Java Community Process (JCP) for an approach to implementing a service-oriented architecture (SOA). The JCP reference is JSR 208 for JBI 1.0 and JSR 312 for JBI 2.0. JSR 312 was removed from the JCP balloting process on 17 Dec, 2010 by the submitters without being accepted.
Mule is a lightweight enterprise service bus (ESB) and integration framework provided by MuleSoft. The platform is Java-based, but can broker interactions between other platforms such as .NET using web services or sockets.
Mobile app development is the act or process by which a mobile app is developed for mobile devices, such as personal digital assistants, enterprise digital assistants or mobile phones. These applications can be pre-installed on phones during manufacturing platforms, or delivered as web applications using server-side or client-side processing to provide an "application-like" experience within a Web browser. Application software developers also must consider a long array of screen sizes, hardware specifications, and configurations because of intense competition in mobile software and changes within each of the platforms. Mobile app development has been steadily growing, in revenues and jobs created. A 2013 analyst report estimates there are 529,000 direct app economy jobs within the EU 28 members, 60% of which are mobile app developers.
IONA Technologies was an Irish software company. It was founded in 1991.

WebSphere Integration Developer (WID) is an integrated development environment for building applications based on service-oriented architecture (SOA). It is the authoring tool for WebSphere Process Server and WebSphere ESB V6.0.
Service-oriented architectures (SOA) are based on the notion of software services, which are high-level software components that include web services. Implementation of an SOA requires tools as well as run-time infrastructure software. This is collectively referred to as a service-oriented architecture implementation framework or (SOAIF). The SOAIF envisions a comprehensive framework that provides all the technology that an enterprise might need to build and run an SOA. An SOAIF includes both design-time and run-time capabilities as well as all the software functionality an enterprise needs to build and operate an SOA, including service-oriented:

Apache Camel is an open source framework for message-oriented middleware with a rule-based routing and mediation engine that provides a Java object-based implementation of the Enterprise Integration Patterns using an application programming interface to configure routing and mediation rules. The domain-specific language means that Apache Camel can support type-safe smart completion of routing rules in an integrated development environment using regular Java code without large amounts of XML configuration files, though XML configuration inside Spring Framework is also supported.
Service-oriented communications (SOC) technologies are designed to be easily used in the context of service-oriented architectures. These technologies are generally software based and are built more like a business application than a traditional PBX business communications system. Service-oriented communications systems allow their services to participate in business processes. They make their services available to other business applications within and SOA and allow for reuse of the services.
The goal of service-oriented communications is to enable business environments to build communications into their business processes, enabling more streamlined collaboration among people within the business. It typically assumes that certain services are provided in the context of an SOA service provider. This is often in the form of a suite of web services, but may also be attached to other means of sharing the services such as an enterprise system bus (ESB).
Red Hat Fuse is an open source integration platform based on Apache Camel. It is a distributed integration platform that provides a standardized methodology, infrastructure, and tools to integrate services, microservices, and application components.
Fuse Services Framework is an open source SOAP and REST web services platform based on Apache CXF for use in enterprise IT organizations. It is productized and supported by the Fuse group at FuseSource Corp. Fuse Services Framework service-enables new and existing systems for use in enterprise SOA infrastructure.

Petals ESB is an open-source ESB developed by Linagora. It is a tool for implementing a service-oriented architecture (SOA). It is standard, modular, and physically distributed, to adapt to large-scale infrastructures.
Event-driven SOA is a form of service-oriented architecture (SOA), combining the intelligence and proactiveness of event-driven architecture with the organizational capabilities found in service offerings. Before event-driven SOA, the typical SOA platform orchestrated services centrally, through pre-defined business processes, assuming that what should have already been triggered is defined in a business process. This older approach does not account for events that occur across, or outside of, specific business processes. Thus complex events, in which a pattern of activities—both non-scheduled and scheduled—should trigger a set of services is not accounted for in traditional SOA 1.0 architecture.
The JBoss Enterprise SOA Platform is free software/open-source Java EE-based service-oriented architecture (SOA) software. The JBoss Enterprise SOA Platform is part of the JBoss Enterprise Middleware portfolio of software. The JBoss Enterprise SOA Platform enables enterprises to integrate services, handle business events, and automate business processes, linking IT resources, data, services and applications. Because it is Java-based, the JBoss application server operates cross-platform: usable on any operating system that supports Java. The JBoss SOA Platform was developed by JBoss, now a division of Red Hat.
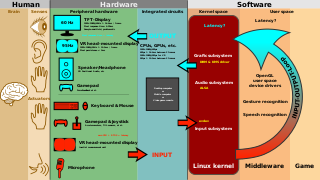
Middleware is computer software that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as "software glue".






