This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+
and hydroxide anions OH−
.

Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3, (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, water-soluble salts. All forms have a strongly alkaline taste and give moderately alkaline solutions in water. Historically it was extracted from the ashes of plants growing in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process.

Sodium hydride is the chemical compound with the empirical formula NaH. This alkali metal hydride is primarily used as a strong, yet combustible base in organic synthesis. NaH is representative of the saline hydrides, meaning it is a salt-like hydride, composed of Na+ and H− ions, in contrast to the more molecular hydrides such as borane, methane, ammonia and water. It is an ionic material that is insoluble in organic solvents (although soluble in molten Na), consistent with the fact that H− remains an unknown anion in solution. Because of the insolubility of NaH, all reactions involving NaH occur at the surface of the solid.

Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 million tonnes, the decahydrate is a major commodity chemical product. It is mainly used for the manufacture of detergents and in the kraft process of paper pulping.

Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBH4. This white solid, usually encountered as a powder, is a reducing agent that finds application in chemistry, both in the laboratory and on a technical scale. It has been tested as pretreatment for pulping of wood, but is too costly to be commercialized. The compound is soluble in alcohols, certain ethers, and even water, although it slowly hydrolyzes
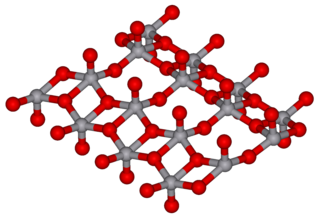
Vanadium(V) oxide (vanadia) is the inorganic compound with the formula V2O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a brown/yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst.

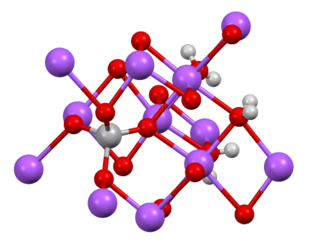
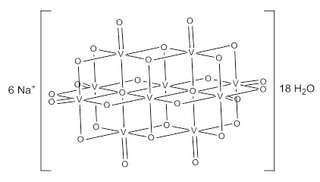
In chemistry, a vanadate is a compound containing an oxoanion of vanadium generally in its highest oxidation state of +5. The simplest vanadate ion is the tetrahedral, orthovanadate, VO3−
4 anion, which is present in e.g. sodium orthovanadate and in solutions of V2O5 in strong base (pH > 13). Conventionally this ion is represented with a single double bond, however this is a resonance form as the ion is a regular tetrahedron with four equivalent oxygen atoms.
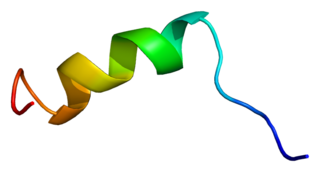
NaV1.5 is an integral membrane protein and tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel subunit. NaV1.5 is found primarily in cardiac muscle, where it mediates the fast influx of Na+-ions (INa) across the cell membrane, resulting in the fast depolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. As such, it plays a major role in impulse propagation through the heart. A vast number of cardiac diseases is associated with mutations in NaV1.5 (see paragraph genetics). SCN5A is the gene that encodes the cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5.

The vanadyl or oxovanadium(IV) cation, VO2+, is functional group that is common in the coordination chemistry of vanadium. Complexes containing this functional group are characteristically blue and paramagnetic. A triple bond is proposed to exist between the V4+ and O2- centers.
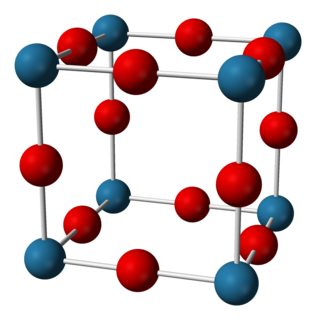
Sodium nitride (Na3N) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na3N. In contrast to lithium nitride and some other nitrides, sodium nitride is an extremely unstable alkali metal nitride. It can be generated by combining atomic beams of sodium and nitrogen deposited onto a low-temperature sapphire substrate.
It readily decomposes into its elements:
Sodium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na3AsO4. Related salts are also called sodium arsenate, including Na2HAsO4 (disodium hydrogen arsenate) and NaH2AsO4 (sodium dihydrogen arsenate). The trisodium salt is a white or colourless solid that is highly toxic. It is usually handled as the dodecahydrate Na3AsO4.12H2O.

Sodium channel, voltage gated, type VIII, alpha subunit also known as SCN8A or Nav1.6 is a membrane protein encoded by the SCN8A gene. Nav1.6 is one sodium channel isoform and is the primary voltage-gated sodium channel at the nodes of Ranvier. The channels are highly concentrated in sensory and motor axons in the peripheral nervous system and cluster at the nodes in the central nervous system.
Organovanadium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to vanadium (V) chemical bond. Organovanadium compounds find only minor use as reagents in organic synthesis but are significant for polymer chemistry as catalysts.

Sodium bismuthate is the inorganic compound with the formula NaBiO3. It is a yellowish solid that is a strong oxidiser. It is not soluble in cold water, which is sometimes convenient since the reagent can be easily removed after the reaction. It is one of the few sodium salts that is insoluble in water. It is commercially available however commercial samples may be a mixture of bismuth(V) oxide, sodium carbonate and sodium peroxide. A related compound with the approximate formula Na3BiO4 also exists.
Sodium orthosilicate is the chemical compound Na
4SiO
4. It is one of the sodium silicates, specifically an orthosilicate, formally a salt of the unstable orthosilicic acid H
4SiO
4.