The Baltic languages belong to the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family. Baltic languages are spoken by the Balts, mainly in areas extending east and southeast of the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe.

The East Slavic languages constitute one of three regional subgroups of Slavic languages, currently spoken throughout Eastern Europe, Northern Asia, and the Caucasus. It is the group with the largest numbers of speakers, far out-numbering the Western and Southern Slavic groups. The existing East Slavic languages are Belarusian, Russian and Ukrainian; Rusyn is considered to be either a separate language or a dialect of Ukrainian.

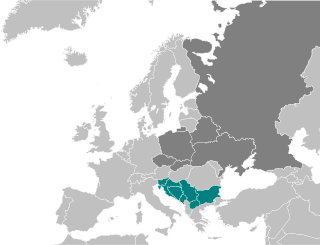
The Macedonian language is a South Slavic language spoken as a first language by around two million people, principally in North Macedonia and the Macedonian diaspora, with a smaller number of speakers throughout the transnational region of Macedonia. It is the official language of North Macedonia and a recognized minority language in parts of Albania, Romania, and Serbia.

Pan-Slavism, a movement which crystallized in the mid-19th century, is the political ideology concerned with the advancement of integrity and unity for the Slavic-speaking peoples. Its main impact occurred in the Balkans, where non-Slavic empires had ruled the South Slavs for centuries. These were mainly the Byzantine Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Venice.

The Slavic languages are the Indo-European languages spoken by the Slavic peoples. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family.
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:

Slavs are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group who speak the various Slavic languages of the larger Balto-Slavic linguistic group. They are native to Eurasia, stretching from Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe all the way north and eastwards to Northeast Europe, Northern Asia (Siberia), the Caucasus, and Central Asia as well as historically in Western Europe and Western Asia. From the early 6th century they spread to inhabit the majority of Central, Eastern and Southeastern Europe. Today, there is a large Slavic diaspora throughout North America, particularly in the United States and Canada as a result of immigration.

Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic, also known as Old Church Slavic or Old Slavic, was the first Slavic literary language. It is also referred to as Paleo-Slavic (Paleoslavic) or Palaeo-Slavic (Palaeoslavic), not to be confused with the Proto-Slavic. It is often abbreviated to OCS.

Ukrainian is an East Slavic language. It is the official state language of Ukraine and first of two principal languages of Ukrainians; it is one of the three official languages in the unrecognized state of Transnistria, the other two being Romanian and Russian. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic script.
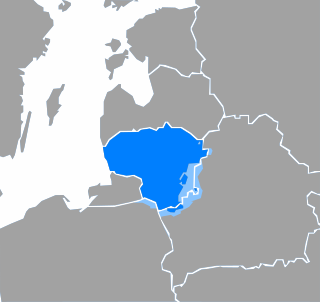
Lithuanian is a Baltic language spoken in the Baltic region. It is the language of Lithuanians and the official language of Lithuania as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.9 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 200,000 abroad.
Macedonian may refer to someone or something from or related to Macedonia, in any of several meanings of that term. More specifically, it may refer to:
Common Eastern Slavic, Common Russian or Old Russian was a language used during the 10th–15th centuries by East Slavs in Kievan Rus' and states which evolved after the collapse of Kievan Rus'. Dialects of it were spoken, though not exclusively, in the area today occupied by Belarus, central and northern Ukraine, and parts of western Russia. It is descended from Proto-Slavic.

The West Slavic languages are a subdivision of the Slavic language group. They include Polish, Czech, Slovak, Silesian, Kashubian, Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian.
West Slavic is usually divided into three subgroups based on similarity and degree of mutual intelligibility, Czecho-Slovak, Lechitic and Sorbian, as follows:

The Balto-Slavic languages are a branch of the Indo-European family of languages. It traditionally comprises the Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European branch, which points to a period of common development. It is now a general consensus among linguists to classify Baltic and Slavic languages into a single branch, even though some details of the nature of their relationship remain in dispute in some circles, usually due to political controversies. Some linguists however, have suggested that Balto-Slavic should be split into three equidistant groups: Eastern Baltic, Western Baltic and Slavic.

The West Slavs are a subgroup of Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages.
They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic languages diversified into their historically attested forms over the 10th to 14th centuries.
The Slavic liquid metathesis refers to the phenomenon of metathesis of liquid consonants in the Common Slavic period in the South Slavic and West Slavic area. The closely related corresponding phenomenon of pleophony occurred in parallel, in the East Slavic languages.

The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies who lived during the Migration Period and Early Middle Ages in Eastern Europe and established the foundations for the Slavic nations through the Slavic states of the High Middle Ages. The first written use of the name "Slavs" dates to the 6th century, when the Slavic tribes inhabited a large portion of Central and Eastern Europe. By that century, nomadic Iranian ethnic groups living on the Eurasian Steppe had been absorbed by the region's Slavic population. Over the next two centuries, the Slavs expanded southwest toward the Balkans and the Alps and northeast towards the Volga River. It's still a matter of controversy where the original habitat of the Slavs was, but scholars believe it was somewhere in Eastern Europe. In the past not much attention was paid to the origin of the Slavic people.

Proto-Slavic is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all the Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 5th to 9th centuries AD. As with most other proto-languages, no attested writings have been found; scholars have reconstructed the language by applying the comparative method to all the attested Slavic languages and by taking into account other Indo-European languages.