
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden.

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months.
Arthralgia literally means joint pain. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness, or an allergic reaction to medication.

Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hips. Eye and bowel problems may occur as well as back pain. Joint mobility in the affected areas generally worsens over time.
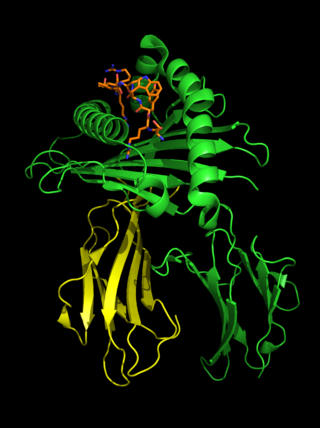
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) B27 is a class I surface antigen encoded by the B locus in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on chromosome 6 and presents antigenic peptides to T cells. HLA-B27 is strongly associated with ankylosing spondylitis and other associated inflammatory diseases, such as psoriatic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and reactive arthritis.

Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. This often happens in association with changes to the nails such as small depressions in the nail (pitting), thickening of the nails, and detachment of the nail from the nailbed. Skin changes consistent with psoriasis frequently occur before the onset of psoriatic arthritis but psoriatic arthritis can precede the rash in 15% of affected individuals. It is classified as a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
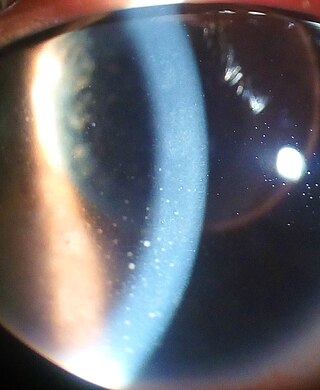
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis (iridocyclitis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20-60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mechanisms may be overcome resulting in inflammation and tissue destruction associated with T-cell activation.
An arthropathy is a disease of a joint.
Reactive arthritis, also known as Reiter's syndrome, is a form of inflammatory arthritis that develops in response to an infection in another part of the body (cross-reactivity). Coming into contact with bacteria and developing an infection can trigger the disease. By the time the patient presents with symptoms, often the "trigger" infection has been cured or is in remission in chronic cases, thus making determination of the initial cause difficult.
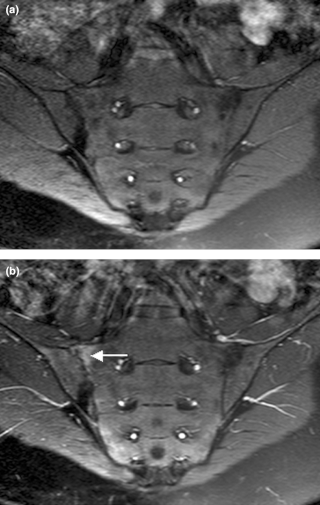
Sacroiliitis is inflammation within the sacroiliac joint. It is a feature of spondyloarthropathies, such as axial spondyloarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis or arthritis related to inflammatory bowel diseases, including ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. It is also the most common presentation of arthritis from brucellosis.

Certolizumab pegol, sold under the brand name Cimzia, is a biopharmaceutical medication for the treatment of Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. It is a fragment of a monoclonal antibody specific to tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and is manufactured by UCB.
The BASDAI or Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index is a validated diagnostic test which allows a physician, usually a rheumatologist, to determine the effectiveness of a current drug therapy, or the need to institute a new drug therapy for the treatment of Ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The BASDAI is one of a group of classification criteria for spondyloarthropathies.
Golimumab is a human monoclonal antibody which is used as an immunosuppressive medication and sold under the brand name Simponi. Golimumab targets tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), a pro-inflammatory molecule and hence is a TNF inhibitor. Profound reduction in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, interleukin (IL)-6, intercellaular adhesion molecules (ICAM)-1, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) demonstrates golimumab as an effective modulator of inflammatory markers and bone metabolism.

Arthritis mutilans is a rare medical condition involving severe inflammation damaging the joints of the hands and feet, and resulting in deformation and problems with moving the affected areas; it can also affect the spine. As an uncommon arthropathy, arthritis mutilans was originally described as affecting the hands, feet, fingers, and/or toes, but can refer in general to severe derangement of any joint damaged by arthropathy. First described in modern medical literature by Marie and Leri in 1913, in the hands, arthritis mutilans is also known as opera glass hand, or chronic absorptive arthritis. Sometimes there is foot involvement in which toes shorten and on which painful calluses develop in a condition known as opera glass foot, or pied en lorgnette.

Secukinumab, sold under the brand name Cosentyx among others, is a human IgG1κ monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis. It binds to the protein interleukin (IL)-17A and is marketed by Novartis.
The Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life (ASQoL) questionnaire is a patient-reported outcome (PRO) measure which assesses the quality of life of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. The ASQoL is based on the needs-based quality of life model. It is a self-administered questionnaire which contains 18 items and takes up to four minutes to complete.

Axial spondyloarthritis is a chronic, autoinflammatory disease predominantly affecting the axial skeleton. The phrase itself is an umbrella term characterizing a diverse disease family united by shared clinical and genetic features, such as the involvement of the axial skeleton. The best-known member of the axial spondyloarthritis disease family is ankylosing spondylitis. The 2009 introduction of the expression axial spondyloarthritis made it possible to refer to (1) less severe forms of spondylitis, (2) the early phase of ankylosing spondylitis and (3) ankylosing spondylitis itself collectively.
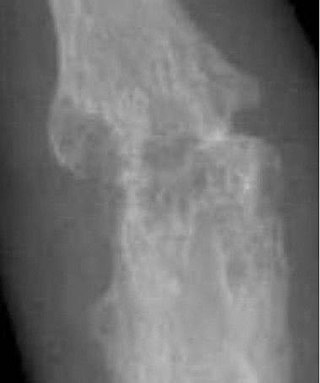
In radiology, a Romanus lesion is the erosion of the anterior and posterior vertebral endplates in patients with an inflammatory spondyloarthropathy – such as ankylosing spondylitis or an enteropathic arthropathy. The anterior erosion in particular causes a loss of anterior vertebral body concavity, causing the vertebra to display a squared contour or even a barrel-shape. Healing of the erosion results in a sclerotic increase in density causing what is known as a shiny corner sign, which can later result in syndesmophyte formation. It is most easily diagnosed using MRI, compared to conventional radiography.
Diagnostic delay is the time interval between the onset of symptoms and confirmed diagnosis of a disease. For a variety of reasons, including the mitigation of disease severity and financial expense, it is desirable for this delay to be minimized.
Ross E. Petty is a Canadian pediatric rheumatologist. He is a professor emeritus in the Department of Pediatrics at the University of British Columbia and a pediatric rheumatologist at BC Children’s Hospital in Vancouver, Canada. He established Canada’s first formal pediatric rheumatology program at the University of Manitoba in 1976, and three years later, he founded a similar program at the University of British Columbia.













