
An impact crater is an approximately circular depression in the surface of a planet, moon, or other solid body in the Solar System or elsewhere, formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller body. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Impact craters range from small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth.

Eros, provisional designation 1898 DQ, is a stony and elongated asteroid of the Amor group and the first discovered and second-largest near-Earth object with a mean-diameter of approximately 16.8 kilometers. Visited by the NEAR Shoemaker space probe in 1998, it became the first asteroid ever studied from orbit.

Meteor Crater is a meteorite impact crater approximately 37 miles (60 km) east of Flagstaff and 18 miles (29 km) west of Winslow in the northern Arizona desert of the United States. Because the United States Board on Geographic Names commonly recognizes names of natural features derived from the nearest post office, the feature acquired the name of "Meteor Crater" from the nearby post office named Meteor. The site was formerly known as the Canyon Diablo Crater and fragments of the meteorite are officially called the Canyon Diablo Meteorite. Scientists refer to the crater as Barringer Crater in honor of Daniel Barringer, who was first to suggest that it was produced by meteorite impact. The crater is privately owned by the Barringer family through their Barringer Crater Company, which proclaims it to be the "best preserved meteorite crater on Earth". Despite its importance as a geological site, the crater is not protected as a national monument, a status that would require federal ownership. It was designated a National Natural Landmark in November 1967.

Eugene Merle Shoemaker, also known as Gene Shoemaker, was an American geologist and one of the founders of the field of planetary science. He is best known for co-discovering the Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 with his wife Carolyn S. Shoemaker and David H. Levy. This comet hit Jupiter in July 1994: the impact was televised around the world.

A ray system comprises radial streaks of fine ejecta thrown out during the formation of an impact crater, looking somewhat like many thin spokes coming from the hub of a wheel. The rays may extend for lengths up to several times the diameter of their originating crater, and are often accompanied by small secondary craters formed by larger chunks of ejecta. Ray systems have been identified on the Moon, Earth, Mercury, and some moons of the outer planets. Originally it was thought that they existed only on planets or moons lacking an atmosphere, but more recently they have been identified on Mars in infrared images taken from orbit by 2001 Mars Odyssey's thermal imager.

Shackleton is an impact crater that lies at the south pole of the Moon. The peaks along the crater's rim are exposed to almost continual sunlight, while the interior is perpetually in shadow. The low-temperature interior of this crater functions as a cold trap that may capture and freeze volatiles shed during comet impacts on the Moon. Measurements by the Lunar Prospector spacecraft showed higher than normal amounts of hydrogen within the crater, which may indicate the presence of water ice. The crater is named after Antarctic explorer Ernest Shackleton.

Buch is an old, worn crater that is located in the rugged southern highlands of the Moon. It was named after German geologist Leopold von Buch. It lies to the northeast of the large crater Maurolycus, and the comparably sized crater Büsching is attached to the northeast rim.

Planetary geology, alternatively known as astrogeology or exogeology, is a planetary science discipline concerned with the geology of the celestial bodies such as the planets and their moons, asteroids, comets, and meteorites. Although the geo- prefix typically indicates topics of or relating to the Earth, planetary geology is named as such for historical and convenience reasons; applying geological science to other planetary bodies. Due to the types of investigations involved, it is also closely linked with Earth-based geology.

Faustini is a lunar impact crater that lies near the south pole of the Moon. It is located nearly due south of the much larger crater Amundsen, and is almost attached to Shoemaker to the southwest. About one crater diameter due south is the smaller crater Shackleton at the south pole. A small crater is attached to the eastern rim of Faustini.
Ben J. Bussey is an American planetary scientist.

Lunar craters are impact craters on Earth's Moon. The Moon's surface has many craters, almost all of which were formed by impacts.

A crater chain is a line of craters along the surface of an astronomical body. The descriptor term for crater chains is catena, as specified by the International Astronomical Union's rules on planetary nomenclature.
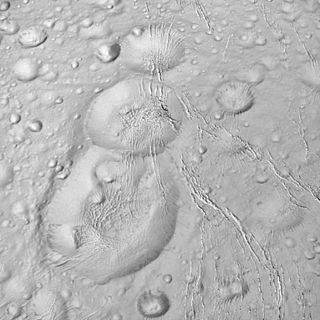
Dunyazad is a large crater on Saturn's moon Enceladus first discovered by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. It is named after Dunyazad, the sister of Scheherazade in The Book of One Thousand and One Nights.

Shahrazad is a large crater on Saturn's moon Enceladus first discovered by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. It is located at 47.3° North Latitude, 199.7° West Longitude and is approximately 20 kilometers across. Shahrazad is the middle crater of a prominent crater triplet on Enceladus' anti-Saturnian hemisphere. Voyager images revealed very little about this crater, however, higher resolution views of Shahrazad taken by the Cassini Spacecraft during a close flyby on March 9, 2005 reveal significant north-south fracturing that runs through all three craters of the triplet. Deep canyons mark the northern and eastern portions of Shahrazad's rim. Some evidence for viscous relaxation can be seen, but it is not nearly as significant as at Dunyazad to its immediate south or at Aladdin elsewhere on the satellite.

In astronomy, a rubble pile is a celestial body that is not a monolith, consisting instead of numerous pieces of rock that have coalesced under the influence of gravity. Rubble piles have low density because there are large cavities between the various chunks that make them up.

The Astrogeology Science Center is the entity within the United States Geological Survey concerned with the study of planetary geology and planetary cartography. It is housed in the Shoemaker Building in Flagstaff, Arizona. The Center was established in 1963 by Eugene Merle Shoemaker to provide lunar geologic mapping and to assist in training astronauts destined for the Moon as part of the Apollo program.

These are tables of space probes which have been deliberately destroyed at their objects of study, typically by hard landings or crash landings at the end of their respective missions and/or functionality. This suicidal endeavor not only precludes the hazards of orbital space debris and planetary contamination, but also provides the opportunity in some cases for terminal science given that the transient light released by the kinetic energy may be available for spectroscopy; the physical ejecta remains in place for further study. Even after soft landings had been mastered, NASA used crash landings to test whether Moon craters contained ice by crashing space probes into craters and testing the debris that got thrown out.















