
North Yorkshire is a non-metropolitan county and largest ceremonial county in England. It is located primarily in the region of Yorkshire and the Humber but partly in the region of North East England. The estimated population of North Yorkshire was 602,300 in mid 2016.

The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between the East Riding of Yorkshire on the north bank and North Lincolnshire on the south bank. Although the Humber is an estuary from the point at which it is formed, many maps show it as the River Humber.
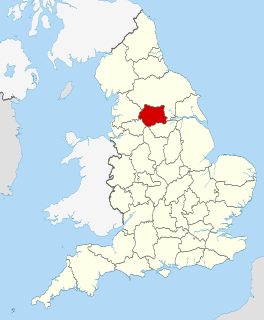
West Yorkshire is a metropolitan county in England. It is an inland and in relative terms upland county having eastward-draining valleys while taking in moors of the Pennines and has a population of 2.2 million. West Yorkshire came into existence as a metropolitan county in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972.

Leeds railway station is the mainline railway station serving the city centre of Leeds in West Yorkshire, England. It is the third-busiest railway station in the UK outside London. It is located on New Station Street to the south of City Square, at the bottom of Park Row, behind the landmark Queens Hotel. It is one of 20 stations managed by Network Rail.

Darton railway station is a railway station in Darton, in the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley, South Yorkshire, England. Train services are provided by Northern.
The London Midland Region (LMR) was one of the six regions created on the formation of the nationalised British Railways (BR), and initially consisted of ex-London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) lines in England and Wales. The region was managed first from buildings adjacent to Euston station, and later from Stanier House in Birmingham. It existed from the creation of BR in 1948, ceased to be an operating unit in its own right in the 1980s, and was wound up at the end of 1992.
The Hull Barnsley & West Riding Junction Railway and Dock Company (HB&WRJR&DCo.) was opened on 20 July 1885. It had a total projected length of 66 miles but never reached Barnsley, stopping a few miles short at Stairfoot. The name was changed to The Hull and Barnsley Railway (H&BR) in 1905. Its Alexandra Dock in Hull opened 16 July 1885.
The Hallam Line is a railway connecting Leeds and Sheffield via Castleford in the West Yorkshire Metro area of northern England. It is a slower route from Leeds to Sheffield than the Wakefield line. Services on this line are operated by Northern. Services from Leeds to Nottingham also use the line.
The Penistone Line is operated by Northern in the West Yorkshire Metro/ Travel South Yorkshire area of northern England. It connects Huddersfield and Sheffield via Penistone and Barnsley, serving many rural communities. Metrocards can be used for travel between Huddersfield and Denby Dale and intermediate stations.
The Wakefield line is a railway line and service in the West Yorkshire Metro and South Yorkshire Passenger Transport Executive areas of northern England. The Wakefield line is coloured yellow on maps and publications by West Yorkshire Metro. The line was electrified in 1989, between Leeds & Wakefield Westgate, as part of the programme to electrify the East Coast Main Line.

Swinton railway station is a railway station in Swinton, South Yorkshire, England. It has three platforms and a small bus station, and lies at the junction of the former North Midland Railway main line between Rotherham Masborough and Leeds via Cudworth and the former South Yorkshire Railway line to Doncaster.

Tinsley railway station was a railway station in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England, opened in March 1869. This station was designed by the company architect John Holloway Sanders. The station served the growing community of Tinsley and the workers at the nearby steelworks which had moved to or had been founded in the lower Don Valley following major changes in manufacturing methods in the mid - late 19th century. The station, opened by the South Yorkshire Railway, was built on the line between Sheffield Victoria and Barnsley and became a junction station with the opening of the line from Tinsley Junction to the original Rotherham station by the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway. The station was located by the main Sheffield to Rotherham road in Tinsley, now on the Sheffield side of M1, Junction 34 in Tinsley.

The South Yorkshire Junction Railway was a railway which ran from Wrangbrook Junction on the main line of the Hull and Barnsley Railway to near Denaby Main Colliery Village, South Yorkshire. It was nominally an independent company sponsored by the Denaby and Cadeby Colliery Company but was worked by the Hull and Barnsley Railway.
The Dearne Valley Railway (DVR) was a railway line which ran through the valley of the River Dearne in South Yorkshire. It was incorporated by an Act of Parliament on 6 August 1897 to build a line between Brierley Junction, on the main line of the Hull and Barnsley Railway, to junctions with the Great Northern Railway and the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Railway south east of Doncaster.

Doncaster railway station was built as a terminus for services on the Hull and Barnsley and Great Central Joint Railway in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. It was reached by a triangular junction from the main line just outside town. The station was set at the north end of town, just beyond the Doncaster Avoiding Line, in the fork of the old A1 and the A19.
The Trent, Ancholme and Grimsby Railway was a railway line in north Lincolnshire which commenced at an end on junction with the South Yorkshire Railway where that railway crossed the River Trent near the village of Gunhouse. This was known as Gunhouse Junction but the village has become known as "Gunness". The line ran for about 14 miles (22.5 km) through Frodingham to Wrawby Junction near Barnetby and included railway stations at Appleby, and Elsham. The line also included two branches to Gunness and Gunhouse Wharf on the River Trent. The line was opened on 1 October 1866.
John Marshall was an English railway historian. He is best known for his three-volume history of the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway 'which he greatly disliked being described as "definitive"' and for compiling The Guinness Railway Book 'which, in its six editions, is arguably the best selling railway book of all time.'
The Swinton–Doncaster line is a short railway line in South Yorkshire between Swinton Junction on the Wakefield Line and Doncaster South Yorkshire Junction on the East Coast Main Line. The line comprises the former North Midland Railway's "Swinton curve" between Swinton and Mexborough and the east end of the former South Yorkshire Railway Blackburn Valley line, between Mexborough and Doncaster. Northern operates passenger trains on the line; TransPennine Express and CrossCountry use the line but do not provide stopping service.









