The Book of Micah is the sixth of the twelve minor prophets in the Hebrew Bible. Ostensibly, it records the sayings of Micah, whose name is Mikayahu, meaning "Who is like Yahweh?", an 8th-century BCE prophet from the village of Moresheth in Judah.

Year 1167 (MCLXVII) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar.

Bohemond II was Prince of Taranto from 1111 to 1128 and Prince of Antioch from 1111/1119 to 1130. He was the son of Bohemond I, who in 1108 was forced to submit to the authority of the Byzantine Empire in the Treaty of Devol. Three years later, the infant Bohemond inherited the Principality of Taranto under the guardianship of his mother, Constance of France. The Principality of Antioch was administered by his father's nephew, Tancred, until 1111. Tancred's cousin, Roger of Salerno, managed the principality from 1111 to 1119. After Roger died in the Battle of the Field of Blood, Baldwin II of Jerusalem took over the administration of Antioch. However, he did acknowledge Bohemond's right to personally rule the principality upon reaching the age of majority.

Genk is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of Limburg near Hasselt. The municipality only comprises the town of Genk itself. It is one of the most important industrial towns in Flanders, located on the Albert Canal, between Antwerp and Liège.

Baldwin II, also known as Baldwin of Bourcq or Bourg, was Count of Edessa from 1100 to 1118, and King of Jerusalem from 1118 until his death. He accompanied his cousins Godfrey of Bouillon and Baldwin of Boulogne to the Holy Land during the First Crusade. He succeeded Baldwin of Boulogne as the second count of Edessa when he left the county for Jerusalem following his brother's death. He was captured at the Battle of Harran in 1104. He was held first by Sökmen of Mardin, then by Jikirmish of Mosul, and finally by Jawali Saqawa. During his captivity, Tancred, the Crusader ruler of the Principality of Antioch, and Tancred's cousin, Richard of Salerno, governed Edessa as Baldwin's regents.
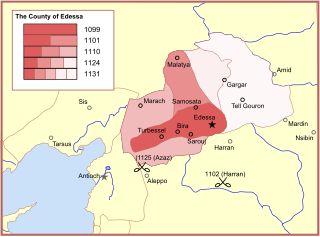
The County of Edessa was a 12th-century Crusader state in Upper Mesopotamia. Its seat was the city of Edessa.

The Principality of Antioch was one of the Crusader states created during the First Crusade which included parts of modern-day Turkey and Syria. The principality was much smaller than the County of Edessa or the Kingdom of Jerusalem. It extended around the northeastern edge of the Mediterranean, bordering the County of Tripoli to the south, Edessa to the east, and the Byzantine Empire or the Kingdom of Armenia to the northwest, depending on the date.

Bertrand of Toulouse was count of Toulouse, and was the first count of Tripoli to rule in Tripoli itself.

The Kingdom of Jerusalem, one of the Crusader states that was created in 1099, was divided into a number of smaller seigneuries. According to the 13th-century jurist John of Ibelin, the four highest crown vassals in the kingdom proper were the count of Jaffa and Ascalon, the prince of Galilee, the lord of Sidon, and the lord of Oultrejordain.

There were six major officers of the kingdom of Jerusalem: the constable, the marshal, the seneschal, the chamberlain, the butler and the chancellor. At certain times there were also bailiffs, viscounts and castellans.

Tancred was an Italo-Norman leader of the First Crusade who later became Prince of Galilee and regent of the Principality of Antioch. Tancred came from the house of Hauteville and was the great-grandson of Norman lord Tancred of Hauteville.

Bertrade of Montfort, also known by other names, was a Norman noble from the House of Montfort. She was countess of Anjou (1089–1092) through her first marriage to Fulk the Rude and then queen consort of France (1092–1108) through her initially bigamous marriage to Philip I. Condemned in her era's ecclesiastical histories, she played a role in the popularization of pigache footwear and founded a daughter house of Fontevraud Abbey at Hautes-Bruyeres.
Ghibbelin of Sabran was Archbishop of Arles (1080–1112), papal legate (1107–1108), and Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem (1108–1112).

Henry I was the count of Limburg and Arlon from 1082 to his death and duke of Lower Lorraine between 1101 and 1106. His mother was Jutta, daughter of Frederick, Duke of Lower Lorraine, and his father is uncertain, but possibly named Count Udon.

Waleran III was initially lord of Montjoie, then count of Luxembourg from 1214. He became count of Arlon and duke of Limburg on his father's death in 1221. He was the son of Henry III of Limburg and Sophia of Saarbrücken.
Gervase of Bazoches, who is also known as Gervaise, was Prince of Galilee from 1105/1106 until his death. He was born into a French noble family but migrated to the Holy Land, where King Baldwin I of Jerusalem made him senechal in the early 1100s and appointed him prince of Galilee in 1105/1106. Gervase was captured during a raid by Toghtekin, atabeg of Damascus, who had Gervase executed after Baldwin I refused to surrender three important towns in exchange for Gervase's release.

The House of Limburg-Stirum, which adopted its name in the 12th century from the immediate county of Limburg an der Lenne in what is now Germany, is one of the oldest families in Europe. It is the eldest and only surviving branch of the House of Berg, which was among the most powerful dynasties in the region of the lower Rhine during the Middle Ages. Some historians link them to an even older dynasty, the Ezzonen, going back to the 9th century.

Helge Limburg is a German politician of the Green Party who has been serving as a member of the Bundestag since the 2021 elections.

The siege of Sidon was an event in the aftermath of the First Crusade. The coastal city of Sidon was captured by the forces of Baldwin I of Jerusalem and Sigurd I of Norway, with assistance from the Ordelafo Faliero, Doge of Venice.
South Limburg is both a COROP (statistical) region as well as a landstreek (area) of the Netherlands located in the province of Limburg. The Dutch term landstreek, literally translated "land area/region", means that the area is not an administrative region but an area that displays cohesion with regard to culture and landscape. With regards to South Limburg this deals with its hilly landscape, especially in the Heuvelland region, sunken lanes, an abundance of castles, and the regional language Limburgish spoken by a significant part of the population alongside Dutch. The region also contains the highest point above sea level in mainland Netherlands, the Vaalserberg being 322.5 metres (1,058 ft) above sea level.














