
A brass instrument is a musical instrument that produces sound by sympathetic vibration of air in a tubular resonator in sympathy with the vibration of the player's lips. Brass instruments are also called labrosones, literally meaning "lip-vibrated instruments".

The tuba (bass) is the largest and lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibration into a large mouthpiece. It first appeared in the mid-19th century, making it one of the newer instruments in the modern orchestra and concert band. The tuba largely replaced the ophicleide. Tuba is Latin for 'trumpet'.

A valve is a device that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin valva, the moving part of a door, in turn from volvere, to turn, roll.
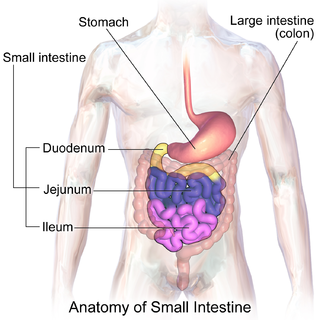
The small intestine or small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract between the stomach and the large intestine, and is where most of the end absorption of food takes place. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum is the shortest part of the small intestine and is where preparation for absorption begins. It also receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct, controlled by the sphincter of Oddi. The primary function of the small intestine is the absorption of nutrients and minerals from food, using small finger-like protrusions called villi.

A camshaft is a shaft to which a cam is fastened or of which a cam forms an integral part.

A four-stroke engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed:
- Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing vacuum pressure into the cylinder through its downward motion. The piston is moving down as air is being sucked in by the downward motion against the piston.
- Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are closed during this stage.
- Combustion: Also known as power or ignition. This is the start of the second revolution of the four stroke cycle. At this point the crankshaft has completed a full 360 degree revolution. While the piston is at T.D.C. the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug or by heat generated by high compression, forcefully returning the piston to B.D.C. This stroke produces mechanical work from the engine to turn the crankshaft.
- Exhaust: Also known as outlet. During the exhaust stroke, the piston, once again, returns from B.D.C. to T.D.C. while the exhaust valve is open. This action expels the spent air-fuel mixture through the exhaust valve.

A heart valve normally allows blood to flow in only one direction through the heart. The four valves are commonly represented in a mammalian heart that determines the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart valve opens or closes incumbent on differential blood pressure on each side.

Steam is a digital distribution platform developed by Valve Corporation for purchasing and playing video games. Steam offers digital rights management (DRM), matchmaking servers, video streaming, and social networking services. Steam provides the user with installation and automatic updating of games, and community features such as friends lists and groups, cloud saving, and in-game voice and chat functionality.

A scroll compressor is a device for compressing air or refrigerant. It is used in air conditioning equipment, as an automobile supercharger and as a vacuum pump. Many residential central heat pump and air conditioning systems and a few automotive air conditioning systems employ a scroll compressor instead of the more traditional rotary, reciprocating, and wobble-plate compressors.

The operculum, meaning little lid, is a corneous or calcareous anatomical structure like a trapdoor which exists in many groups of sea snails and freshwater snails, and also in a few groups of land snails; the structure is found in some marine and freshwater gastropods, and in a minority of terrestrial gastropods, including the families Helicinidae, Cyclophoridae, Aciculidae, Maizaniidae, Pomatiidae, etc.

The circular folds are large valvular flaps projecting into the lumen of the small intestine.

The Liapootah Power Station is a run-of-the-river hydroelectric power station located in the Central Highlands region of Tasmania, Australia. The power station is situated on the Lower River Derwent catchment and is owned and operated by Hydro Tasmania.

The Wayatinah Power Station is a run-of-the-river hydroelectric power station located in the Central Highlands region of Tasmania, Australia. The power station is situated on the Lower River Derwent catchment and is owned and operated by Hydro Tasmania.

The Tungatinah Power Station is a conventional hydroelectric power station located in the Central Highlands region of Tasmania, Australia. The power station is situated on the Upper River Derwent catchment and is owned and operated by Hydro Tasmania.

The Lake Echo Power Station is a conventional hydroelectric power station located in the Central Highlands region of Tasmania, Australia. The power station is situated on the Upper River Derwent catchment and is owned and operated by Hydro Tasmania.

AMERICAN Cast Iron Pipe Company, headquartered in Birmingham, Alabama, is a manufacturer of ductile iron pipe, spiral-welded steel pipe, fire hydrants and valves for the waterworks industry and electric-resistance-welded steel pipe for the oil and natural gas industry. AMERICAN's diversified product line also includes static castings and high performance fire pumps.

The Rhynchonelata is a class of Lower Cambrian to Recent articulate brachiopods that combines orders from within the Rhynchonelliformea with well developed pedicle attachment. Shell forms vary from those with wide hinge lines to beaked forms with virtually no hinge line and from generally smooth to strongly plicate. Most all are biconvex. Lophophores vary and include both looped and spiraled forms. Although morphologically distinct, included orders follow a consistent phylogenetic sequence.

A horn is any of a family of musical instruments made of a tube, usually made of metal and often curved in various ways, with one narrow end into which the musician blows, and a wide end from which sound emerges. In horns, unlike some other brass instruments such as the trumpet, the bore gradually increases in width through most of its length—that is to say, it is conical rather than cylindrical. In jazz and popular-music contexts, the word may be used loosely to refer to any wind instrument, and a section of brass or woodwind instruments, or a mixture of the two, is called a horn section in these contexts.















